Abstract
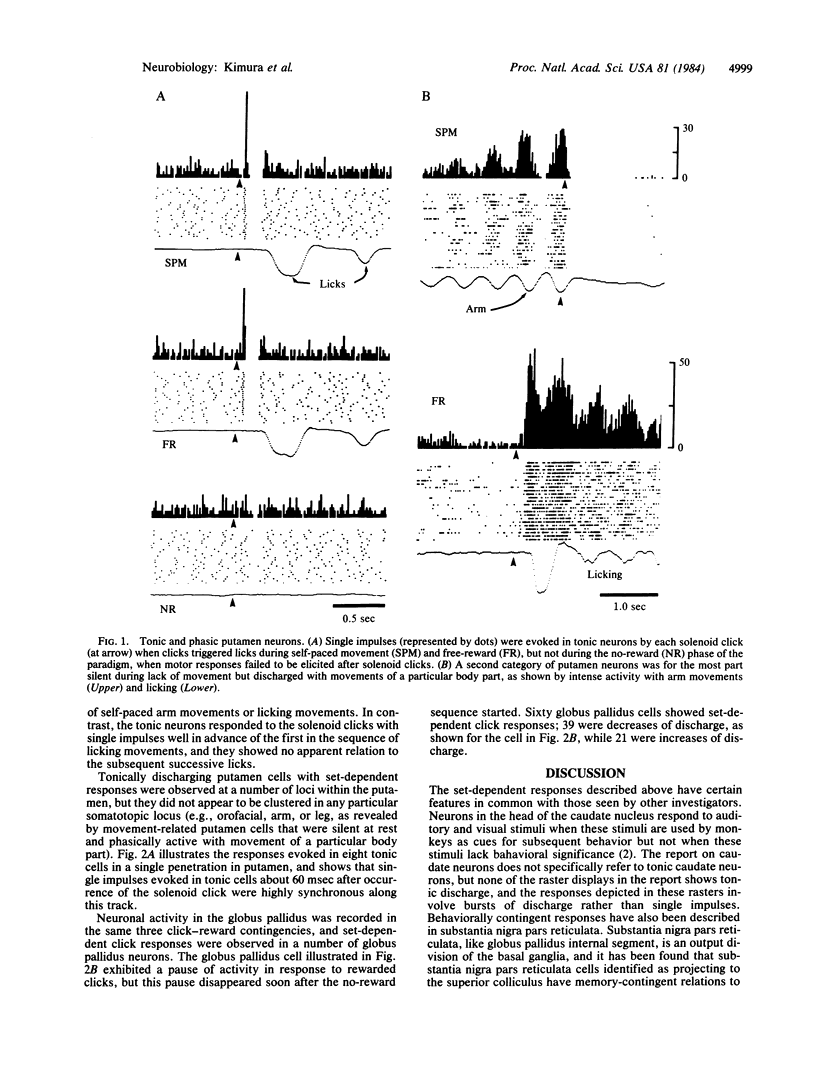
Previous microelectrode recordings in the putamen of monkeys have revealed a class of tonically active neurons without apparent behavioral correlates. The present study shows that such neurons have responses to stimuli that trigger movement but that these responses disappear when motor responses to the stimuli are extinguished. The short latency of the responses (less than for other putamen neurons) suggests that they may play a role in linking conditioned stimuli and responses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crutcher M. D., DeLong M. R. Single cell studies of the primate putamen. II. Relations to direction of movement and pattern of muscular activity. Exp Brain Res. 1984;53(2):244–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00238154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong M. R., Crutcher M. D., Georgopoulos A. P. Relations between movement and single cell discharge in the substantia nigra of the behaving monkey. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1599–1606. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFiglia M., Pasik P., Pasik T. A Golgi study of neuronal types in the neostriatum of monkeys. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 17;114(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C. The organization and some projections of cholinergic neurons of the mammalian forebrain. Brain Res. 1982 Nov;257(3):327–388. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(82)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale K., Hong J. S., Ghidotti A. Presence of substance P and GABA in separate striatonigral neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90813-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka O., Wurtz R. H. Visual and oculomotor functions of monkey substantia nigra pars reticulata. III. Memory-contingent visual and saccade responses. J Neurophysiol. 1983 May;49(5):1268–1284. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.5.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Yang H. Y., Racagni G., Costa E. Projections of substance P containing neurons from neostriatum to substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90464-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa I., Emson P. C., Cuello A. C. Evidence for the existence of substance P-containing fibres in striato-nigral and pallido-nigral pathways in rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 7;119(2):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., McGeer P. L., Peng J. H., McGeer E. G. The central cholinergic system studied by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Aug 1;200(2):151–201. doi: 10.1002/cne.902000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata K., Yoshida M. Caudate-evoked inhibition and actions of GABA and other substances on cat pallidal neurons. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 21;64:455–459. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasik P., Pasik T., DiFiglia M. Quantitative aspects of neuronal organization in the neostriatum of the macaque monkey. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1976;55:57–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Precht W., Yoshida M. Blockage of caudate-evoked inhibition of neurons in the substantia nigra by picrotoxin. Brain Res. 1971 Sep 10;32(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolls E. T., Thorpe S. J., Maddison S. P. Responses of striatal neurons in the behaving monkey. 1. Head of the caudate nucleus. Behav Brain Res. 1983 Feb;7(2):179–210. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(83)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


