Abstract
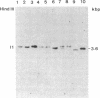
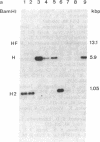
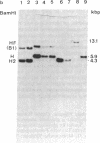
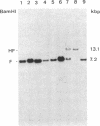
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), although not an indispensable factor for the development of Burkitt lymphoma, is apparently associated with the 20-fold higher incidence of the disease in Equatorial Africa compared to the incidence in other parts of the world. To determine whether different EBV subtypes are associated with the appearance of the malignant phenotype, we have compared the EBV genomes carried in the Burkitt tumor cells with those carried in the nonmalignant lymphoblastoid cells from the same individuals. From three patients with EBV -associated Burkitt lymphoma, tumor cell lines as well as spontaneously established lymphoblastoid cell lines representing the nonmalignant counterparts were obtained. The viral DNA in these cell lines was analyzed by Southern blot hybridization, using a set of cloned EBV DNA fragments as probes that recognize polymorphic regions in the viral genome. Using a number of different polymorphic markers to distinguish one isolate from another, the virus genome found in the tumor cells could also be identified in the nonmalignant cells of the same patient. In one case, in which two independent lymphoblastoid cell lines were established, evidence was obtained that this patient was infected by at least two distinct EBV subtypes. These results strongly suggest that in Burkitt lymphoma, the risk associated with EBV is related to cofactors such as chronic malaria and the mode of infection rather than to peculiar viral subtypes. The situation seems to be totally different from papillomavirus-associated diseases, in which the risk of progression to malignancy appears to be associated with particular viral strains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., Klein G., Zeigler J. L., Henle W. Association of Epstein-Barr viral genomes with American Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):357–359. doi: 10.1038/260357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKITT D. A children's cancer dependent on climatic factors. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:232–234. doi: 10.1038/194232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKITT D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg. 1958 Nov;46(197):218–223. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004619704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim A., Berger R., Lenoir G. Cytogenetic studies on African Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines: t(8;14), t(2;8) and t(8;22) translocations. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1981 Jun;3(4):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(81)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Delius H., Zimber U., Hudewentz J., Epstein M. A. Comparison of Epstein-Barr virus strains of different origin by analysis of the viral DNAs. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):603–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.603-618.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Hudewentz J., Freese U. K., Zimber U. Deletion of the nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus strain P3HR-1 causes fusion of the large internal repeat to the DSL region. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):952–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.952-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese U. K., Laux G., Hudewentz J., Schwarz E., Bornkamm G. W. Two distant clusters of partially homologous small repeats of Epstein-Barr virus are transcribed upon induction of an abortive or lytic cycle of the virus. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):731–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.731-743.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geser A., Lenoir G. M., Anvret M., Bornkamm G., Klein G., Williams E. H., Wright D. H., De-The G. Epstein-Barr virus markers in a series of Burkitt's lymphomas from the West Nile District, Uganda. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983 Oct;19(10):1393–1404. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(93)90009-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissmann L., Wolnik L., Ikenberg H., Koldovsky U., Schnürch H. G., zur Hausen H. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 DNA sequences in genital and laryngeal papillomas and in some cervical cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):560–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward S. D., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward G. S. Organization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. II. Fine mapping of the boundaries of the internal repeat cluster of B95-8 and identification of additional small tandem repeats adjacent to the HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):201–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.201-212.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Henderson A., Kieff E. Repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is related to cell DNA sequences interspersed on human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5916–5920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudewentz J., Delius H., Freese U. K., Zimber U., Bornkamm G. W. Two distant regions of the Epstein-Barr virus genome with sequence homologies have the same orientation and involve small tandem repeats. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Dambaugh T., Heller M., Dowling J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA XII. A variable region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome is included in the P3HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):979–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.979-986.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolov G., Manolova Y. Marker band in one chromosome 14 from Burkitt lymphomas. Nature. 1972 May 5;237(5349):33–34. doi: 10.1038/237033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Jhanwar S. C., Chaganti R. S., Hayward W. S. Two human c-onc genes are located on the long arm of chromosome 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7842–7846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Mounts P., Hayward G. S. Homology between mammalian cell DNA sequences and human herpesvirus genomes detected by a hybridization procedure with high-complexity probe. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90406-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack A., Hartl G., Zimber U., Freese U. K., Laux G., Takaki K., Hohn B., Gissmann L., Bornkamm G. W. A complete set of overlapping cosmid clones of M-ABA virus derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its similarity to other Epstein-Barr virus isolates. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Jarvis J. E., Crawford D. H., Epstein M. A. Observations on the type of infection by Epstein-Barr virus in peripheral lymphoid cells of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Int J Cancer. 1974 Dec 15;14(6):704–715. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zech L., Haglund U., Nilsson K., Klein G. Characteristic chromosomal abnormalities in biopsies and lymphoid-cell lines from patients with Burkitt and non-Burkitt lymphomas. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):47–56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Hummel M., Kieff E. RNA encoded by the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in latently infected, growth-transformed cells. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.424-433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]