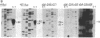Abstract
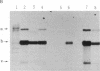
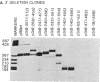
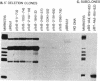
Plasmid clones containing a human Alu family repeat can be transcribed efficiently by RNA polymerase III in HeLa cell extract. This generated three RNA species, all of which initiated from the first base (+1) of the repeat. By studying the transcriptional properties of deletion clones, subclones, and topologically different DNA templates, we demonstrated that: supercoiled DNA templates are transcribed 3- to 5-fold more efficiently than are linear or nicked circular DNA molecules; a contiguous DNA helix in the transcription complexes that extends into the 5' flanking region of positions -30 to -85 is absolutely required for initiation to occur (this interaction does not involve recognition of specific DNA sequences); and similar to the adenovirus VAI RNA and tRNA genes, the Alu repeat 3' to the alpha 1-globin gene (designated 3'-alpha 1 Alu) contains a split intragenic promoter: an anterior element (positions +4 to +37) and a posterior element (positions +70 to +82). However, the promoter of the Alu repeat functions in distinctive ways in comparison to those of other RNA polymerase III-dependent genes. The posterior promoter element alone is sufficient and necessary for an accurate initiation to occur. The presence of the anterior promoter element, which by itself does not initiate transcription, enhances the transcriptional efficiency by a factor of 10- to 20-fold. Furthermore, the distance between the initiation sites and the posterior promoter element, but not the anterior promoter element, remains constant. These results suggest that the promoter of this Alu family repeat consists of at least two functionally different domains: a "directing element" (the posterior promoter element) that determines the accuracy of initiation and an "enhancing element" (the anterior promoter element) that is mainly responsible for the transcriptional efficiency.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Goh S. H., Hall B. D. The promoter sequence of a yeast tRNAtyr gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. Cloned single repeating units of 5S DNA direct accurate transcription of 5S RNA when injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrara G., Di Segni G., Otsuka A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Deletion of the 3' half of the yeast tRNA-Leu3 gene does not abolish promotor function in vitro. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Cortese R. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:59–88. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Raugei G., Costanzo F., Dente L., Cortese R. Common and interchangeable elements in the promoters of genes transcribed by RNA polymerase iii. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Traboni C., Cortese R. Relationship between the two components of the split promoter of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1921–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Sharp S., Söll D. Identification of regulatory sequences contained in the 5'-flanking region of Drosophila lysine tRNA2 genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12424–12429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Burke D. J., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. The 5- flanking sequences of Drosophila tRNAArg genes control their in vitro transcription in a Drosophila cell extract. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14738–14744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. Stable transcription complex formation of eukaryotic tRNA genes is dependent on a limited separation of the two intragenic control regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10395–10402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Jagadeeswaran P., Wang R. R., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of templates and RNA polymerase III transcripts of Alu family sequences interspersed among the human beta-like globin genes. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Hofstetter H. A detailed mutational analysis of the eucaryotic tRNAmet1 gene promoter. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Shen C. K., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. The organization of repetitive sequences in mammalian globin gene clusters. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):761–765. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Deininger P. L., LaPorte P., Friedmann T., Geiduschek E. P. Analysis of transcription of the human Alu family ubiquitous repeating element by eukaryotic RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6439–6456. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R., Weinmann R. Control region for adenovirus VA RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3378–3382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Weintraub H., McKnight S. L. Transcription of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is influenced by template topology. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):38–43. doi: 10.1038/302038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Fox M., Schmid C., Shen C. K. Molecular evolution of the human adult alpha-globin-like gene region: insertion and deletion of Alu family repeats and non-Alu DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5970–5974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Clarkson S. G. 5'-flanking sequences that inhibit in vitro transcription of a xenopus laevis tRNA gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Association of a 5S gene transcription factor with 5S RNA and altered levels of the factor during cell differentiation. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Short interspersed repetitive DNA elements in eucaryotes: transposable DNA elements generated by reverse transcription of RNA pol III transcripts? Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90296-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Specific interactions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with a promoter region of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Clarkson S. G., Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Smith M. Mutations of the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: transcription of the mutant genes in vitro. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):415–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Hofstetter H., Di Capua E., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. A tRNA gene of Xenopus laevis contains at least two sites promoting transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1749–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. Directed semisynthetic point mutational analysis of an RNA polymerase III promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7695–7700. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Ogden R. C., Abelson J. tRNA gene transcription in yeast: effects of specified base substitutions in the intragenic promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan J., Elder J. T., Duncan C. H., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of interspersed repetitive polymerase III transcription units in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1151–1170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Dingermann T., Farrell P., Söll D. Internal control regions for transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6657–6661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., Dingermann T., Schaack J., DeFranco D., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. I. Analysis of control regions using a competition assay. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2440–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The organization, structure, and in vitro transcription of Alu family RNA polymerase III transcription units in the human alpha-like globin gene cluster: precipitation of in vitro transcripts by lupus anti-La antibodies. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):343–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague K. U., Larson D., Morton D. 5' flanking sequence signals are required for activity of silkworm alanine tRNA genes in homologous in vitro transcription systems. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The yeast his3 promoter contains at least two distinct elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Arsdell S. W., Denison R. A., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Direct repeats flank three small nuclear RNA pseudogenes in the human genome. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. J. Adenovirus DNA-directed transcription of 5.5S RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]