Abstract
We present the complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit of 60,000 Da. The keratin possesses a central alpha-helical domain of four tracts (termed 1A, 1B, 2A, and 2B) that can form coiled-coils, interspersed by short linker sequences, and has non-alpha-helical terminal domains. This pattern of secondary structure is emerging as common to all intermediate filament subunits. The alpha-helical sequences conform to the type II class of keratins. Accordingly, this is the first type II keratin for which complete sequence information is available, and thus it facilitates elucidation of the fundamental distinctions between type I and type II keratins. It has been observed that type I keratins are acidic and type II keratins are neutral--basic in charge. We suggest that the basis for this empirical correlation between type and charge resides in the respective net charges of the 1A and 2B tracts. Calculations on interchain interactions between charged residues in the alpha-helical domains indicate that this keratin prefers to participate in dimers according to an in-register parallel arrangement. The terminal domains of this keratin possess characteristic glycine-rich sequences, and the carboxyl-terminal domain is highly homologous to that of a human epidermal keratin of 56,000 Da. According to the hypothesis that end-domains are located on the periphery of keratin filaments, we conclude that the corresponding mouse and human keratins are closely related, both structurally and functionally.
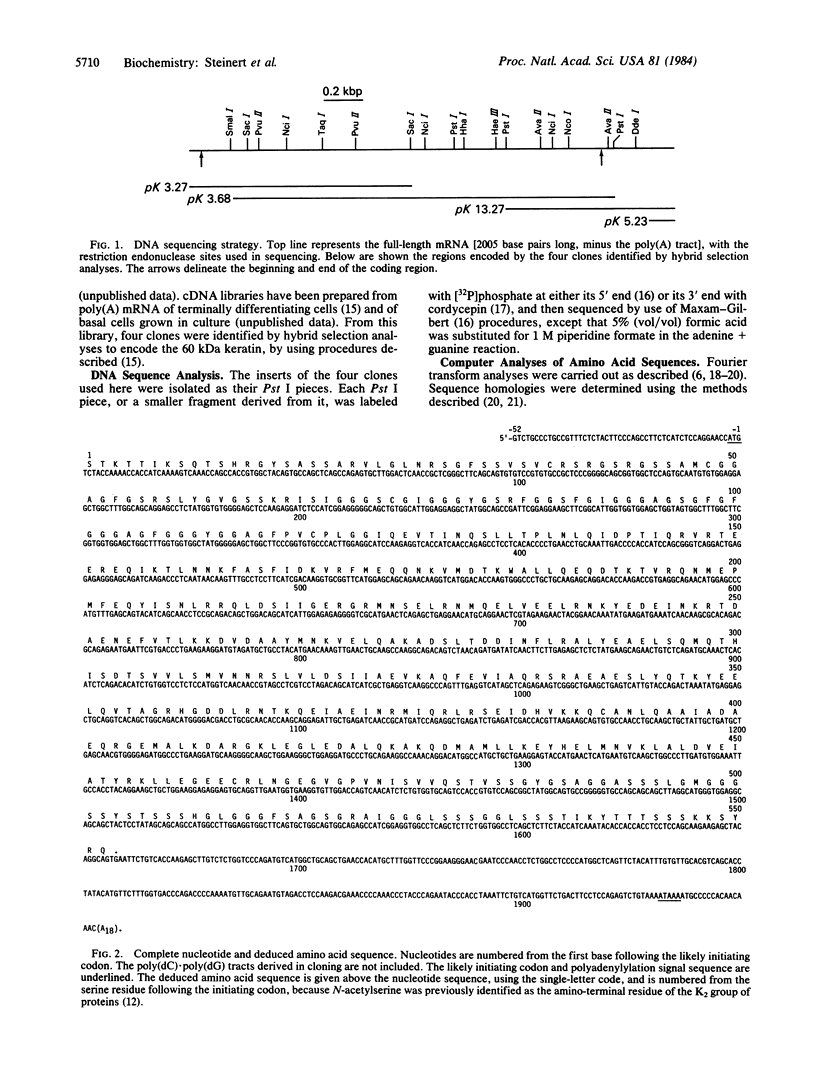
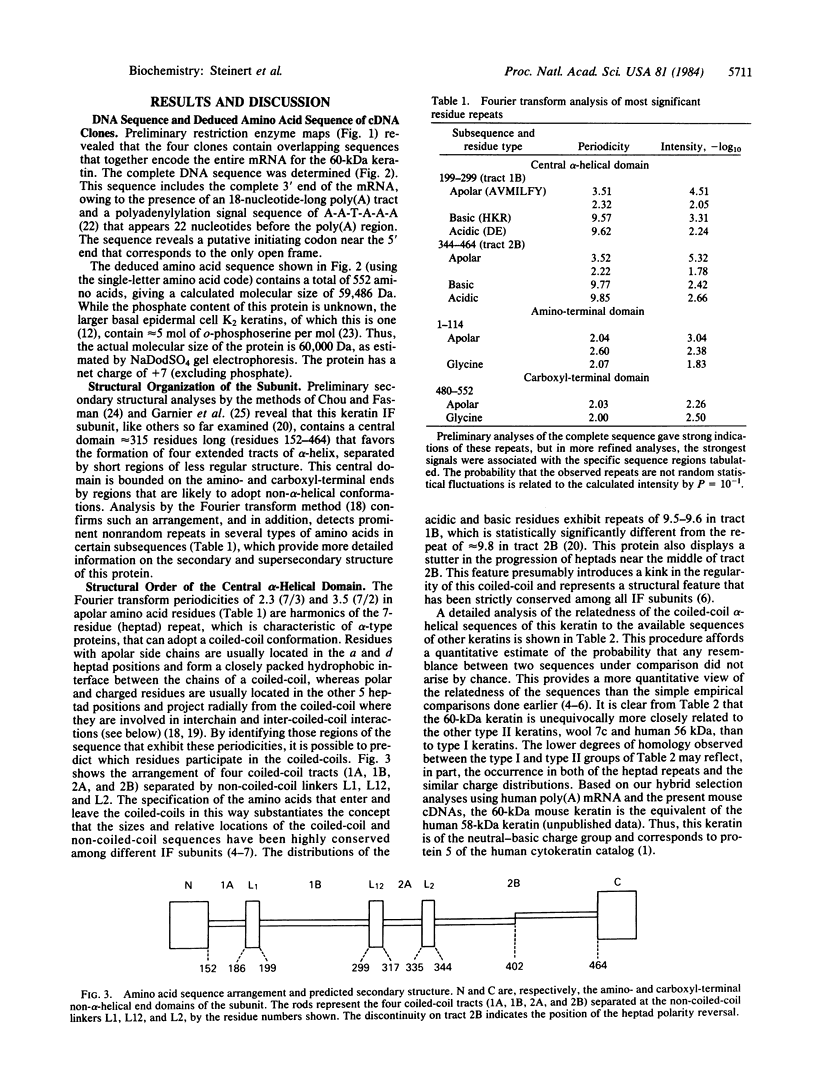
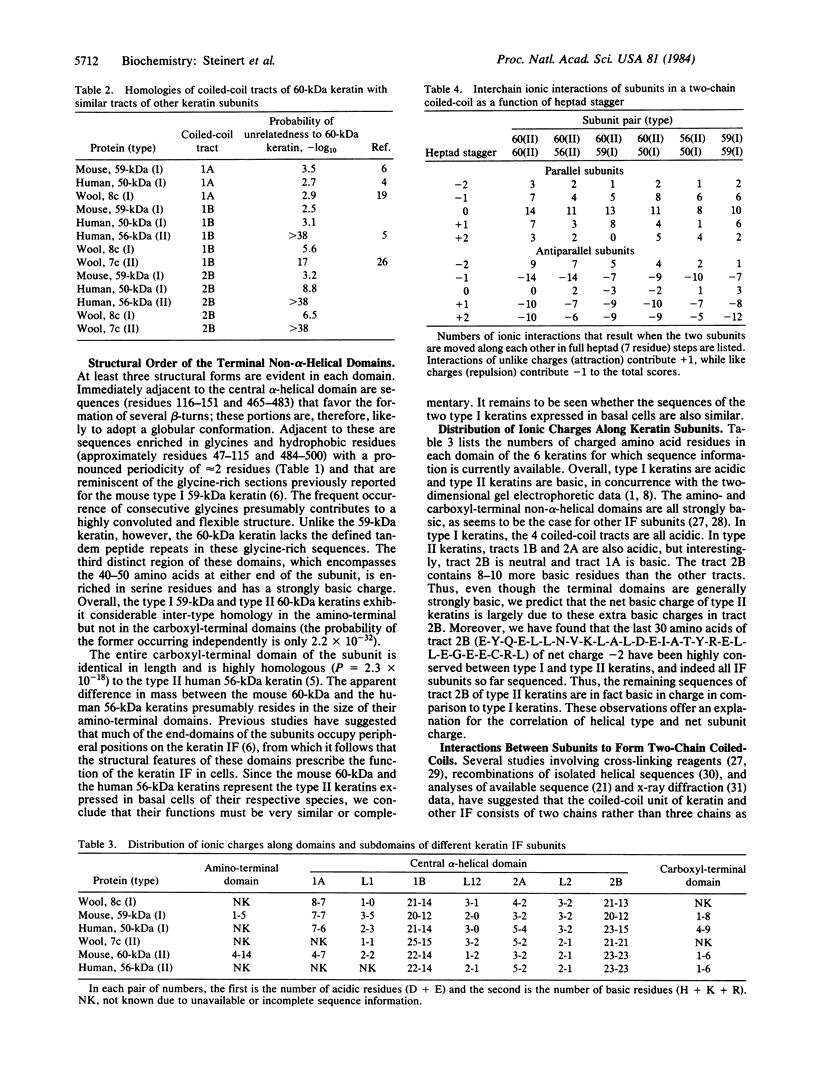
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling L. M., Parry D. A., Sparrow L. G. Structural homology between hard alpha-keratin and the intermediate filament proteins desmin and vimentin. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jan;3(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01121573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Winter S. Protein complexes of intermediate-sized filaments: melting of cytokeratin complexes in urea reveals different polypeptide separation characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7113–7117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P. The structure of the alpha-keratin microfibril. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jun;3(6):517–525. doi: 10.1007/BF01120695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough K. H., Inglis A. S., Crewther W. G. Amino acid sequences of alpha-helical segments from S-carbosymethylkerateine-A. Complete sequence of a type-I segment. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):373–385. doi: 10.1042/bj1730373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruen L. C., Woods E. F. Structural studies on the microfibrillar proteins of wool. Interaction between alpha-helical segments and reassembly of a four-chain structure. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2090587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Crewther W. G., Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P. Structure of alpha-keratin: structural implication of the amino acid sequences of the type I and type II chain segments. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 25;113(2):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Cheng C. K., Yuspa S. H. Keratin gene expression in mouse epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):716–720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells and bovine epidermal keratinocytes have similar ultrastructures and subunit domain structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Poirier M. C., Katoh Y., Stoner G. D., Yuspa S. H. Subunit structure of the mouse epidermal keratin filament. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 27;577(1):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Zimmerman S. B. Self-assembly of bovine epidermal keratin filaments in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 15;108(3):547–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M. Structure of the three-chain unit of the bovine epidermal keratin filament. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jul 25;123(1):49–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Wantz M. L., Idler W. W. O-phosphoserine content of intermediate filament subunits. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 5;21(1):177–183. doi: 10.1021/bi00530a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P., Idler W., Aynardi-Whitman M., Zackroff R., Goldman R. D. Heterogeneity of intermediate filaments assembled in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Eichner R., Nelson W. G., Tseng S. C., Weiss R. A., Jarvinen M., Woodcock-Mitchell J. Keratin classes: molecular markers for different types of epithelial differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):109s–115s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trus B. L., Piez K. A. Molecular packing of collagen: three-dimensional analysis of electrostatic interactions. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 25;108(4):705–732. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. P., Cohen S. N. 3'-end labeling of DNA with [alpha-32P]cordycepin-5'-triphosphate. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


