Abstract
Simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor (T) antigen isolated from mammalian cells undergoing lytic or transforming infection is associated with small RNA fragments ("T-antigen RNA") that are protected from nuclease digestion. The rather high complexity of the ribonuclease T1 fingerprints of T-antigen RNA suggested that it is mainly derived from cellular heterogeneous nuclear RNAs. In the present study, 5'-32P-labeled T-antigen RNA was hybridized to monkey, mouse, and human Alu and SV40 DNA, and the nucleotide sequence of 37 T1 oligonucleotides was determined. The results suggest that the bulk of T-antigen RNA is derived from noncoding, double-stranded, ordered regions of cellular heterogeneous nuclear RNAs that exhibit sequence homologies with interspersed repetitive elements of the cellular genome. The possible biological implications of these results are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachellerie J. P., Michot B., Raynal F. Recognition signals for mouse pre-rRNA processing. A potential role for U3 nucleolar RNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00777477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W. Vitamin A and retinoids: from nutrition to pharmacotherapy in dermatology and oncology. Lancet. 1983 Apr 16;1(8329):860–863. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91394-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Hough B. R., Amenson C. S., Britten R. J. General interspersion of repetitive with non-repetitive sequence elements in the DNA of Xenopus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 15;77(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Jolly D. J., Rubin C. M., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Base sequence studies of 300 nucleotide renatured repeated human DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. F., Allet B., Weil R., Ahmad-Zadeh C. Synthesis of the tumour antigen and the major capsid protein of simian virus 40 in a cell-free system derived from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):361–379. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N. Nucleotide sequences of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of mouse and hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Attenuation in the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houck C. M., Rinehart F. P., Schmid C. W. A ubiquitous family of repeated DNA sequences in the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):289–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Loche M., Darlix J. L., Cramer R., Türler H., Weil R. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen: a "RNA binding protein"? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1139–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Ryskov A. P., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. The nucleotide sequence of the ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequence B1 complementary to the most abundant class of mouse fold-back RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1201–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
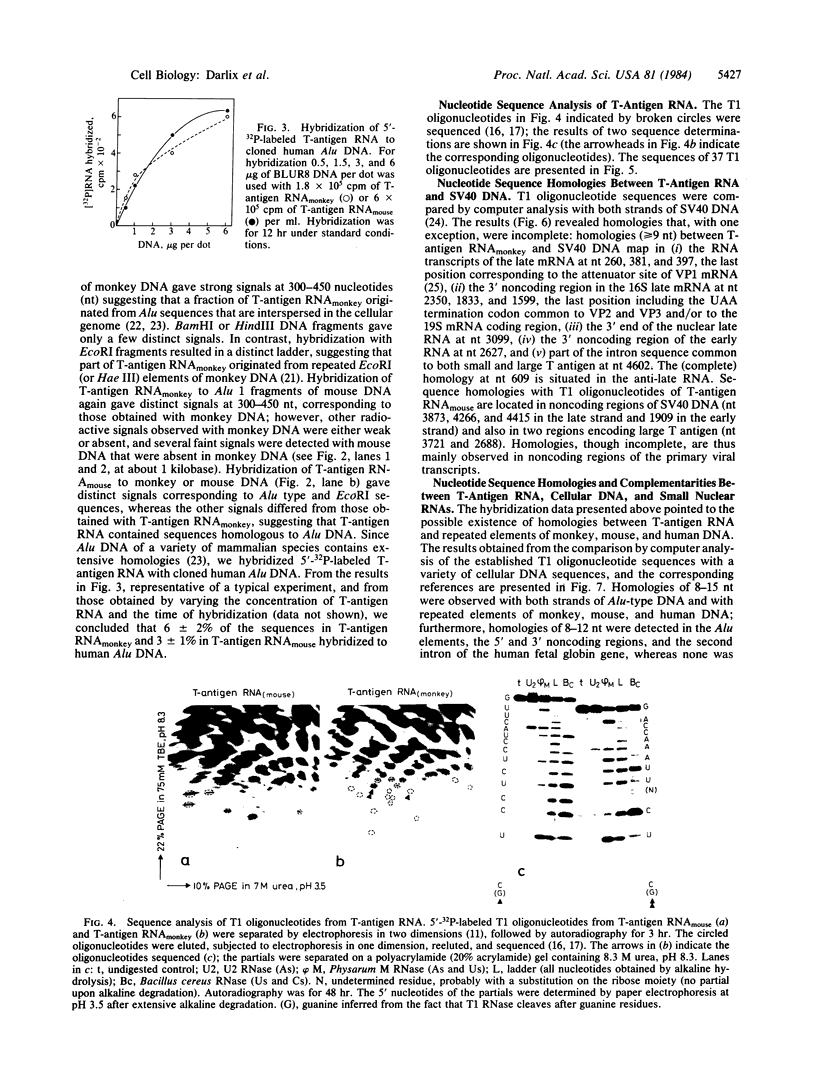
- Krayev A. S., Markusheva T. V., Kramerov D. A., Ryskov A. P., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. Ubiquitous transposon-like repeats B1 and B2 of the mouse genome: B2 sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7461–7475. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Repeating restriction fragments of human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3063–3076. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Wu J. C. Homology between human and simian repeated DNA. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):92–94. doi: 10.1038/276092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Setlow V. P., Edwards C. A., Vembu D. The roles of the simian virus 40 tumor antigens in transformation of Chinese hamster lung cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter J. M., Tiercy J. M., Weil R. Sequential stimulation of cellular RNA synthesis in polyoma-infected mouse kidney cell cultures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6611–6629. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Lai C., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Brain-specific genes have identifier sequences in their introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):713–717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. Substitutions, insertions, and deletions in two highly conserved U3 RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):7029–7033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Ro-Choi T. S., Henning D., Busch H. Primary sequence of U-1 nuclear ribonucleic acid of Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6486–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ro-Choi T. S., Redy R., Henning D., Takano T., Taylor C. W., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of 4.5 S ribonucleic acid of Novikoff hepatoma cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3205–3222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Dickson E., Jelinek W. Determination of nucleotide sequences from double-stranded regions of HeLa cell nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 5;115(4):571–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K., Imaizumi-Scherrer M. T., Reynaud C. A., Therwath A. On pre-messenger RNA and transcriptions. A review. Mol Biol Rep. 1979 May 31;5(1-2):5–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00777484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyzer M., Tai Y., Studer E., Michel M. R. Binding sites for monoclonal antibodies and for mRNPs on SV40 large T-antigen determined with a cleavage map. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):303–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07829.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Inactivity of purified reovirus RNA as a template for E. coli polymerases in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1721–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Slightom J. L., Smithies O. A history of the human fetal globin gene duplication. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):191–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Carbon J., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.664-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A., Brownlee G. G., Brown R. S., Rubin J. R., Guilley H. New rapid gel sequencing method for RNA. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):833–836. doi: 10.1038/269833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C., Rifkin D. B., Sleigh M. J. SV40 mutants with an altered small-t protein are tumorigenic in newborn hamsters. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil R. Viral 'tumor antigens': A novel type of mammalian regulator protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):301–388. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]