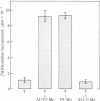
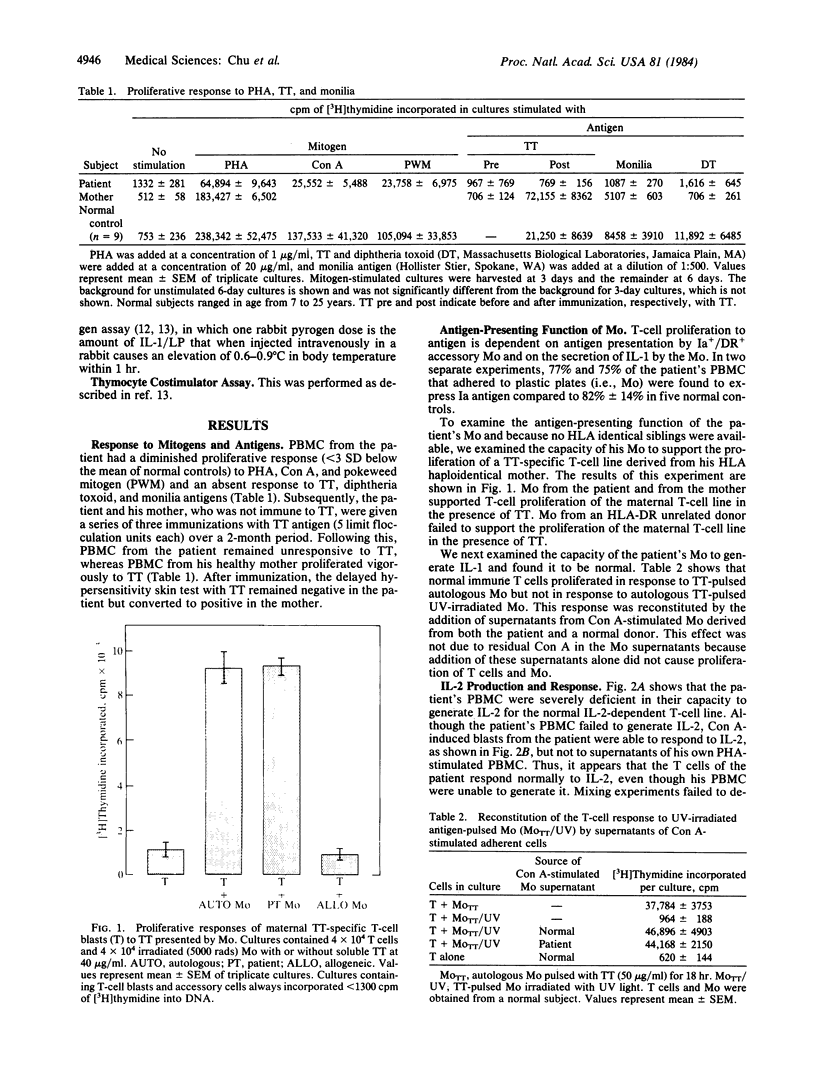
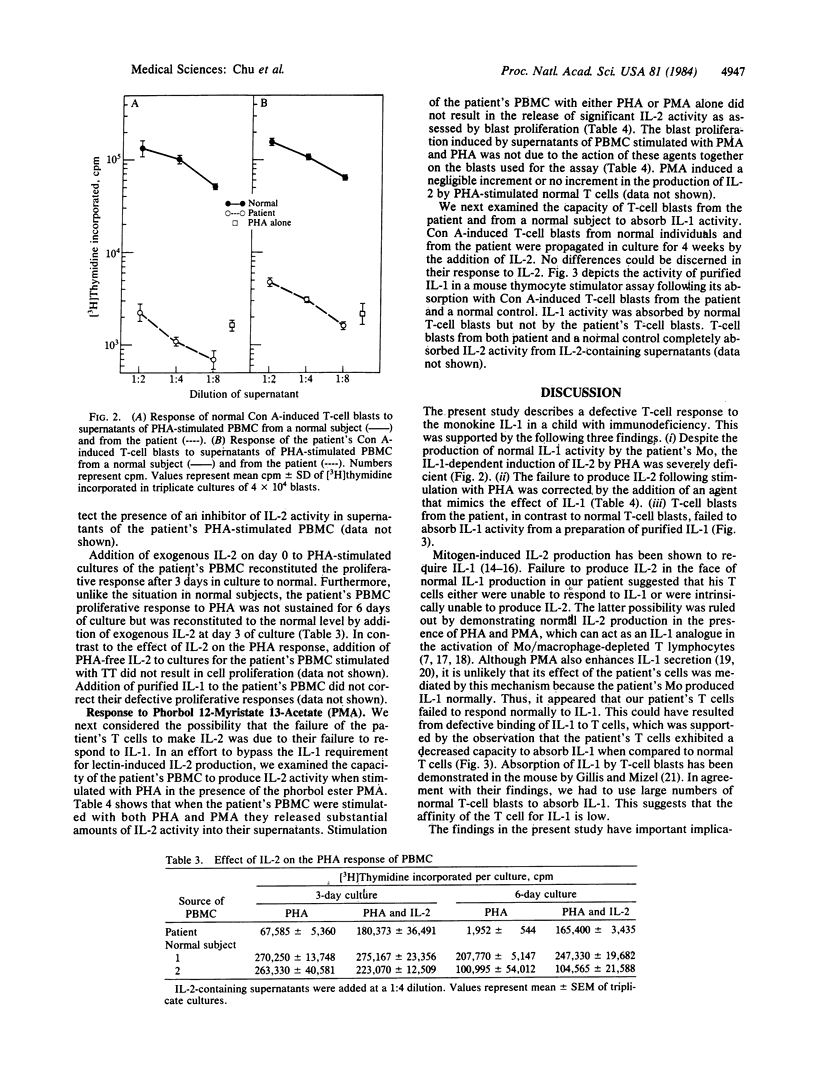
Abstract
Normal proliferation of T cells in vitro requires production of and response to the lymphokine interleukin 2 (IL-2). Optimal IL-2 production by T cells is dependent on the monokine interleukin 1 (IL-1). A 10-year-old male with recurrent infections and failure to thrive was evaluated for possible defects in the production and response to IL-1 and IL-2. The patient had normal levels of serum immunoglobulins and a normal distribution of circulating T-cell subsets. However, the in vitro proliferative response of his peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to phytohemagglutinin was depressed (40% of normal) and the response of his PBMC to antigens was absent. Delayed hypersensitivity skin tests and in vitro response to tetanus toxoid remained absent despite repeated immunizations. Monocyte function in this patient was normal as judged by the following criteria: normal expression of Ia antigens (77% +), normal IL-1 production, and normal capacity to present tetanus toxoid to a maternal T-cell line specific for tetanus toxoid antigen. The abnormal phytohemagglutinin response of the patient's PBMC was corrected by the addition of exogenous IL-2. IL-2 production by the patient's phytohemagglutin-stimulated PBMC was severely deficient but was corrected by the addition of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, suggesting a defective response to IL-1. T-cell blasts derived from a normal subject but not T-cell blasts derived from the patient absorbed out IL-1 activity from a preparation of purified human IL-1. These results indicate that the patient's T-cell deficiency was due to a defective T-cell response to IL-1 and suggest that IL-1 plays an important role in the in vivo immune response.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert S. D., Jonsen M. E., Broff M. D., Schneeberger E., Geha R. S. Macrophage T-cell interaction in man: handling of tetanus toxoid antigen by human monocytes. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):21–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00915473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu E., Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A., Lareau M., Geha R. S. Role of interleukin 1 in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1311–1316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFreitas E. C., Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M., Chiller J. M. Macrophage-dependent activation of antigen-specific T cells requires antigen and a soluble monokine. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Benjamin W. R., Hilfiker M. L., Howard M., Farrar W. L., Fuller-Farrar J. The biochemistry, biology, and role of interleukin 2 in the induction of cytotoxic T cell and antibody-forming B cell responses. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:129–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Hyslop N., Alami S., Farah F., Schneeberger E. E., Rosen F. S. Hyper immunoglobulin M immunodeficiency. (Dysgammaglobulinemia). Presence of immunoglobulin M-secreting plasmacytoid cells in peripheral blood and failure of immunoglobulin M-immunoglobulin G switch in B-cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):385–391. doi: 10.1172/JCI109473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N. Accessory cell stimulation of T cell proliferation requires active antigen processing, Ia-restricted antigen presentation, and a separate nonspecific 2nd signal. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1964–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mizel S. B. T-Cell lymphoma model for the analysis of interleukin 1-mediated T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Union N. A., Baker P. E., Smith K. A. The in vitro generation and sustained culture of nude mouse cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1460–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz T., Jebara H., Geha R. S. Induction of proliferation of human T cells and T-cell blasts by monocyte-derived factors and lectin. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jun;23(3):634–647. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Daniele R. P., Nowell P. C. A phorbol ester (TPA) can replace macrophages in human lymphocyte cultures stimulated with a mitogen but not with an antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1776–1780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnick J. T., Altevogt P., Lindblom J., Sjöberg O., Danneus A., Wigzell H. Long-term maintenance of HLA-D restricted T cells specific for soluble antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(2):131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Iscove N. N., Coutinho A. Two distinct factors are required for induction of T-cell growth. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):664–666. doi: 10.1038/283664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Thompson P. A., Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A. The role of interleukin 1 in human B cell activation: inhibition of B cell proliferation and the generation of immunoglobulin-secreting cells by an antibody against human leukocytic pyrogen. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2708–2714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Oppenheim J. J. Bidirectional amplification of macrophage-lymphocyte interactions: enhanced lymphocyte activation factor production by activated adherent mouse peritoneal cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Rosenstreich D. L., Oppenheim J. J. Phorbol myristic acetate stimulates LAF production by the macrophage cell line, P388D. Cell Immunol. 1978 Sep 15;40(1):230–235. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orosz C. G., Roopernian D. C., Bach F. H. Phorbol myristate acetate and in vitro T lymphocyte function. I. PMA may contaminate lymphokine preparations and can interfere with interleukin bioassays. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1764–1769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L. The role of Ia molecules in the activation of T lymphocytes. I. The activation of an IL 1-dependent IL 2-producing T cell hybridoma by Con A requires an interaction, which is not H-2-restricted, with an Ia-bearing accessory cell. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1360–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Mizel S. B. Signal requirements for T lymphocyte activation. I. Replacement of macrophage function with phorbol myristic acetate. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A. Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to enhance phytohemagglutinin induced murine thymocyte proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A., Rosenthal A. S. Adherent cell function in murine T-lymphocyte antigen recognition. IV. Enhancement of murine T-cell antigen recognition by human leukocytic pyrogen. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):709–714. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scala G., Oppenheim J. J. Antigen presentation by human monocytes: evidence for stimulant processing and requirement for interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1160–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Lachman L. B., Oppenheim J. J., Favata M. F. The functional relationship of the interleukins. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyth-Dreese F. A., van der Reijden H. J., de Vries J. E. Phorbol-ester-mediated induction and augmentation of mitogenesis and interleukin-2 production in human T-cell lymphoproliferative disease. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1437–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]