Abstract
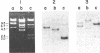
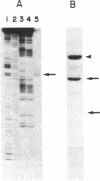
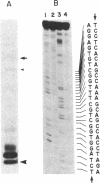
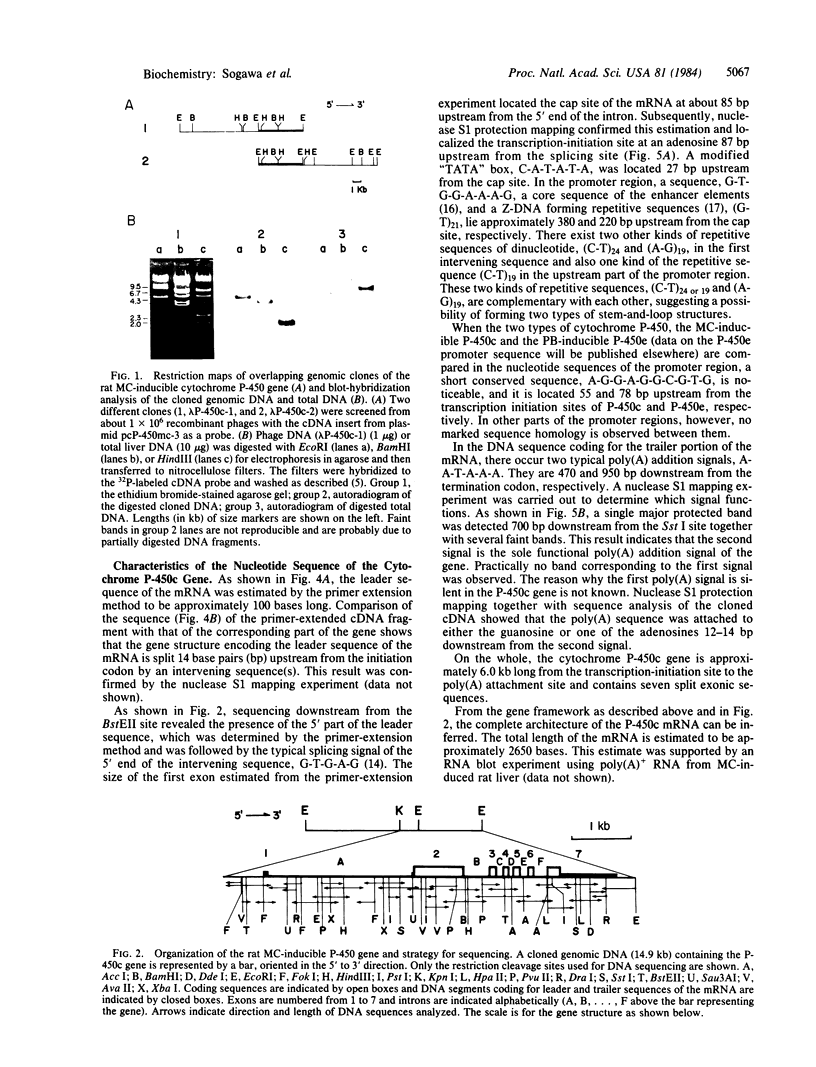
The complete nucleotide sequence of the methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochrome P-450c gene was determined by sequence analysis of cloned genomic DNA and the sequence, consisting of 524 amino acids, of the protein was deduced therefrom. The gene for the cytochrome was approximately 6.0 kilobases long and was split into seven exons. Comparison of the gene with that of the phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450e showed that the gene structures for the two types of cytochrome P-450 differ greatly; the location, number, and size of intervening sequences are very dissimilar. However, the sequence homology between the two types of cytochrome suggests that the two genes have evolved from a common ancestor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M., Adesnik M. A cytochrome P-450 multigene family. Characterization of a gene activated by phenobarbital administration. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11285–11295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botelho L. H., Ryan D. E., Yuan P. M., Kutny R., Shively J. E., Levin W. Amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal sequence of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450d, a unique hemoprotein from rats treated with isosafrole. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1152–1155. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durica D. S., Schloss J. A., Crain W. R., Jr Organization of actin gene sequences in the sea urchin: molecular cloning of an intron-containing DNA sequence coding for a cytoplasmic actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5683–5687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Timm R., Kimmel A. R., McKeown M. Unusual nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of actin genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Mizukami Y., Kawajiri K., Sogawa K., Muramatsu M. Primary structure of a cytochrome P-450: coding nucleotide sequence of phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 cDNA from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2793–2797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O., Tagashira Y., Iizuka T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structural characteristics of cytochrome P-450. Possible location of the heme-binding cysteine in determined amino-acid sequences. J Biochem. 1983 Mar;93(3):807–817. doi: 10.1093/jb/93.3.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniu M., Yuan P. M., Ryan D. E., Levin W., Shively J. E. Structural analysis of the cysteine-containing peptides from the major 3-methylcholanthrene-induced isozyme of cytochrome P-450 (P-450c) in rat liver microsomes. Biochemistry. 1984 May 22;23(11):2478–2482. doi: 10.1021/bi00306a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. P., Gonzalez F. J., Kasper C. B. Cloning of DNA complementary to cytochrome P-450 induced by pregnenolone-16 alpha-carbonitrile. Characterization of its mRNA, gene, and induction response. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10182–10186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri K., Gotoh O., Sogawa K., Tagashira Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Coding nucleotide sequence of 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochrome P-450d cDNA from rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1649–1653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri K., Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Tagashira Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Molecular cloning of a complementary DNA to 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochrome P-450 mRNA from rat liver. J Biochem. 1983 Nov;94(5):1465–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara S., Harada N., Yoshioka H., Miyata T., Omura T. Purification and characterization of four forms of cytochrome P-450 from liver microsomes of phenobarbital-treated and 3-methylcholanthrene-treated rats. J Biochem. 1984 Mar;95(3):703–714. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht M., Long G. L., Chandra T., Kurachi K., Kidd V. J., Mace M., Jr, Davie E. W., Woo S. L. Sequence homology and structural comparison between the chromosomal human alpha 1-antitrypsin and chicken ovalbumin genes. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):655–659. doi: 10.1038/297655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., West S. B. Multiplicity of mammalian microsomal cytochromes P-45. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Dec;31(4):277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Fritsch E. F., Lauer J., Lawn R. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobins. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:145–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M. Multiplicity of deoxyribonucleic acid sequences with homology to a cloned complementary deoxyribonucleic acid coding for rat phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1223–1229. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Sogawa K., Suwa Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder A., Leder P. Unusual alpha-globin-like gene that has cleanly lost both globin intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Catterall J. F., Kristo P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Ovomucoid intervening sequences specify functional domains and generate protein polymorphism. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Comparative analysis of the structural organization of two closely related vitellogenin genes in X. laevis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabusaki Y., Shimizu M., Murakami H., Nakamura K., Oeda K., Ohkawa H. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA coding for 3-methylcholanthrene-induced rat liver cytochrome P-450MC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2929–2938. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]