Abstract
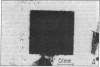
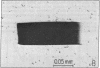
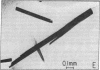
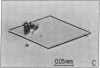
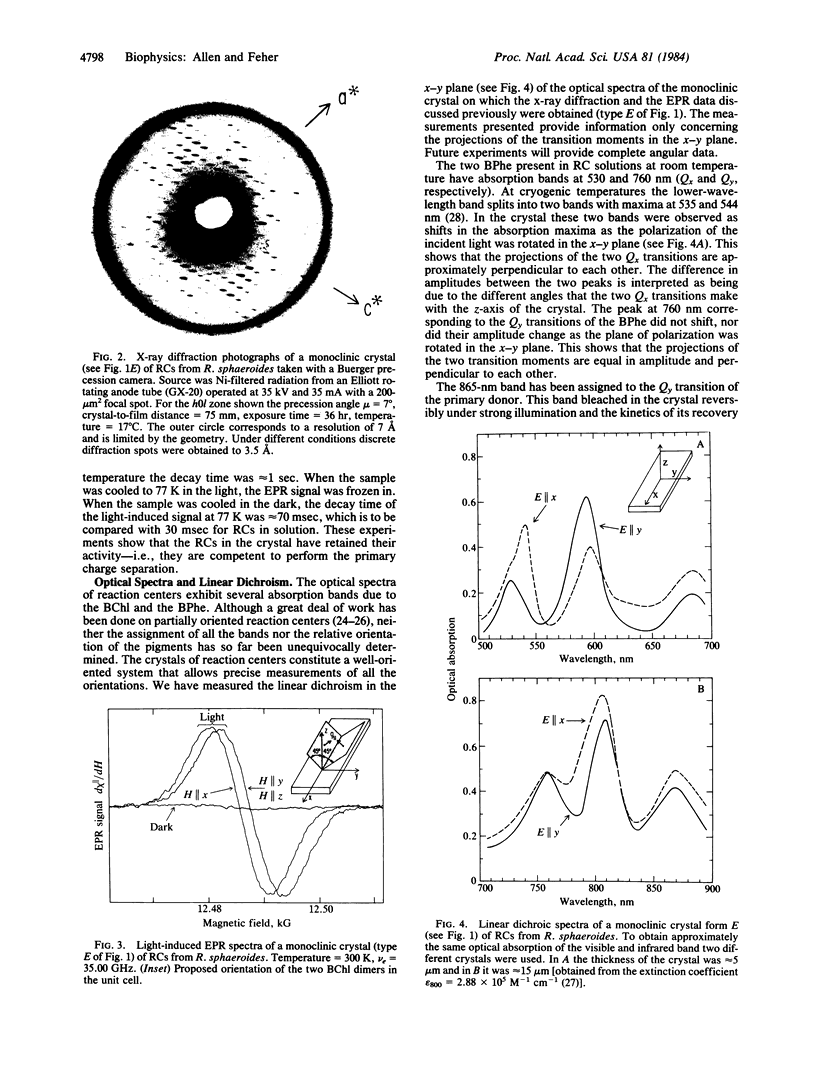
Reaction centers (RCs), integral membrane proteins that mediate the conversion of light into chemical energy, were crystallized by two different vapor diffusion techniques. In one method, small amphipathic molecules (1,2,3-heptanetriol and triethylammonium phosphate) were added to the RCs that had been solubilized in detergent. In the second method, crystallization occurred near the phase boundaries of a two-phase system created by the addition of polyethylene glycol and NaCl to RCs in octyl beta-D-glucoside. Several different crystal forms were obtained; two were analyzed by x-ray diffraction. One was monoclinic (space group P2) with beta = 105 degrees, and a = 70 A, b = 105 A, and c = 85 A, two RCs per unit cell, and one RC per asymmetric unit; the crystal diffracted to 3.5 A at 17 degrees C. The other crystal form was orthorhombic (space group C222) with a = 185 A, b = 170 A, and c = 105 A, with eight RCs per unit cell and one RC per asymmetric unit. Reversible light-induced EPR signals of the primary donor (bacteriochlorophyll dimer) showed that the RCs in the crystal were fully active. From the angular dependence of the EPR signal the molecular g anisotropy of the bacteriochlorophyll dimer was deduced to be g perpendicular - g parallel = (64 +/- 3) X 10(-5). Linear dichroism measurements were performed on the monoclinic crystal. The two bands at 535 and 544 nm assigned to the Qx transitions of the bacteriopheophytins were resolved and preliminary orientations of some of the pigments were obtained.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler W. F., Calvo R., Fredkin D. R., Isaacson R. A., Okamura M. Y., Feher G. The electronic structure of Fe2+ in reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. III. EPR measurements of the reduced acceptor complex. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):947–973. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84241-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feher G., Hoff A. J., Isaacson R. A., Ackerson L. C. ENDOR experiments on chlorophyll and bacteriochlorophyll in vitro and in the photosynthetic unit. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:239–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feher G. Some chemical and physical properties of a bacterial reaction center particle and its primary photochemical reactants. Photochem Photobiol. 1971 Sep;14(3):373–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1971.tb06180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garavito R. M., Jenkins J., Jansonius J. N., Karlsson R., Rosenbusch J. P. X-ray diffraction analysis of matrix porin, an integral membrane protein from Escherichia coli outer membranes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garavito R. M., Rosenbusch J. P. Three-dimensional crystals of an integral membrane protein: an initial x-ray analysis. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):327–329. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):491–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElroy J. D., Feher G., Mauzerall D. C. Characterization of primary reactants in bacterial photosynthesis. I. Comparison of the light-induced EPR signal (g=2.0026) with that of a bacteriochlorophyll radical. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 25;267(2):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Oesterhelt D. Three-dimensional crystals of membrane proteins: bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1283–1285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H. Three-dimensional crystals of a membrane protein complex. The photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):567–572. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris J. R., Scheer H., Katz J. J. Models for antenna and reaction center chlorophylls. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:260–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Suzuki H., Tanaka M. Crystallization of part of the mitochondrial electron transfer chain: cytochrome c oxidase--cytochrome c complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):928–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachence J. M., Dutton P. L., Blasie J. K. The reaction center profile structure derived from neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 13;635(2):267–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parson W. W. Photosynthetic bacterial reaction centers: interactions among the bacteriochlorophylls and bacteriopheophytins. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:57–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Parson W. W., Mauzerall D. C., Clayton R. K. Pigment content and molar extinction coefficients of photochemical reaction centers from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 28;305(3):597–609. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkirs G. E., Feher G. Topography of reaction center subunits in the membrane of the photosynthetic bacterium, rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):179–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Steiner L. A., Ogden R. C., Simon M. I., Feher G. Primary structure of the M subunit of the reaction center from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6505–6509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]