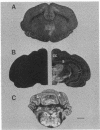
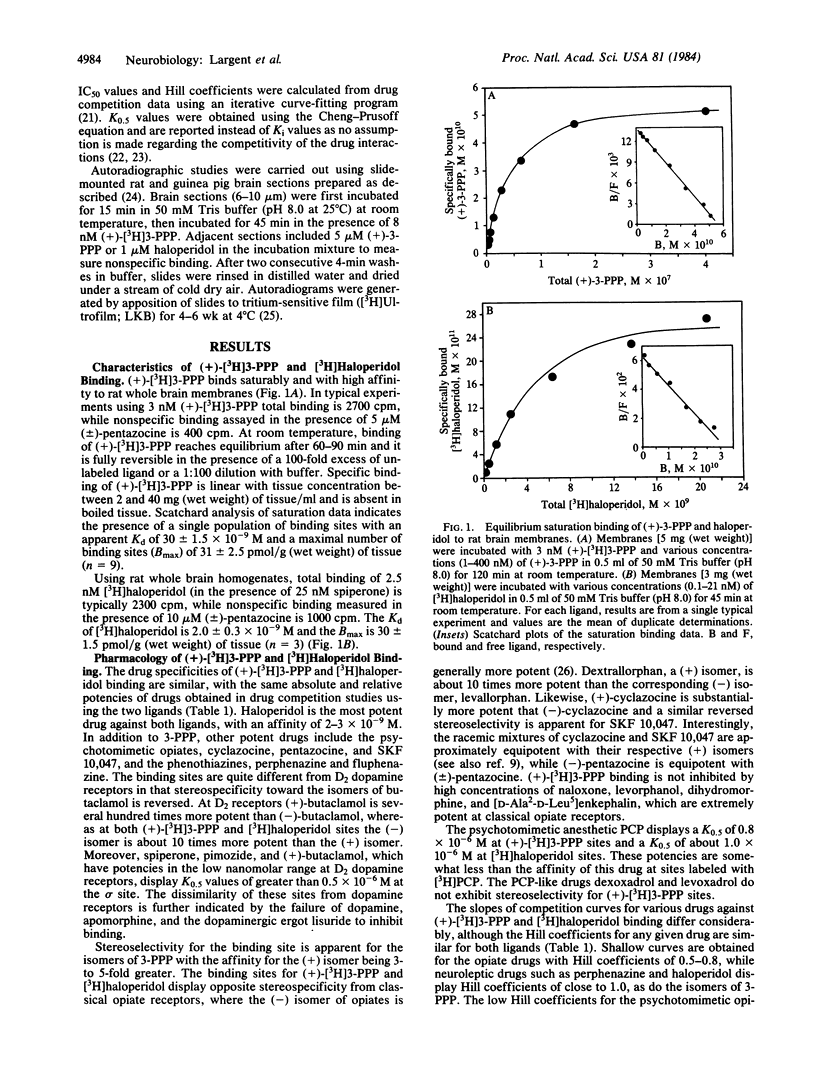
Abstract
3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine (3-PPP) has been proposed as a selective dopamine autoreceptor agonist in the central nervous system. This report describes the pharmacology and localization of specific high-affinity binding sites for (+)-[3H]3-PPP in brain. The drug specificity of (+)-[3H]3-PPP binding is identical to that of sigma receptors, which may mediate psychotomimetic effects of some opiates. Haloperidol and the opioid derivatives, pentazocine, cyclazocine, and SKF 10,047 are potent inhibitors of (+)-[3H]3-PPP binding. Stereoselectivity is exhibited for the (+) isomers of cyclazocine and SKF 10,047 at the sigma site, opposite to the stereoselectivity seen at mu, delta, and kappa opiate receptors. (+)-[3H]3-PPP does not label dopamine receptors, as potent dopamine agonists and antagonists are weak inhibitors of binding and the localization of specific (+)-[3H]3-PPP binding sites does not parallel that of dopamine neurons. Discrete localizations of (+)-[3H]3-PPP binding sites in many brain areas including limbic, midbrain, brainstem, and cerebellar regions may explain psychotomimetic actions of opiates and behavioral effects of 3-PPP.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnt J., Bøgesø K. P., Christensen A. V., Hyttel J., Larsen J. J., Svendsen O. Dopamine receptor agonistic and antagonistic effects of 3-PPP enantiomers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;81(3):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00427262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady K. T., Balster R. L., May E. L. Stereoisomers of N-allylnormetazocine: phencyclidine-like behavioral effects in squirrel monkeys and rats. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.6274022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone E. J., McQuinn R. L., Shannon H. E. Structure-activity relationship studies of phencyclidine derivatives in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costall B., Lim S. K., Naylor R. J. Characterisation of the mechanisms by which purported dopamine agonists reduce spontaneous locomotor activity of mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):175–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan A. Simple in vivo tests that differentiate prototype agonists at opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Apr 6;28(14):1559–1570. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese I., Sibley D. R., Hamblin M. W., Leff S. E. The classification of dopamine receptors: relationship to radioligand binding. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:43–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H. Kappa opiate receptors localized by autoradiography to deep layers of cerebral cortex: relation to sedative effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J., Young W. S., 3rd Differentiation of delta and mu opiate receptor localizations by light microscopic autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Medzihradsky F., Woods J. H., Dahlstrom P. J. Stereospecific binding of 3H-phencyclidine in brain membranes. Life Sci. 1982 Jun 21;30(25):2147–2154. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubrich D. R., Pflueger A. B. The autoreceptor control of dopamine synthesis. An in vitro and in vivo comparison of dopamine agonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S., Carlsson A., Clark D., Svensson K., Wikström H., Sanchez D., Lindberg P., Hacksell U., Arvidsson L. E., Johansson A. Central dopamine receptor agonist and antagonist actions of the enantiomers of 3-PPP. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;81(2):89–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00428999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S., Carlsson A., Wikström H., Lindberg P., Sanchez D., Hacksell U., Arvidsson L. E., Svensson U., Nilsson J. L. 3-PPP, a new centrally acting DA-receptor agonist with selectivity for autoreceptors. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 16;28(11):1225–1238. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto E. T. Locomotor activity and antinociception after putative mu, kappa and sigma opioid receptor agonists in the rat: influence of dopaminergic agonists and antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 May;217(2):451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markstein R., Lahaye D. In vitro effect of the racemic mixture and the (-)enantiomer of N-n-propyl-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-piperidine (3-PPP) on postsynaptic dopamine receptors and on a presynaptic dopamine autoreceptor. J Neural Transm. 1983;58(1-2):43–53. doi: 10.1007/BF01249123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwaha J. Candidate mechanisms underlying phencyclidine-induced psychosis: an electrophysiological behavioral, and biochemical study. Biol Psychiatry. 1982 Feb;17(2):155–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meibach R. C., Glicks D., Cox R., Maayani S. Localisation of phencyclidine-induced changes in brain energy metabolism. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):625–626. doi: 10.1038/282625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: autoradiographic localization in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. H. Dopamine autoreceptors: pharmacology, function and comparison with post-synaptic dopamine receptors. Commun Psychopharmacol. 1979;3(6):429–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Sep;32(3):229–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon H. E. Pharmacological evaluation of N-allynormetazocine (SKF 10,047) on the basis of its discriminative stimulus properties in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Apr;225(1):144–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifer B. L., Balster R. L. Reinforcing properties of stereoisomers of the putative sigma agonists N-allylnormetazocine and cyclazocine in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jun;225(3):522–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sminia P., Mulder A. H. Failure of 3-PPP to activate dopamine autoreceptors in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 22;89(1-2):183–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90628-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Goodman R. R. Multiple neurotransmitter receptors. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):5–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter S. M., Lo M. M., Javitch J. A., Snyder S. H. Autoradiographic visualization of angiotensin-converting enzyme in rat brain with [3H]captopril: localization to a striatonigral pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1599–1603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P. Evidence for sigma opioid receptor: binding of [3H]SKF-10047 to etorphine-inaccessible sites in guinea-pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W. Naloxone-inaccessible sigma receptor in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6703–6707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J., Palacios J. M. Quantitative receptor autoradiography using [3H]ultrofilm: application to multiple benzodiazepine receptors. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jul;6(1-2):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel D. B. Naltrexone fails to antagonize the sigma effects of PCP and SKF 10,047 in the dog. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 2;92(3-4):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kartalovski B., Geneste P., Kamenka J. M., Lazdunski M. Interaction of phencyclidine ("angel dust") with a specific receptor in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative analysis of drug-receptor interactions: I. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium properties. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 27;29(4):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Holtzman S. G. Three-choice drug discrimination: phencyclidine-like stimulus effects of opioids. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;80(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00427484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolverton W. L., Martin B. R., Balster R. L. Modification of the behavioral effects of phencyclidine by repeated drug exposure and body weight changes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1980 May;12(5):761–766. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(80)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Zukin S. R. Demonstration of [3H]cyclazocine binding to multiple opiate receptor sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):246–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Zukin R. S. Specific [3H]phencyclidine binding in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]