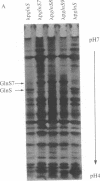
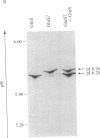
Abstract
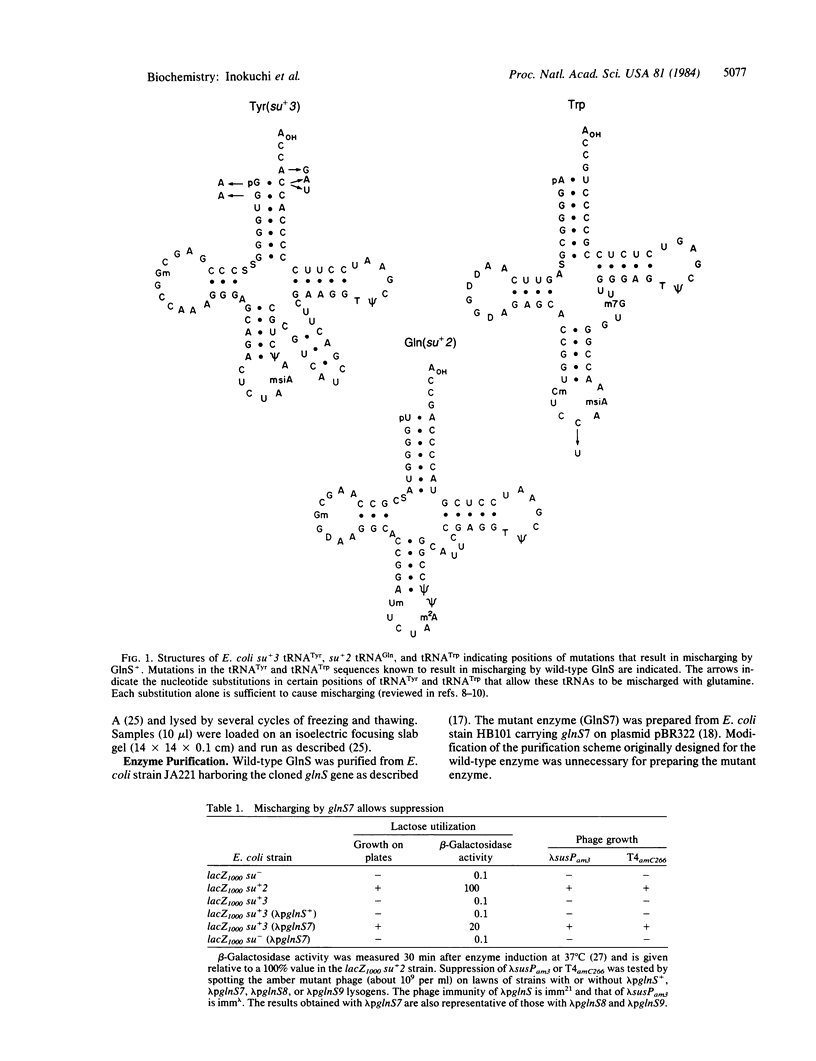
We have isolated mutations in the Escherichia coli glnS gene encoding glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase [GlnS; L-glutamine:tRNAGln ligase (AMP-forming), EC 6.1.1.18] that give rise to gene products with altered specificity for tRNA and are designated "mischarging" enzymes. These were produced by nitrosoguanine mutagenesis of the glnS gene carried on a transducing phage (lambda pglnS+). We then selected for mischarging of su+3 tRNATyr with glutamine by requiring suppression of a glutamine-requiring beta-galactosidase amber mutation (lacZ1000). Three independently isolated mutants (glnS7, glnS8, and glnS9) were characterized by genetic and biochemical means. The enzymes encoded by glnS7, glnS8, and glnS9 appear to be highly selective for su+3 tRNATyr, because in vivo mischarging of other amber suppressor tRNAs was not detected. The GlnS mutants described here retain their capacity to correctly aminoacylate tRNAGln. All three independently isolated mutant genes encode proteins with isoelectric points that differ from those of the wild-type enzyme but are identical to each other. This suggests that only a single site in the enzyme structure is altered to give the observed mischarging properties. In vitro aminoacylation reactions with purified GlnS7 protein show that this enzyme can also mischarge some tRNA species lacking the amber anticodon. This is an example of mischarging phenotype conferred by a mutation in an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase gene; the results are discussed in the context of earlier genetic studies with mutant tRNAs.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson J. N., Gefter M. L., Barnett L., Landy A., Russell R. L., Smith J. D. Mutant tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jan 14;47(1):15–28. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Coulondre C., Miller J. H. Suppressor su+7 inserts tryptophan in addition to glutamine. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):729–734. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Hooper M. L., Smith J. D. Amino acid acceptor stem of E. coli suppressor tRNA tyr is a site of synthetase recognition. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 29;244(139):261–264. doi: 10.1038/newbio244261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysen A., Celis J. E. Mischarging single and double mutants of Escherichia coli sup3 tyrosine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar;83(3):333–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoben P., Royal N., Cheung A., Yamao F., Biemann K., Söll D. Escherichia coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. II. Characterization of the glnS gene product. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11644–11650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M. L., Russell R. L., Smith J. D. Mischarging in mutant tyrosine transfer RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J., Yamane T., Yue V., Coutts S. M. Direct experimental evidence for kinetic proofreading in amino acylation of tRNAIle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi H., Celis J. E., Smith J. D. Letter: Mutant tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli: construction by recombination of a double mutant A1G82 chargeable with glutamine. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi H., Kodaira M., Yamao F., Ozeki H. Identification of transfer RNA suppressors in Escherichia coli. II. Duplicate genes for tRNA2Gln. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):663–677. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner A., Magee B. B., Liska B., Low K. B., Adelberg E. A., Söll D. Isolation and partial characterization of a temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli mutant with altered glutaminyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):154–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.154-158.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftfield R. B., Vanderjagt D. The frequency of errors in protein biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1353–1356. doi: 10.1042/bj1281353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels C. A., Zipser D. Mapping of polypeptide reinitiation sites within the beta-galactosidase structural gene. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D., Khorana H. G. Studies on polynucleotides, lix. Further codon assignments from amino Acid incorporations directed by ribopolynucleotides containing repeating trinucleotide sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1899–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan S., Körner A., Low K. B., Söll D. Regulation of biosynthesis of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and of tRNA in Escherichia coli. I. Isolation and characterization of a mutant with elevated levels of tRNAGln 1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 25;117(4):1013–1031. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami A., Inokuchi H., Hirota Y., Ozeki H., Yamagishi H. Characterization of dnaA gene carried by lambda transducing phage. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;180(2):235–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00425835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. R., Söll D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: general features and recognition of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:601–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno T., Agris P. F., Söll D. Involvement of the anticodon region of Escherichia coli tRNAGln and tRNAGlu in the specific interaction with cognate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Alteration of the 2-thiouridine derivatives located in the anticodon of the tRNAs by BrCN or sulfur deprivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 31;349(3):328–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura Y., Aono H., Ozeki H., Sarabhai A., Lamfrom H., Abelson J. Mutant tyrosine tRNA of altered amino acid specificity. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Barnett L., Brenner S., Russell R. L. More mutant tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 28;54(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Celis J. E. Mutant tyrosine transfer RNA that can be charged with glutamine. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 16;243(124):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamao F., Inokuchi H., Cheung A., Ozeki H., Söll D. Escherichia coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase. I. Isolation and DNA sequence of the glnS gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11639–11643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Folk W. R., Berg P., Soll L. A single mutational modification of a tryptophan-specific transfer RNA permits aminoacylation by glutamine and translation of the codon UAG. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]