Abstract
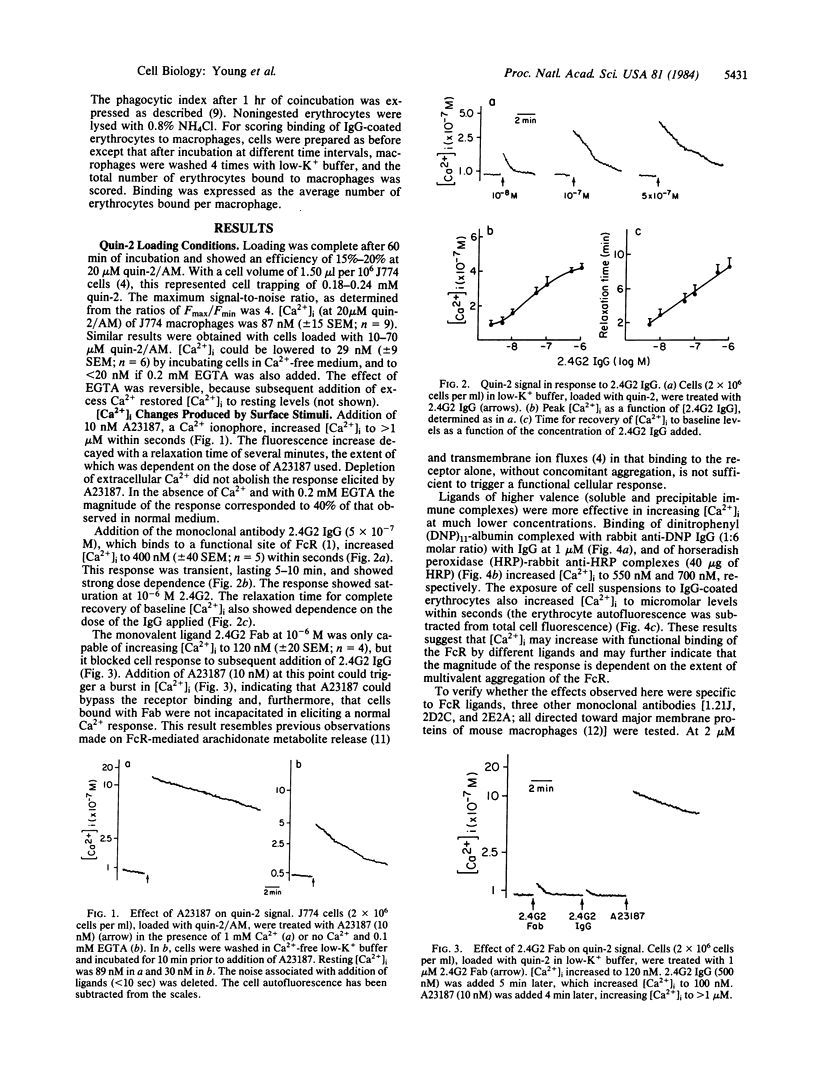
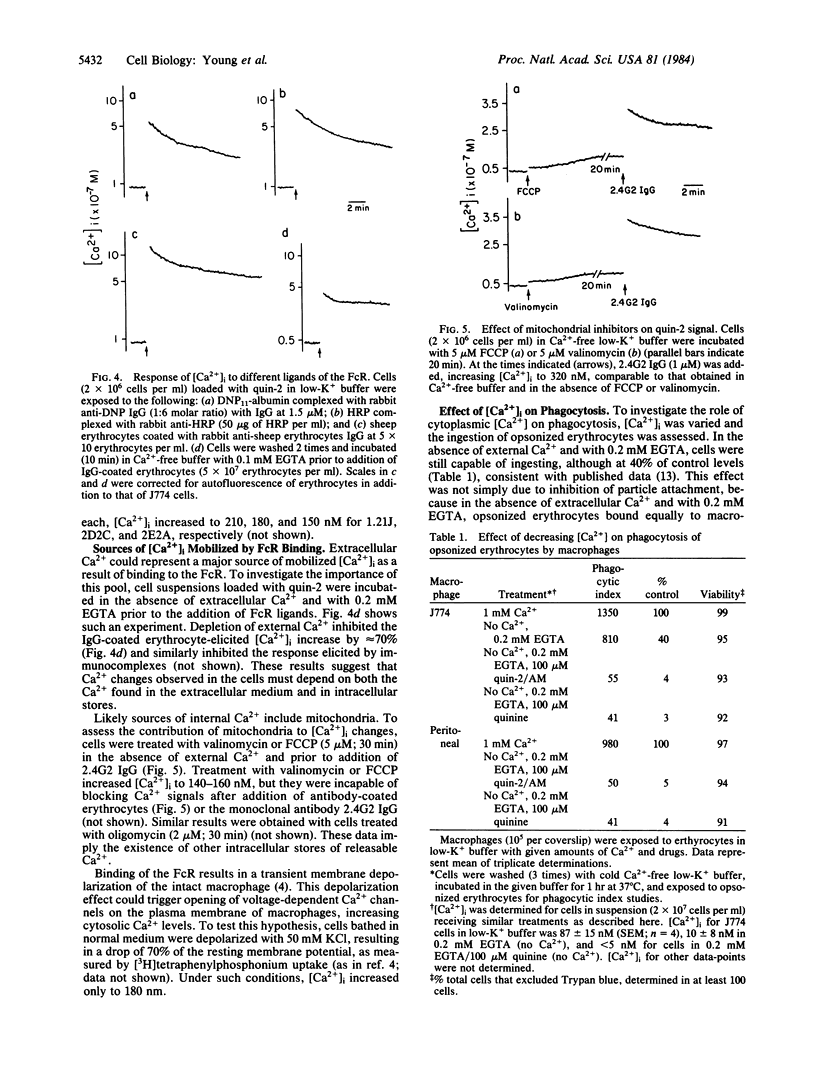
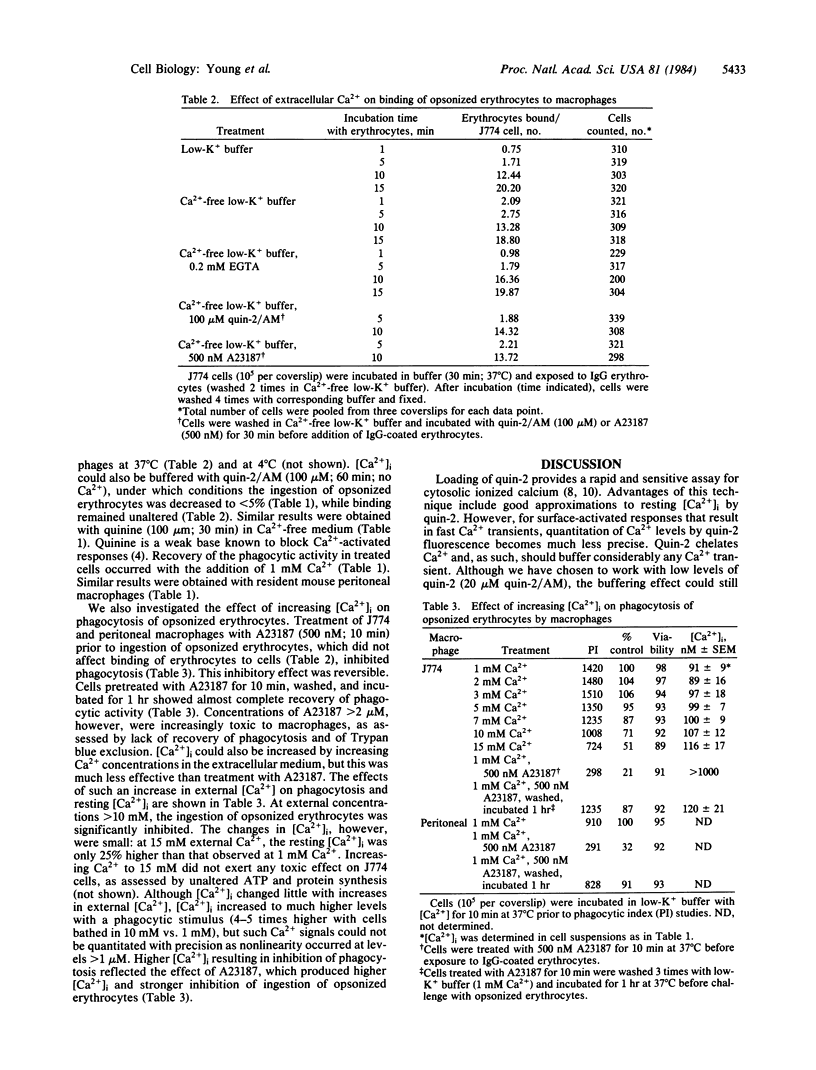
The concentration of cytosolic free calcium, [Ca2+]i, was measured in J774 mouse macrophages by use of the fluorescent indicator quin-2. Resting [Ca2+]i was 87 nM. Addition of a number of specific ligands to the immunoglobulin gamma 2b/gamma 1 Fc receptor resulted in a transient increase in [Ca2+]i, the magnitude of which depended on the extent of receptor aggregation. Monovalent ligands gave only a small Ca2+ signal but blocked cell response to subsequent addition of multivalent ligands. Incubation with antibody-coated erythrocytes raised macrophage [Ca2+]i to micromolar levels. [Ca2+]i changes were only partially inhibited by the absence of external Ca2+, suggesting the release of Ca2+ from internal stores in addition to an influx of external Ca2+. These internal stores were not limited to mitochondria. An optimal range of [Ca2+]i was required for phagocytosis. Buffering [Ca2+]i with quin-2 and treating cells with quinine in the absence of external Ca2+ resulted in inhibition of phagocytosis. Increasing [Ca2+]i to micromolar levels with the calcium ionophore A23187 also resulted in similar inhibitory effects. We suggest the involvement of localized cytosolic Ca2+ gradients in generating the signals necessary for phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S. T. Ultrastructural demonstration of calcium loss from local regions of the plasma membrane of surface-stimulated human granulocytes. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1395–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loike J. D., Silverstein S. C. A fluorescence quenching technique using trypan blue to differentiate between attached and ingested glutaraldehyde-fixed red blood cells in phagocytosing murine macrophages. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 25;57(1-3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I. S., Steinman R. M., Unkeless J. C., Cohn Z. A. Selective iodination and polypeptide composition of pinocytic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):712–722. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Griffin F. M., Jr Phagocytosis requires repeated triggering of macrophage phagocytic receptors during particle ingestion. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):409–411. doi: 10.1038/289409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Hartwig J. H., Yin H. L., Stendahl O. The motor of amoeboid leucocytes. Biochem Soc Symp. 1980;45:51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Quantitative studies of phagocytosis. Kinetic effects of cations and heat-labile opsonin. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):346–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):527–528. doi: 10.1038/290527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Fleit H., Mellman I. S. Structural Aspects and Heterogeneity of Immunoglobulin Fc Receptors. Adv Immunol. 1981;31:247–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60922-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Gordon S. Monoclonal antibody defines a macrophage intracellular Ca2+-binding protein which is phosphorylated by phagocytosis. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):70–72. doi: 10.1038/299070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Kaback H. R., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage membrane potential changes associated with gamma 2b/gamma 1 Fc receptor-ligand binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1357–1361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Kaback H. R., Cohn Z. A. Mouse macrophage Fc receptor for IgG gamma 2b/gamma 1 in artificial and plasma membrane vesicles functions as a ligand-dependent ionophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1636–1640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Unkeless J. C., Young T. M., Mauro A., Cohn Z. A. Role for mouse macrophage IgG Fc receptor as ligand-dependent ion channel. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):186–189. doi: 10.1038/306186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


