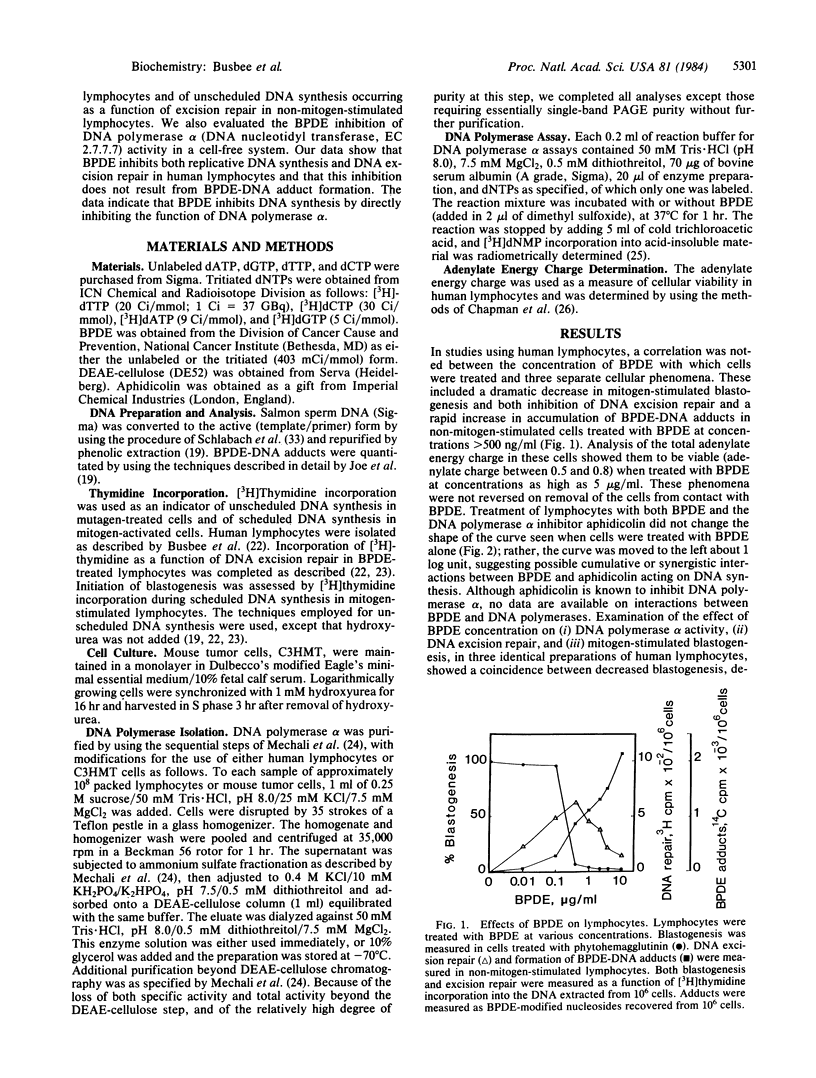
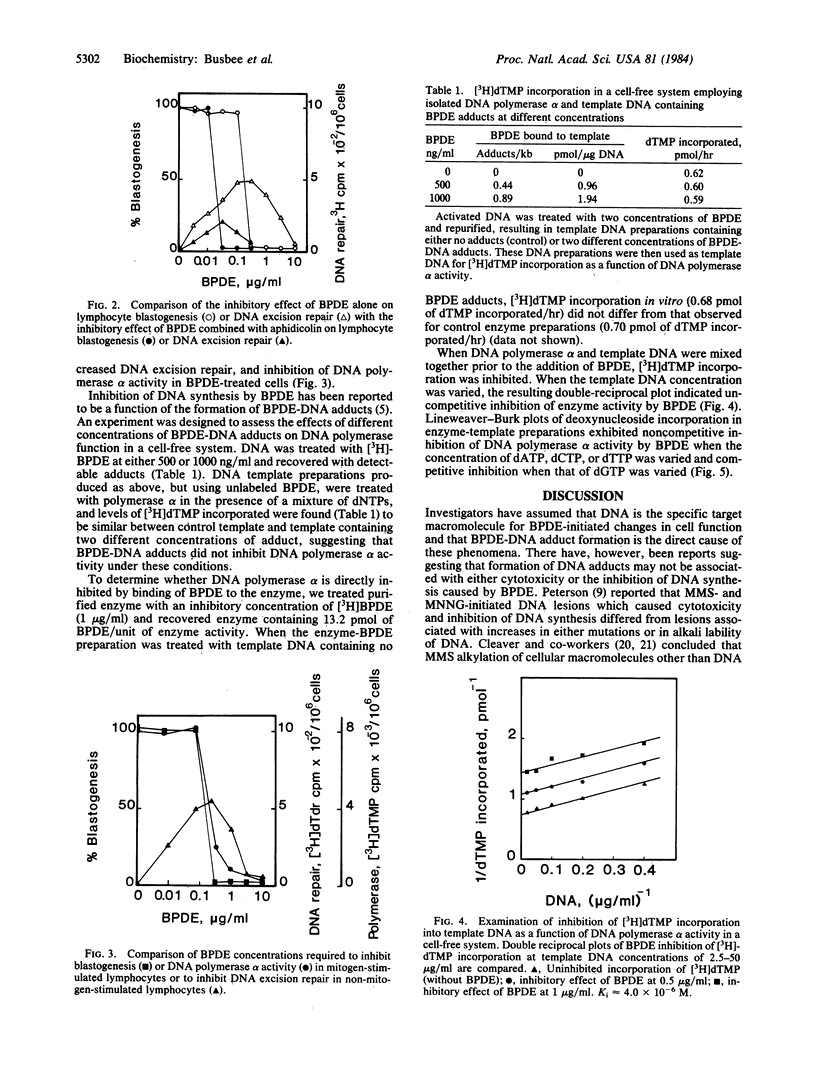
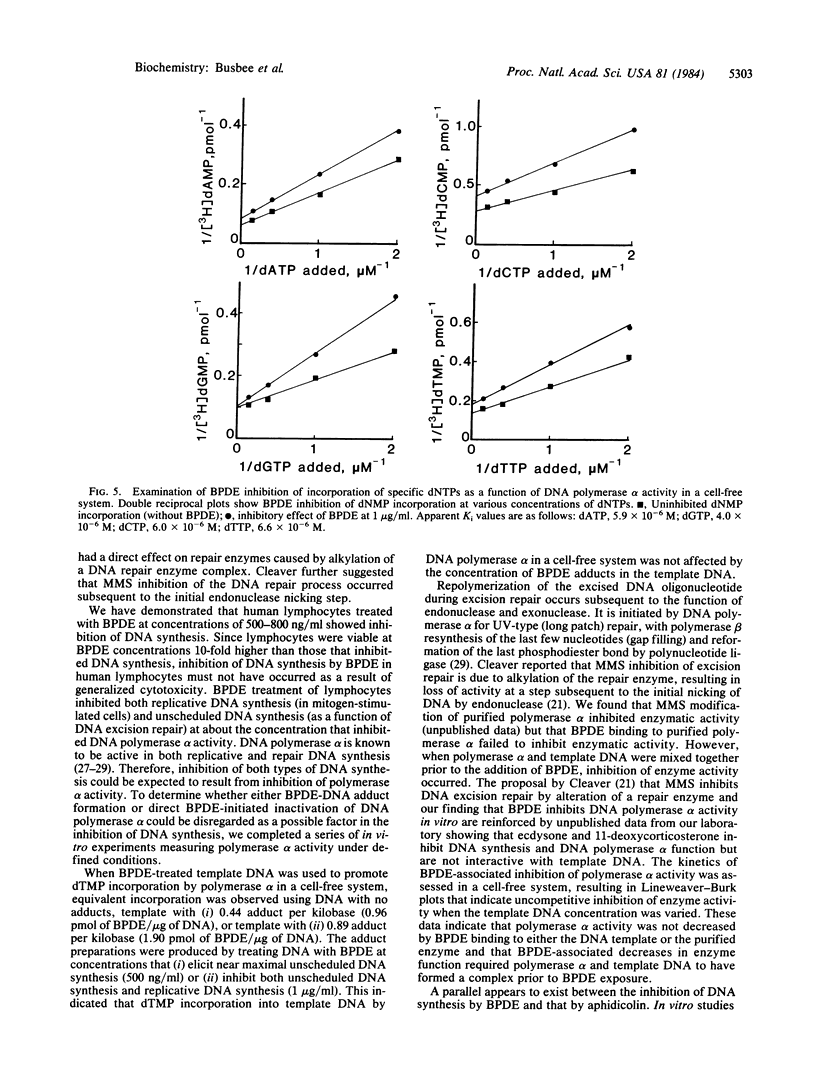
Abstract
Mitogen-stimulated scheduled DNA synthesis and DNA excision repair in human lymphocytes, as well as DNA polymerase a activity in a cell-free system, were inhibited by an electrophilic metabolite of benzo[a]pyrene. This metabolite, (+/-)-anti-(7r,8t)-dihydroxy-(9,10t)-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahyd robenzo[a]pyrene (BPDE), covalently binds to cellular macromolecules and is mutagenic, carcinogenic, and cytotoxic. Human lymphocytes treated with BPDE at concentrations greater than 500-800 ng/ml showed decreases in both mitogen-stimulated DNA synthesis and excision repair of damaged DNA but did not exhibit overt cytotoxicity (excluded trypan blue and maintained an adenylate charge of greater than 0.7). Formation of, and total concentration of, BPDE-DNA adducts was not correlated with inhibition of DNA synthesis. DNA polymerase alpha studies using a cell-free system showed that enzymatic activity was not diminished when purified polymerase was treated with BPDE prior to the addition of template DNA. When the template DNA concentration was varied, BPDE inhibition of enzyme activity was uncompetitive. BPDE inhibition of enzyme activity was found to be noncompetitive when concentrations of dATP, dCTP, or dTTP were varied and competitive when the concentration of dGTP was varied. The data indicate that BPDE competitively inhibits interaction of dGTP with the template-DNA polymerase alpha complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brookes P., Osborne M. R. Mutation in mammalian cells by stereoisomers of anti-benzo[a] pyrene-diolepoxide in relation to the extent and nature of the DNA reaction products. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(10):1223–1226. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.10.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busbee D. L., Rankin P. W., Payne D. M., Jasheway D. W. Binding of benzo[a]pyrene and intracellular transport of a bound electrophilic benzo[a]pyrene metabolite by lipoproteins. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(10):1107–1112. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.10.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busbee D. L., Rankin P., Mitchell V. R., Cantrell E. T., Jacobson M. K. Correlation of carcinogen-induced unscheduled DNA synthesis and NAD reduction in fresh human lymphocytes. Cancer Lett. 1980 Dec;11(2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(80)90106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti P. A., Sessions F., Hariharan P. V., Lusby A. Repair of DNA damage induced by benzo(a)pyrene diol-epoxides I and II in human alveolar tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):2118–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Fall L., Atkinson D. E. Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli during growth and starvation. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1072–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1072-1086.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Inactivation of ultraviolet repair in normal and xeroderma pigmentosum cells by methyl methanesulfonate. Cancer Res. 1982 Mar;42(3):860–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Painter R. B. Absence of specificity in inhibition of DNA repair replication by DNA-binding agents, cocarcinogens, and steroids in human cells. Cancer Res. 1975 Jul;35(7):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Repair replication of mammalian cell DNA: effects of compounds that inhibit DNA synthesis or dark repair. Radiat Res. 1969 Feb;37(2):334–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Structure of repaired sites in human DNA synthesized in the presence of inhibitors of DNA polymerases alpha and beta in human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 15;739(3):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detera S. D., Becerra S. P., Swack J. A., Wilson S. H. Studies on the mechanism of DNA polymerase alpha. Nascent chain elongation, steady state kinetics, and the initiation phase of DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6933–6943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S. E., Larcom L. L. Inhibition of unscheduled DNA synthesis in human lymphocytes by chemical carcinogens. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Aug 15;46(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin D., Guthrie L., Yielding K. L. DNA repair inhibition: a new mechanism of action of steroids with possible implications for tumor therapy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jun;146(2):401–405. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanaoka F., Kato H., Ikegami S., Oashi M., Yamada M. Aphidicolin does inhibit repair replication in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 30;87(2):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91833-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami S., Taguchi T., Ohashi M., Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):458–460. doi: 10.1038/275458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joe C. O., Rankin P. W., Busbee D. L. Human lymphocytes treated with r-7,t-8-dihydroxy-t-9,10-epoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene require low-density lipoproteins for DNA excision repair. Mutat Res. 1984 Jan;131(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod M. C., Kootstra A., Mansfield B. K., Slaga T. J., Selkirk J. K. Specificity in interaction of benzo[a]pyrene with nuclear macromolecules: implication of derivatives of two dihydrodiols in protein binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6396–6400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechali M., Abadiedebat J., de Recondo A. M. Eukaryotic DNA polymerase alpha. Structural analysis of the enzyme from regenerating rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2114–2122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Chinault D. N. The roles of DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma in DNA repair synthesis induced in hamster and human cells by different DNA damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10204–10209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguro M., Suzuki-Hori C., Nagano H., Mano Y., Ikegami S. The mode of inhibitory action by aphidicolin on eukaryotic DNA polymerase alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):603–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. D., Choi K. H., Hong S. W., Cleaver J. E. Inhibition of excision-repair of ultraviolet damage in human cells by exposure to methyl methanesulfonate. Mutat Res. 1981 Jul;82(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(81)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. R. DNA synthesis, mutagenesis, DNA damage, and cytotoxicity in cultured mammalian cells treated with alkylating agents. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):682–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier M. C., De Cicco B. T., Lieberman M. W. Nonspecific inhibition of DNA repair synthesis by tumor promoters in human diploid fibroblasts damaged with N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene. Cancer Res. 1975 Jun;35(6):1392–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen R. E. Inhibition of DNA replicative synthesis and DNA repair synthesis in human and mouse cells in culture by cigarette smoke condensate fractions. Life Sci. 1975 Sep 1;17(5):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. L., Moses R. E. Effect of bleomycin on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in toluene-treated Escherichia coli cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):239–246. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlabach A., Fridlender B., Bolden A., Weissbach A. DNA-dependent DNA polymerases from HeLa cell nuclei. II. Template and substrate utilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):879–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90793-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara K., Cerutti P. A. Excision repair of benzo[a]pyrene-deoxyguanosine adducts in baby hamster kidney 21/C13 cells and in secondary mouse embryo fibroblasts C57BL/6J. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):979–983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomatis L. The IARC program on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;271:396–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb23139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



