Abstract
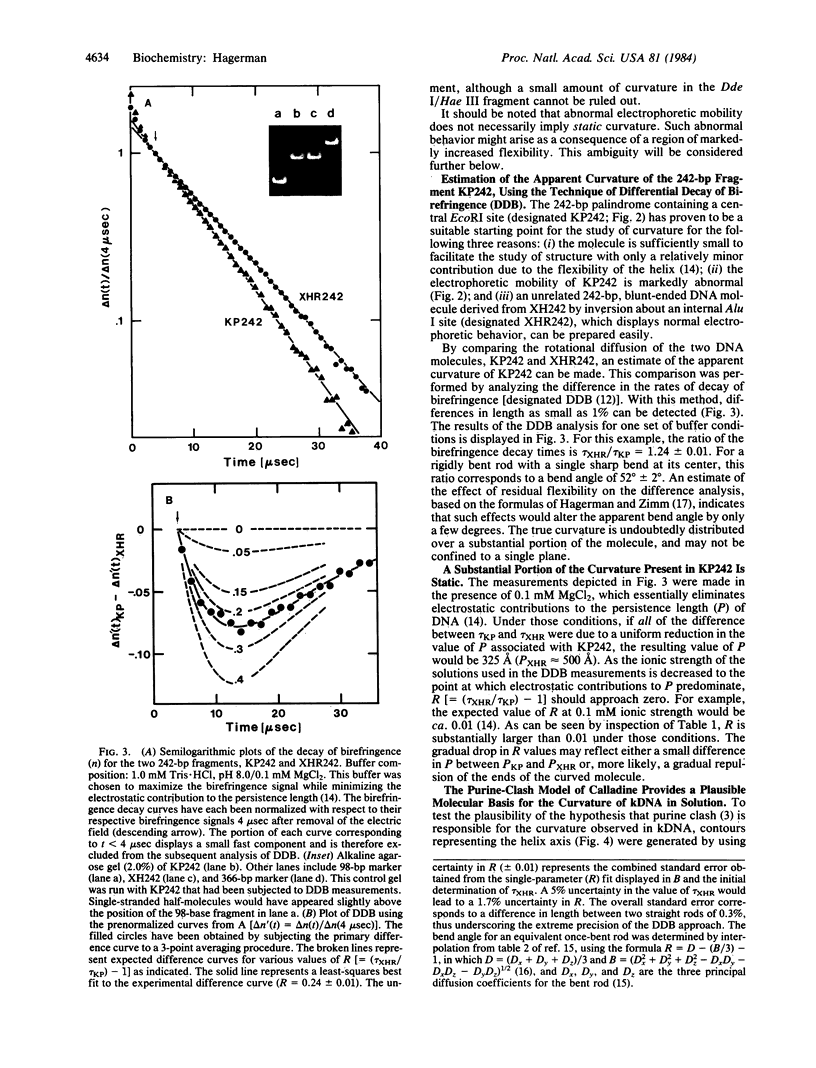
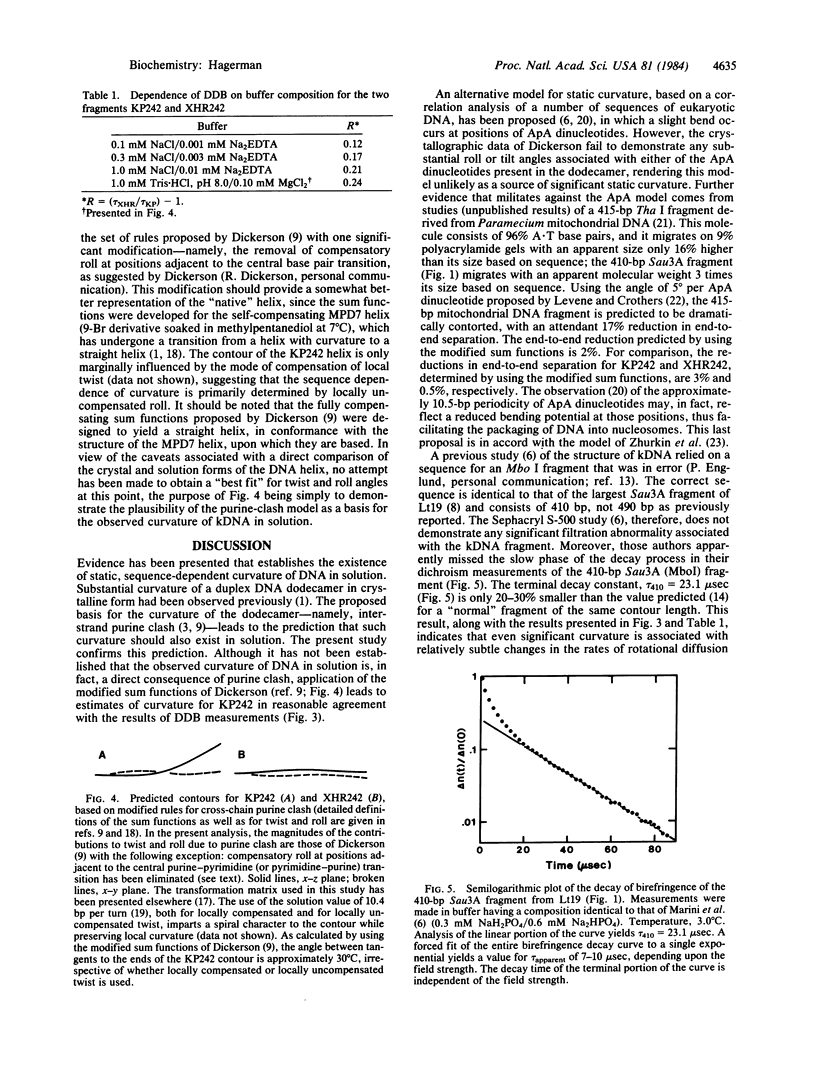
A 121-base-pair DNA restriction fragment derived from the kinetoplast minicircle, Lt19, of Leishmania tarentolae displays substantially abnormal electrophoretic behavior on polyacrylamide gels. The electrophoretic behavior of a series of palindromic dimers containing all or part of the 121-base-pair fragment has been used to establish that curvature of the DNA helix is the basis of the abnormal behavior. One of the palindromic dimers, KP242, has been examined in more detail by using the technique of differential decay of birefringence (DDB). The technique consists of analyzing the difference in the rates of decay of birefringence for two DNA fragments, each consisting of an identical number of base pairs, and is capable of resolving differences in length as small as 1%. This approach has yielded an estimate for the apparent curvature of the dimer which, when represented as an equivalent rod with a single bend at its center, equals approximately 52 degrees. DDB measurements made at several ionic strengths indicate that a substantial portion of the curvature is static, rather than a simple consequence of increased flexibility.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg S. S., Englund P. T. Heterogeneity of minicircles in kinetoplast DNA of Leishmania tarentolae. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):447–472. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Kopka M. L., Pjura P. A random-walk model for helix bending in B-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7099–7103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Reversible bending and helix geometry in a B-DNA dodecamer: CGCGAATTBrCGCG. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14686–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Investigation of the flexibility of DNA using transient electric birefringence. Biopolymers. 1981 Jul;20(7):1503–1535. doi: 10.1002/bip.1981.360200710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidane G. Z., Hughes D., Simpson L. Sequence heterogeneity and anomalous electrophoretic mobility of kinetoplast minicircle DNA from Leishmania tarentolae. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. A computer graphics study of sequence-directed bending in DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):429–435. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Tecklenburg M. Cloning and characterization of the natural lactose operator. Gene. 1981 Jan-Feb;13(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Langowski J., Baldwin R. L. DNA flexibility studied by covalent closure of short fragments into circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. Isolation of maxicircle component of kinetoplast DNA from hemoflagellate protozoa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N., Sussman J. L. The pitch of chromatin DNA is reflected in its nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Helical repeat of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):200–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurkin V. B., Lysov Y. P., Ivanov V. I. Anisotropic flexibility of DNA and the nucleosomal structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):1081–1096. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





