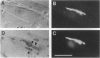
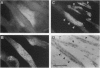
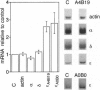
Abstract
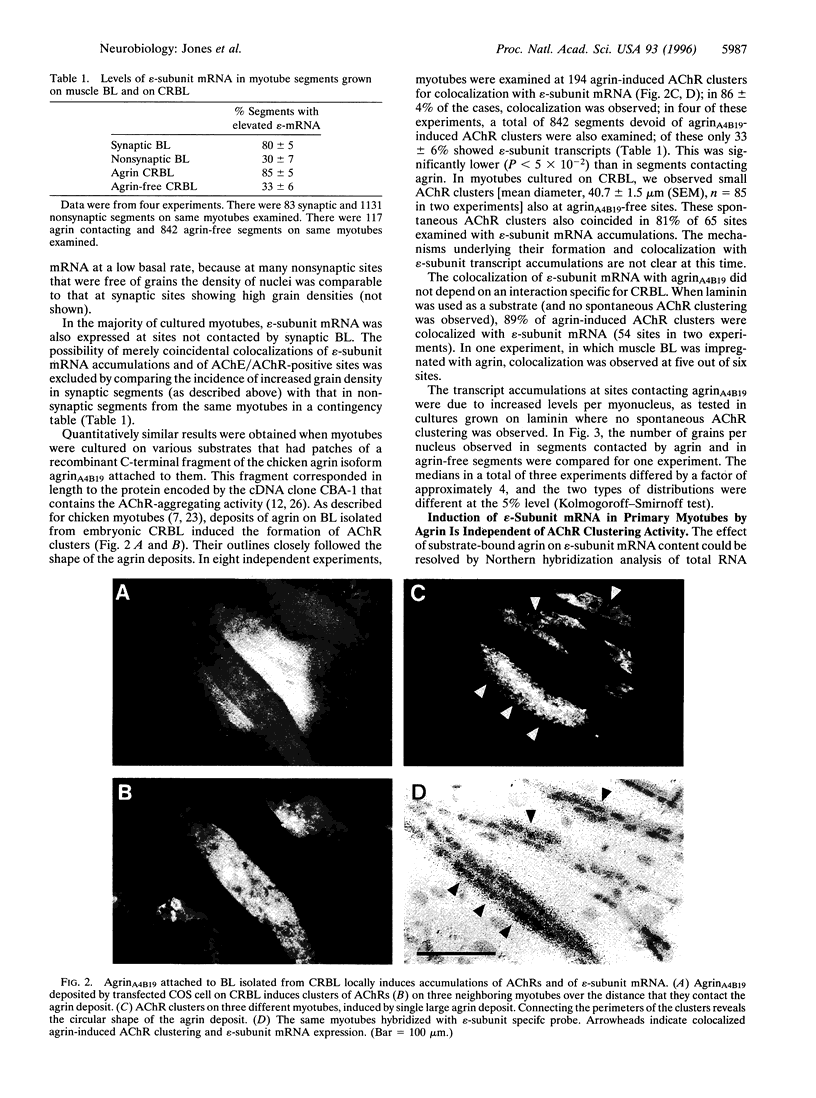
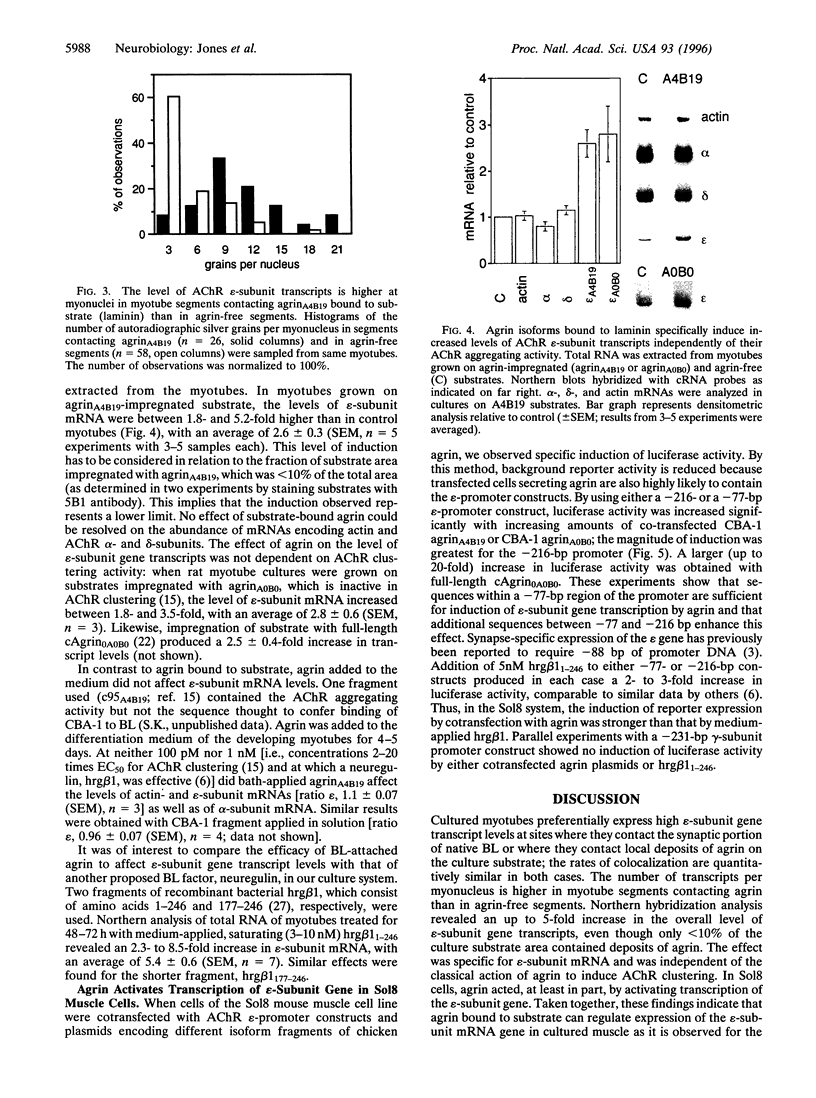
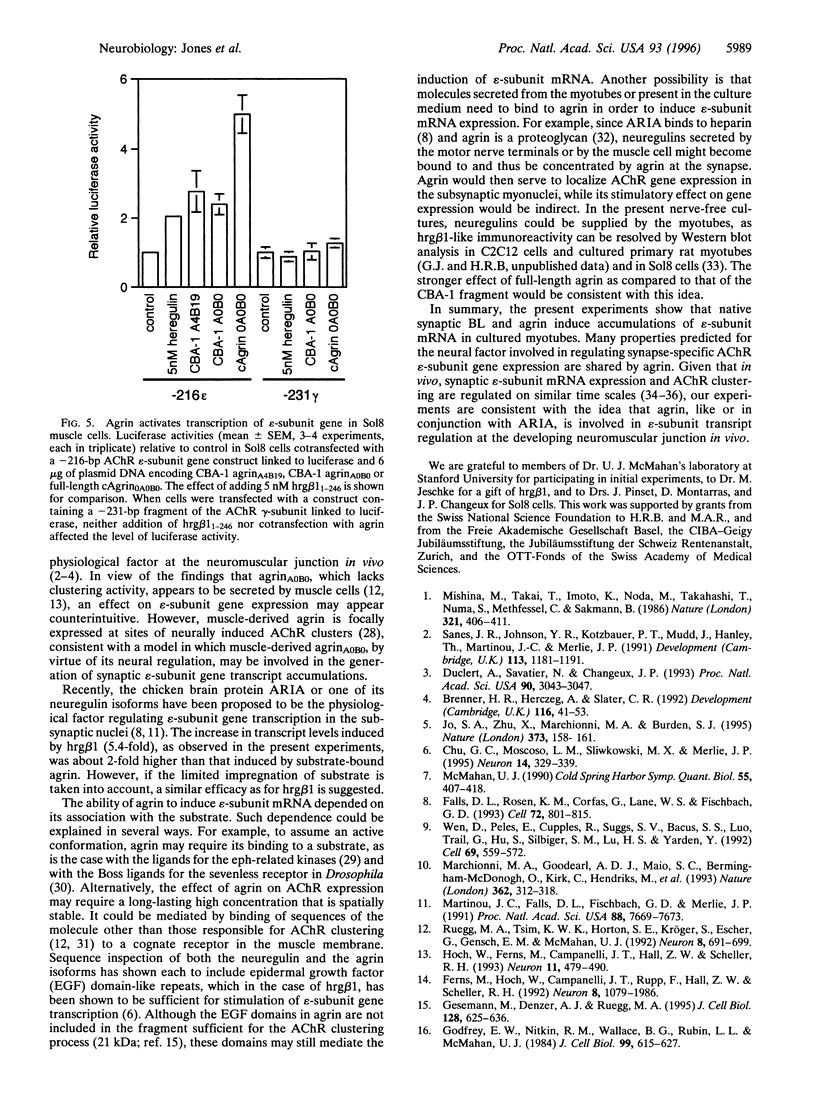
Expression of the epsilon-subunit gene of the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) by myonuclei located at the neuromuscular junction is precisely regulated during development. A key role in this regulation is played by the synaptic portion of the basal lamina, a structure that is also known to contain agrin, a component responsible for the formation of postsynaptic specializations. We tested whether agrin has a function in synaptic AChR gene expression. Synaptic basal lamina from native adult muscle and recombinant agrin bound to various substrates induced in cultured rat myotubes AChR clusters that were colocalized with epsilon-subunit mRNA. Estimation of transcript levels by Northern hybridization analysis of total RNA showed a significant increase when myotubes were grown on substrate impregnated with agrin, but were unchanged when agrin was applied in the medium. The effect was independent of the receptor aggregating activity of the agrin isoform used, and agrin acted, at least in part, at the level of epsilon-subunit gene transcription. These findings are consistent with a role of agrin in the regulation of AChR subunit gene expression at the neuromuscular junction, which would depend on its binding to the synaptic basal lamina.
Full text
PDF
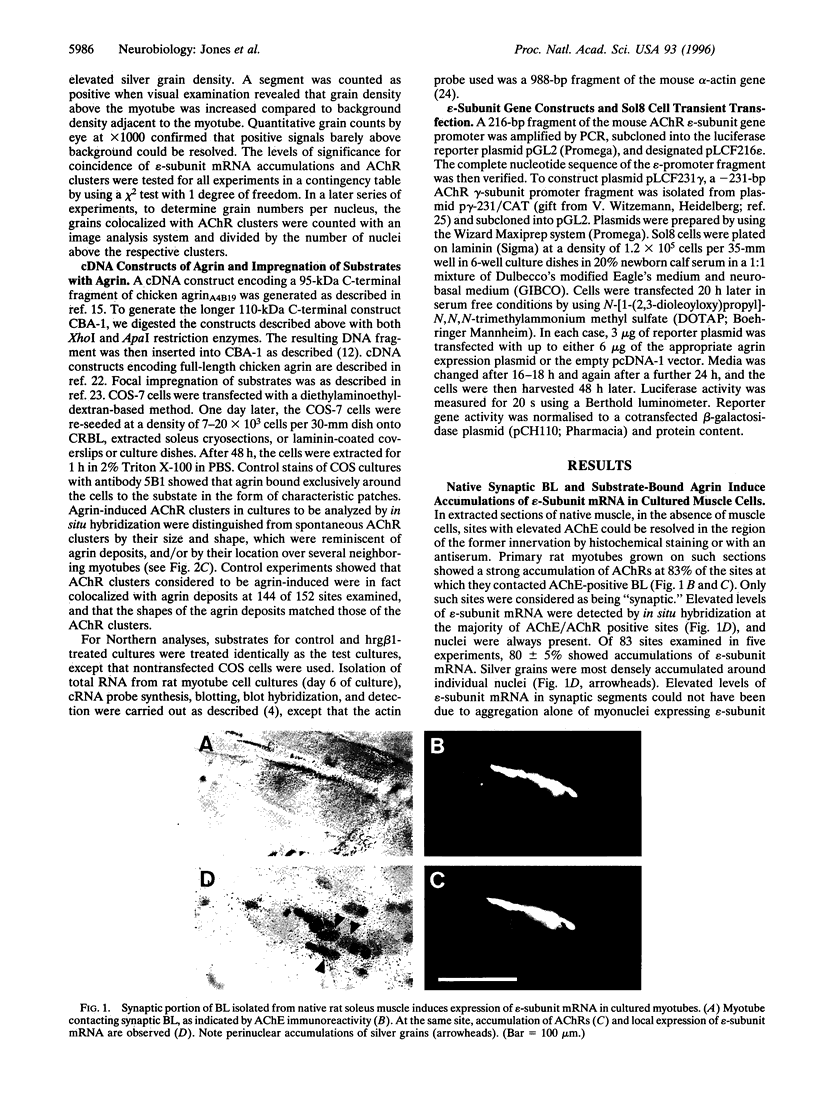

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner H. R., Herczeg A., Slater C. R. Synapse-specific expression of acetylcholine receptor genes and their products at original synaptic sites in rat soleus muscle fibres regenerating in the absence of innervation. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):41–53. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner H. R., Rotzler S., Kues W. A., Witzemann V., Sakmann B. Nerve-dependent induction of AChR epsilon-subunit gene expression in muscle is independent of state of differentiation. Dev Biol. 1994 Oct;165(2):527–536. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G. C., Moscoso L. M., Sliwkowski M. X., Merlie J. P. Regulation of the acetylcholine receptor epsilon subunit gene by recombinant ARIA: an in vitro model for transynaptic gene regulation. Neuron. 1995 Feb;14(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Gale N. W., Aldrich T. H., Maisonpierre P. C., Lhotak V., Pawson T., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. Ligands for EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinases that require membrane attachment or clustering for activity. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):816–819. doi: 10.1126/science.7973638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denzer A. J., Gesemann M., Schumacher B., Ruegg M. A. An amino-terminal extension is required for the secretion of chick agrin and its binding to extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 1):1547–1560. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duclert A., Savatier N., Changeux J. P. An 83-nucleotide promoter of the acetylcholine receptor epsilon-subunit gene confers preferential synaptic expression in mouse muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3043–3047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falls D. L., Rosen K. M., Corfas G., Lane W. S., Fischbach G. D. ARIA, a protein that stimulates acetylcholine receptor synthesis, is a member of the neu ligand family. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90407-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Campanelli J. T., Hoch W., Scheller R. H., Hall Z. The ability of agrin to cluster AChRs depends on alternative splicing and on cell surface proteoglycans. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90153-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M., Hoch W., Campanelli J. T., Rupp F., Hall Z. W., Scheller R. H. RNA splicing regulates agrin-mediated acetylcholine receptor clustering activity on cultured myotubes. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Gautvik K., Sommerschild H. Persistence of junctional acetylcholine receptors following denervation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:275–281. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesemann M., Denzer A. J., Ruegg M. A. Acetylcholine receptor-aggregating activity of agrin isoforms and mapping of the active site. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):625–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey E. W., Nitkin R. M., Wallace B. G., Rubin L. L., McMahan U. J. Components of Torpedo electric organ and muscle that cause aggregation of acetylcholine receptors on cultured muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):615–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter W., Reckhaus W., Kröger S. Nondirected axonal growth on basal lamina from avian embryonic neural retina. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3712–3722. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03712.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart A. C., Krämer H., Zipursky S. L. Extracellular domain of the boss transmembrane ligand acts as an antagonist of the sev receptor. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):732–736. doi: 10.1038/361732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herczeg A., Jones G., Brenner H. R. Involvement of extracellular matrix in acetylcholine receptor epsilon-subunit gene expression at the rat neuromuscular junction. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Jun 23;193(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11661-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch W., Ferns M., Campanelli J. T., Hall Z. W., Scheller R. H. Developmental regulation of highly active alternatively spliced forms of agrin. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90152-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeschke M., Wels W., Dengler W., Imber R., Stöcklin E., Groner B. Targeted inhibition of tumor-cell growth by recombinant heregulin-toxin fusion proteins. Int J Cancer. 1995 Mar 3;60(5):730–739. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910600527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jo S. A., Zhu X., Marchionni M. A., Burden S. J. Neuregulins are concentrated at nerve-muscle synapses and activate ACh-receptor gene expression. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):158–161. doi: 10.1038/373158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieth E., Fallon J. R. Muscle agrin: neural regulation and localization at nerve-induced acetylcholine receptor clusters. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2509–2514. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02509.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M. A., Goodearl A. D., Chen M. S., Bermingham-McDonogh O., Kirk C., Hendricks M., Danehy F., Misumi D., Sudhalter J., Kobayashi K. Glial growth factors are alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous system. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):312–318. doi: 10.1038/362312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Grassi J., Vigny M., Massoulié J. An immunological study of rat acetylcholinesterase: comparison with acetylcholinesterases from other vertebrates. J Neurochem. 1984 Jul;43(1):204–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou J. C., Falls D. L., Fischbach G. D., Merlie J. P. Acetylcholine receptor-inducing activity stimulates expression of the epsilon-subunit gene of the muscle acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7669–7673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J. The agrin hypothesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:407–418. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Takai T., Imoto K., Noda M., Takahashi T., Numa S., Methfessel C., Sakmann B. Molecular distinction between fetal and adult forms of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):406–411. doi: 10.1038/321406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscoso L. M., Chu G. C., Gautam M., Noakes P. G., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. Synapse-associated expression of an acetylcholine receptor-inducing protein, ARIA/heregulin, and its putative receptors, ErbB2 and ErbB3, in developing mammalian muscle. Dev Biol. 1995 Nov;172(1):158–169. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numberger M., Dürr I., Kues W., Koenen M., Witzemann V. Different mechanisms regulate muscle-specific AChR gamma- and epsilon-subunit gene expression. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2957–2964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reist N. E., Magill C., McMahan U. J. Agrin-like molecules at synaptic sites in normal, denervated, and damaged skeletal muscles. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2457–2469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg M. A., Tsim K. W., Horton S. E., Kröger S., Escher G., Gensch E. M., McMahan U. J. The agrin gene codes for a family of basal lamina proteins that differ in function and distribution. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90090-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Johnson Y. R., Kotzbauer P. T., Mudd J., Hanley T., Martinou J. C., Merlie J. P. Selective expression of an acetylcholine receptor-lacZ transgene in synaptic nuclei of adult muscle fibers. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1181–1191. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsen G., Halfter W., Kröger S., Cole G. J. Agrin is a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3392–3399. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsim K. W., Ruegg M. A., Escher G., Kröger S., McMahan U. J. cDNA that encodes active agrin. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):677–689. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90089-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Peles E., Cupples R., Suggs S. V., Bacus S. S., Luo Y., Trail G., Hu S., Silbiger S. M., Levy R. B. Neu differentiation factor: a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90456-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]