Abstract
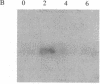
The c-myc oncogene has been implicated in a wide spectrum of B-cell neoplasias. In normal cells, the level of expression of the c-myc gene correlates with growth status. In the present study, we examined the effect of receptor-mediated inhibition of growth on c-myc expression in a B-cell lymphoma. The murine lymphoma line WEHI 231 has been characterized as an early B cell; it bears surface-bound IgM and has unrearranged c-myc genes. Following treatment of a WEHI 231 culture with anti-mouse Ig antiserum, the cells undergo one round of division and further proliferation is inhibited. We observed that this treatment specifically affected cytoplasmic levels of c-myc mRNA. An initial early increase is followed by a precipitous drop such that by 4 hr (after exposure) the amount of c-myc mRNA is below control values by a factor of approximately equal to 10. The drop in c-myc precedes cessation of DNA synthesis. During the 2- to 4-hr period, c-myc mRNA had a maximal half-life of between 20 and 30 min. In contrast, even 24 hr after anti-Ig exposure, the amounts of most major mRNAs, including mu heavy chain and actin, were not significantly altered. These results indicate that expression of an unrearranged c-myc gene can be selectively responsive to receptor-mediated regulatory events.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gerondakis S., Webb E., Mitchell J., Bernard O., Cory S. Transcriptionally active DNA region that rearranges frequently in murine lymphoid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6966–6970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., Baltimore D. Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3' ends. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alterman R. B., Ganguly S., Schulze D. H., Marzluff W. F., Schildkraut C. L., Skoultchi A. I. Cell cycle regulation of mouse H3 histone mRNA metabolism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):123–132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Goding J. W., Schrader J. W. The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. I. Lipopolysaccharide-induced differentiation. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2461–2465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Schrader J. W. The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. II. The inhibition of WEHI 231 by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2466–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Kent R. B., Sonenshein G. E. Transcriptional activation of immunoglobulin alpha heavy-chain genes by translocation of the c-myc oncogene. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):443–446. doi: 10.1038/305443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. Modification of B lymphocyte differentiation by anti-immunoglobulins. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1974;3:193–225. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3045-5_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongini P., Friedman S., Wortis H. Accessory cell requirement for anti-IgM-induced proliferation of B lymphocytes. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):709–711. doi: 10.1038/276709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno C., Hale C., Hewett R., Esdaile J. Induction and persistence of B-cell tolerance to the thymus-dependent component of the alpha(1 leads to 6) glucosyl determinant of dextran. Recovery induced by treatment with dextranase in vivo. Immunology. 1981 Nov;44(3):517–527. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L., Battye F. L. Mechanisms of clonal abortion tolerogenesis. II. Clonal behaviour of immature B cells following exposure to anti-mu chain antibody. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):203–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C. Separable helper factors support B cell proliferation and maturation to Ig secretion. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):469–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C., Wadsworth D. C., Schneider G. B. Activation of murine B lymphocytes by anti-immunoglobulin is an inductive signal leading to immunoglobulin secretion. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):138–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P. A., Siekevitz M., Schwartz R. C., Gefter M. L., Sonenshein G. E. Transcription of immunoglobulin heavy-chain sequences from the excluded allele. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):594–596. doi: 10.1038/291594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Hamlyn P. H., Baer R. Altered nucleotide sequences of a translocated c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):760–765. doi: 10.1038/306760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Mallick U., Ponta H., Herrlich P. A B-lymphocyte-specific high-turnover protein: constitutive expression in resting B cells and induction of synthesis in proliferating cells. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P. Functional subsets of murine and human B lymphocyte cell lines. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:107–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo B. Z., Weinberg R. A. DNA sequences homologous to vertebrate oncogenes are conserved in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6789–6792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Control of proliferation and differentiation in B lymphocytes by anti-Ig antibodies and a serum-derived cofactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieckmann D. G., Scher I., Asofsky R., Mosier D. E., Paul W. E. Activation of mouse lymphocytes by anti-immunoglobulin. II. A thymus-independent response by a mature subset of B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1628–1643. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]