Abstract
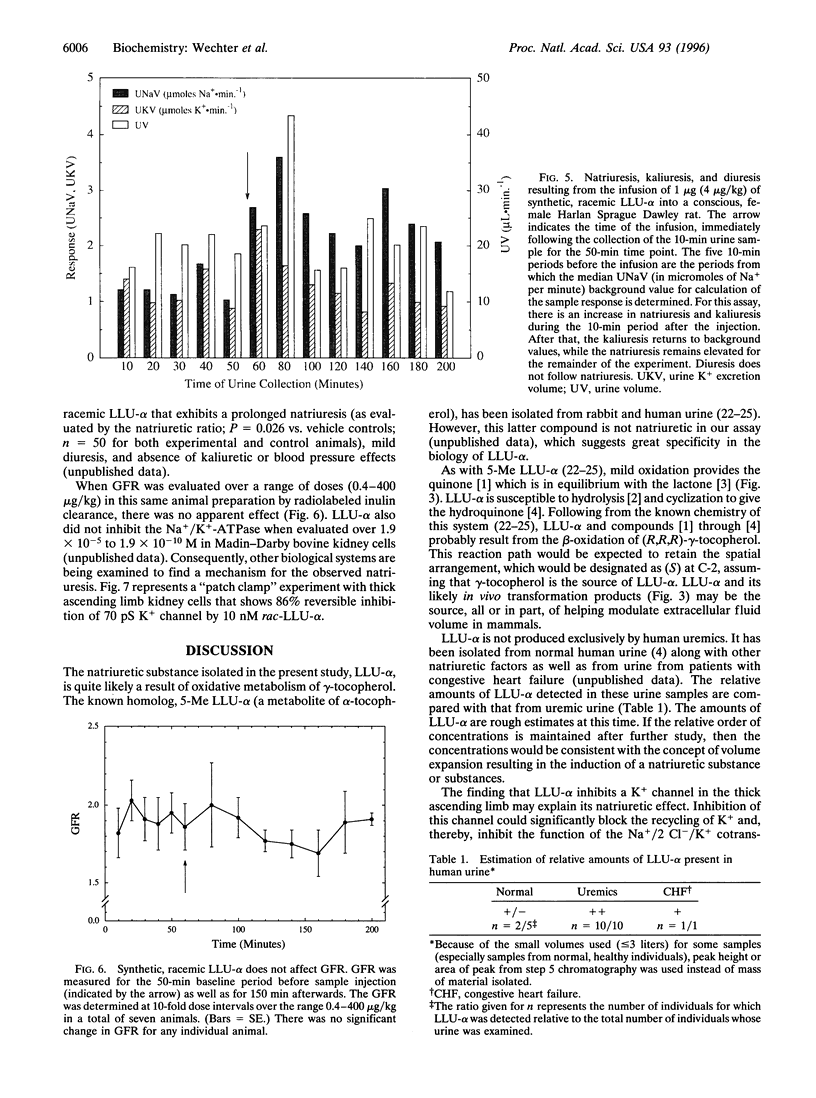
For over three decades, renal physiology has sought a putative natriuretic hormone (third factor) that might control the body's pool of extracellular fluid, an important determinant in hypertension, congestive heart failure, and cirrhosis. In our search for this hormone, we have isolated several pure natriuretic factors from human uremic urine that would appear, alone or in combination, to mark a cluster of phenomena previously presumed to be that of a single "natriuretic hormone." This paper reports the purification, chemical structure, and total synthesis of the first of these compounds, LLU-alpha, which proved to be 2,7,8-trimethyl-2-(beta-carboxyethyl)-6-hydroxychroman, presumably a metabolite of gamma-tocopherol. Both natural LLU-alpha and synthetic material are identical (except for optical activity) with respect to structure and biological activity. It appears that the natriuretic activity of LLU-alpha is mediated by inhibition of the 70 pS K+ channel in the apical membrane of the thick ascending limb of the kidney.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benaksas E. J., Murray E. D., Jr, Rodgers C. L., Pham T., Bigornia A. E., DeWind S. A., Giebel R., Brubacher E. S., Wechter W. J. Endogenous natriuretic factors 1: sodium pump inhibition does not correlate with natriuretic or pressor activities from uremic urine. Life Sci. 1993;52(12):1045–1054. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90197-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabos M., Grichois M. L., Guicheney P., Wainer I. W., Cloix J. F. Further biochemical characterization of an Na+ pump inhibitor purified from human urine. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WARDENER H. E., MILLS I. H., CLAPHAM W. F., HAYTER C. J. Studies on the efferent mechanism of the sodium diuresis which follows the administration of intravenous saline in the dog. Clin Sci. 1961 Oct;21:249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENGART A., MILHORAT A. T., SIMON E. J., SUNDHEIM L. The metabolism of vitamin E. II. Purification and characterization of urinary metabolites of alpha-tocopherol. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):807–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS C. S., MILHORAT A. T., SIMON E. J. The metabolism of vitamin E. I. The absorption and excretion of d-alpha-tocopheryl-5-methyl-C14-succinate. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):797–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz K. L. Evidence that atriopeptin is not a physiological regulator of sodium excretion. Hypertension. 1990 Jan;15(1):9–19. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto A., Ishiguro T., Yamada K., Ishii M., Yoshioka M., Eguchi C., Shimora M., Sugimoto T. Isolation of a urinary digitalis-like factor indistinguishable from digoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1093–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80898-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R. Ion transport mechanisms in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol Rev. 1985 Jul;65(3):760–797. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.3.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R., Schlatter E. Presence of luminal K+, a prerequisite for active NaCl transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Nov;392(1):92–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00584588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddy F. J., Overbeck H. W. The role of humoral agents in volume expanded hypertension. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 1;19(7):935–947. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert S. C., Andreoli T. E. Control of NaCl transport in the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F745–F756. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludens J. H., Clark M. A., DuCharme D. W., Harris D. W., Lutzke B. S., Mandel F., Mathews W. R., Sutter D. M., Hamlyn J. M. Purification of an endogenous digitalislike factor from human plasma for structural analysis. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):923–929. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludens J. H., Clark M. A., Smith M. P., Humphrey S. J. Renal and vascular effects of chemically distinct ATP-sensitive K+ channel blockers in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;25(3):404–409. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199503000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews W. R., DuCharme D. W., Hamlyn J. M., Harris D. W., Mandel F., Clark M. A., Ludens J. H. Mass spectral characterization of an endogenous digitalislike factor from human plasma. Hypertension. 1991 Jun;17(6 Pt 2):930–935. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.6.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. D., Jr, Kantoci D., DeWind S. A., Bigornia A. E., D'Amico D. C., King J. G., Jr, Pham T., Levine B. H., Jung M. E., Wechter W. J. Endogenous natriuretic factors 3: isolation and characterization of human natriuretic factors LLU-alpha, LLU-beta 1, and LLU-gamma. Life Sci. 1995;57(23):2145–2161. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(95)02207-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamnani M. B., Chen S., Bryant H. J., Schooley J. F., Jr, Eliades D. C., Yuan C. M., Haddy F. J. Effects of three sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase inhibitors. Hypertension. 1991 Sep;18(3):316–324. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.3.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricone S. C., Humphrey S. J., Skaletzky L. L., Graham B. E., Zandt R. A., Zins G. R. Synthesis and diuretic activity of alkyl- and arylguanidine analogs of N,N'-dicyclohexyl-4-morpholinecarboxamidine in rats and dogs. J Med Chem. 1994 Oct 28;37(22):3693–3700. doi: 10.1021/jm00048a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner W. Endogenous digitalis-like factors. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1992;14(5):767–814. doi: 10.3109/10641969209036220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld A., Schultz M., Petrizka M., Gassmann B. A novel metabolite of RRR-alpha-tocopherol in human urine. Nahrung. 1993;37(5):498–500. doi: 10.1002/food.19930370514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekihara H., Yazaki Y. Ouabain causes kaliuresis and works synergistically with aldosterone in vivo. Life Sci. 1993;53(12):975–980. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90119-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. D., Templeton J. F., Sashi Kumar V. P., Yan Y., Widajewicz W., LaBella F. S. Digitaloid pregnanes promote potassium-sparing diuresis in the guinea pig. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 May;70(5):723–727. doi: 10.1139/y92-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tymiak A. A., Norman J. A., Bolgar M., DiDonato G. C., Lee H., Parker W. L., Lo L. C., Berova N., Nakanishi K., Haber E. Physicochemical characterization of a ouabain isomer isolated from bovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8189–8193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Wang W. H., Klein-Robbenhaar G., Giebisch G. Effects of a novel KATP channel blocker on renal tubule function and K channel activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jun;273(3):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H. Two types of K+ channel in thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):F599–F605. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.4.F599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechter W. J., Benaksas E. J. Natriuretic hormones. Prog Drug Res. 1990;34:231–260. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7128-0_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao N., Lo L. C., Berova N., Nakanishi K., Tymiak A. A., Ludens J. H., Haupert G. T., Jr Na,K-ATPase inhibitors from bovine hypothalamus and human plasma are different from ouabain: nanogram scale CD structural analysis. Biochemistry. 1995 Aug 8;34(31):9893–9896. doi: 10.1021/bi00031a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zeeuw D., Janssen W. M., de Jong P. E. Atrial natriuretic factor: its (patho)physiological significance in humans. Kidney Int. 1992 May;41(5):1115–1133. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]