Abstract
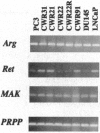
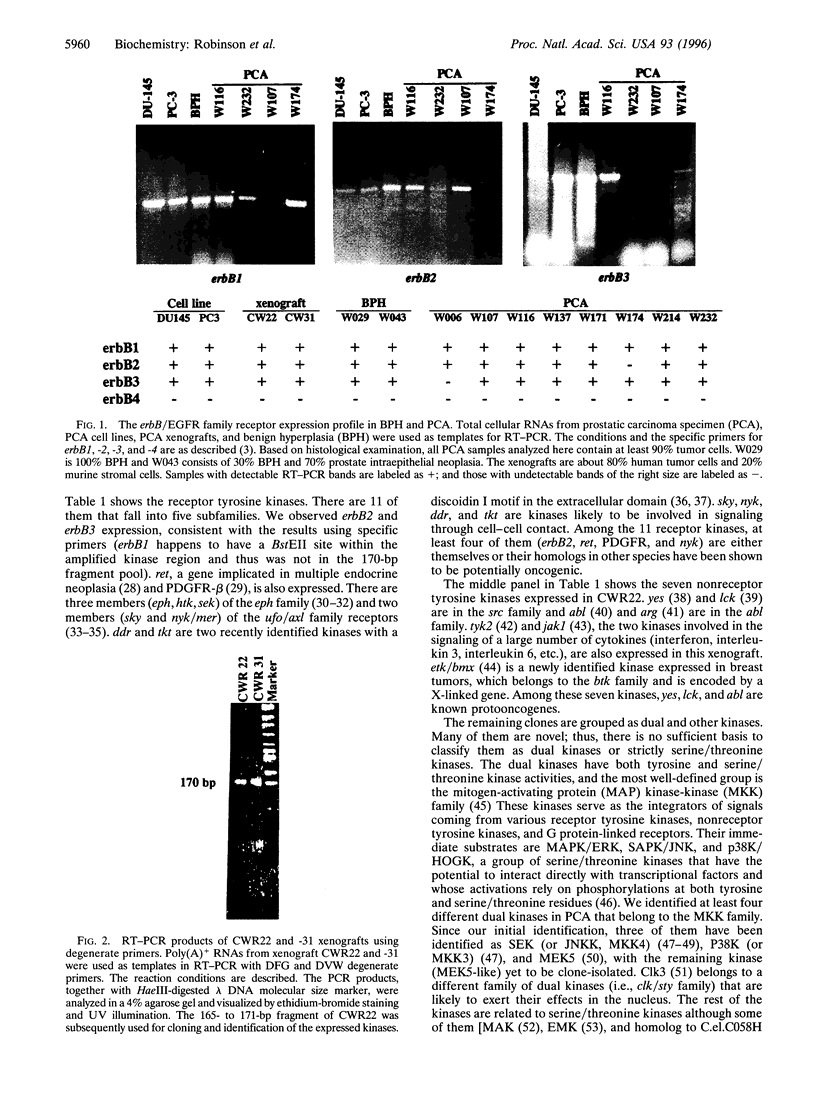
Tyrosine kinases play central roles in the growth and differentiation of normal and tumor cells. In this study, we have analyzed the general tyrosine kinase expression profile of a prostate carcinoma (PCA) xenograft, CWR22. We describe here an improved reverse transcriptase-PCR approach that permits identification of nearly 40 different kinases in a single screening; several of these kinases are newly cloned kinases and some are novel. According to this, there are 11 receptor kinases, 9 nonreceptor kinases, and at least 7 dual kinases expressed in the xenograft tissue. The receptor kinases include erbB2, erbB3, Ret, platelet-derived growth factor receptor, sky, nyk, eph, htk, sek (eph), ddr, and tkt. The nonreceptor kinases are lck, yes, abl, arg, JakI, tyk2, and etk/bmx. Most of the dual kinases are in the mitogen-activating protein (MAP) kinase-kinase (MKK) family, which includes MKK3, MKK4, MEK5, and a novel one. As a complementary approach, we also analyzed by specific reverse transcriptase-PCR primers the expression profile of erbB/epidermal growth factor receptor family receptors in a variety of PCA specimens, cell lines, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. We found that erbB1, -2, and -3 are often coexpressed in prostate tissues, but not in erbB4. The information established here should provide a base line to study the possible growth and oncogenic signals of PCA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A. Growth factors and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1146–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.1659742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett B. D., Wang Z., Kuang W. J., Wang A., Groopman J. E., Goeddel D. V., Scadden D. T. Cloning and characterization of HTK, a novel transmembrane tyrosine kinase of the EPH subfamily. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14211–14218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Raingeaud J., Barrett T., Wu I. H., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7839144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firmbach-Kraft I., Byers M., Shows T., Dalla-Favera R., Krolewski J. J. tyk2, prototype of a novel class of non-receptor tyrosine kinase genes. Oncogene. 1990 Sep;5(9):1329–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Nieto M. A., Frain M., Mattéi M. G., Chestier A., Wilkinson D. G., Charnay P. An Eph-related receptor protein tyrosine kinase gene segmentally expressed in the developing mouse hindbrain. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):1103–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. K., Dawson T. L., Mullaney D. L., Snodgrass H. R., Earp H. S. Cloning and mRNA expression analysis of a novel human protooncogene, c-mer. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Jun;5(6):647–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Heisterkamp N., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Homology between phosphotyrosine acceptor site of human c-abl and viral oncogene products. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):167–169. doi: 10.1038/304167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwald R. G., Grant F. J., Haldeman B. A., Hart C. E., O'Hara P. J., Hagen F. S., Ross R., Bowen-Pope D. F., Murray M. J. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor: evidence for more than one receptor class. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3435–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes J., von der Kammer H., Klaudiny J., Scheit K. H. Characterization by cDNA cloning of two new human protein kinases. Evidence by sequence comparison of a new family of mammalian protein kinases. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 16;244(5):665–672. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Maru Y., Hagiwara K., Nishida J., Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1717–1720. doi: 10.1126/science.2825356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90405-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn T., Holtrich U., Bräuninger A., Böhme B., Wolf G., Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Strebhardt K. Structure, expression and chromosomal mapping of TKT from man and mouse: a new subclass of receptor tyrosine kinases with a factor VIII-like domain. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3433–3440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Myers J. N., Wada T., Brown V. I., LeVea C. M., Davis J. G., Dobashi K., Greene M. I. Synergistic interaction of p185c-neu and the EGF receptor leads to transformation of rodent fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90843-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruh G. D., Perego R., Miki T., Aaronson S. A. The complete coding sequence of arg defines the Abelson subfamily of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5802–5806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. J., Kurnot R. A., Sesterhenn I. A., Chang E. H., Moul J. W. Expression of the c-erbB-2 (HER-2/neu) oncoprotein in human prostatic carcinoma. J Urol. 1993 Nov;150(5 Pt 1):1427–1433. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Lemke G. An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):691–704. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laval S., Butler R., Shelling A. N., Hanby A. M., Poulsom R., Ganesan T. S. Isolation and characterization of an epithelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase from an ovarian cancer cell line. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Nov;5(11):1173–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Minden A., Martinetto H., Claret F. X., Lange-Carter C., Mercurio F., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):286–290. doi: 10.1126/science.7716521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L., Kung H. J. Mitogenic signals and transforming potential of Nyk, a newly identified neural cell adhesion molecule-related receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6582–6592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell D. K., Lee A., Lansing T. J., Crosby R. M., Jung K. D., Willard D., Luther M., Rodriguez M., Berman J., Gilmer T. M. Involvement of pp60c-src with two major signaling pathways in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):83–87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald A., Habib F. K. Divergent responses to epidermal growth factor in hormone sensitive and insensitive human prostate cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1992 Feb;65(2):177–182. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Jinno A., Takagi N., Shibuya M. A novel mammalian protein kinase gene (mak) is highly expressed in testicular germ cells at and after meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2261–2268. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder E., van Loon D., de Boer W., Schuurmans A. L., Bolt J., Voorhorst M. M., Kuiper G. G., Brinkmann A. O. Mechanism of androgen action: recent observations on the domain structure of androgen receptors and the induction of EGF-receptors by androgens in prostate tumor cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1989 Jan;32(1B):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi K., Mizuno K., Kuma K., Miyata T., Nakamura T. Cloning of the cDNA for a novel receptor tyrosine kinase, Sky, predominantly expressed in brain. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):699–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Peet R., Ziegler S. F., Wilson C. B. Structure and expression of lck transcripts in human lymphoid cells. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Oct;38(2):117–126. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240380206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent S. A., Gullick W. J. Identification of c-erbB-3 binding sites for phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase and SHC using an EGF receptor/c-erbB-3 chimera. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2831–2841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06577.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roessler B. J., Bell G., Heidler S., Seino S., Becker M., Palella T. D. Cloning of two distinct copies of human phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):193–193. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. S., Nazeer T., Church K., Amato C., Figge H., Rifkin M. D., Fisher H. A. Contribution of HER-2/neu oncogene expression to tumor grade and DNA content analysis in the prediction of prostatic carcinoma metastasis. Cancer. 1993 Nov 15;72(10):3020–3028. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931115)72:10<3020::aid-cncr2820721026>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivan R., Morgan R., Jennings S., Austenfeld M., Van Veldhuizen P., Stephens R., Noble M. Overexpression of Her-2/neu may be an indicator of poor prognosis in prostate cancer. J Urol. 1993 Jul;150(1):126–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35413-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. J., Nigg E. A. Identification of 21 novel human protein kinases, including 3 members of a family related to the cell cycle regulator nimA of Aspergillus nidulans. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Oct;4(10):821–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwkowski M. X., Schaefer G., Akita R. W., Lofgren J. A., Fitzpatrick V. D., Nuijens A., Fendly B. M., Cerione R. A., Vandlen R. L., Carraway K. L., 3rd Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14661–14665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Carraway K. L., 3rd, Prigent S. A., Gullick W. G., Cantley L. C. ErbB3 is involved in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3550–3558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa J., Semba K., Yamanashi Y., Nishizawa M., Miyajima N., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Characterization of cDNA clones for the human c-yes gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Cooper G. M. ret transforming gene encodes a fusion protein homologous to tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1378–1385. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagnone L., Lahtinen I., Mustonen T., Virtaneva K., Francis F., Muscatelli F., Alitalo R., Smith C. I., Larsson C., Alitalo K. BMX, a novel nonreceptor tyrosine kinase gene of the BTK/ITK/TEC/TXK family located in chromosome Xp22.2. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3683–3688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson J. K., Rose D. P. Density-dependent regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in DU 145 human prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 1991;19(1):53–61. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990190106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Suggs S. V., Karunagaran D., Liu N., Cupples R. L., Luo Y., Janssen A. M., Ben-Baruch N., Trollinger D. B., Jacobsen V. L. Structural and functional aspects of the multiplicity of Neu differentiation factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1909–1919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding G., Valverius E., Knabbe C., Gelmann E. P. Role of transforming growth factor-alpha in human prostate cancer cell growth. Prostate. 1989;15(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Harpur A. G., Kurban R. R., Ralph S. J., Zürcher G., Ziemiecki A. Two novel protein-tyrosine kinases, each with a second phosphotransferase-related catalytic domain, define a new class of protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2057–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F. Two putative protein-tyrosine kinases identified by application of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo P. A., Tong T., Bolden S. Cancer statistics, 1995. CA Cancer J Clin. 1995 Jan-Feb;45(1):8–30. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.45.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhau H. E., Pisters L. L., Hall M. C., Zhao L. S., Troncoso P., Pollack A., Chung L. W. Biomarkers associated with prostate cancer progression. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1994;19:208–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G., Bao Z. Q., Dixon J. E. Components of a new human protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12665–12669. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]