Abstract
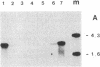
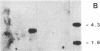
Injection of extracts from Xenopus liver nuclei that are enriched 2000 times in estradiol receptor into Xenopus oocytes induces transcription of the silent vitellogenin locus, which is activated in liver by estradiol, but not of the albumin locus, which is active in liver but suppressed by high levels of estradiol. Transcription initiates within the 5'-end region of the gene we have studied and probably continues into the 3' third. The activation seems to be very efficient, but most of the primary transcripts are probably rapidly and inaccurately processed. New proteins are also made and secreted by the oocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Estrogen regulates the absolute rate of transcription of the Xenopus laevis vitellogenin genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5449–5455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic segregation of proteins and RNAs. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K., Anderson J. N., Hayward M. A., Shapiro D. J. Nuclease sensitivity and DNA methylation in estrogen regulation of Xenopus laevis vitellogenin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8908–8914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortune J. E. Steroid production by Xenopus ovarian follicles at different developmental stages. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):502–509. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber-Huber S., May F. E., Westley B. R., Felber B. K., Hosbach H. A., Andres A. C., Ryffel G. U. In contrast to other Xenopus genes the estrogen-inducible vitellogenin genes are expressed when totally methylated. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., ten Heggeler B., Schubiger J. L., Walker P., Westley B., Wahli W. Vitellogenin B2 gene in Xenopus laevis: isolation, in vitro transcription and relation to other vitellogenin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):2979–2997. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. D., Tata J. R. Direct induction by estradiol on vitellogenin synthesis in organ cultures of male Xenopus laevis liver. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Methods for nuclear transplantation in amphibia. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:125–139. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward M. A., Mitchell T. A., Shapiro D. J. Induction of estrogen receptor and reversal of the nuclear/cytoplasmic receptor ratio during vitellogenin synthesis and withdrawal in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11308–11312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Gurdon J. B. The reactivation of developmentally inert 5S genes in somatic nuclei injected into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):461–465. doi: 10.1038/289461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D., Champion J., Colman A., James T. C., Applebaum S. W. The fate of Xenopus and locust vitellogenins made in Xenopus oocytes. An export-import processing model. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):529–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Ryffel G. U., Weber R., Westley B. R. Estrogen dramatically decreases albumin mRNA levels and albumin synthesis in Xenopus laevis liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13919–13923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Wahli W., Weber R. Quantitation of vitellogenin messenger RNA in the liver of male Xenopus toads during primary and secondary stimulation by estrogen. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. Steroid hormone regulation of vitellogenin gene expression. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Mar;12(3):187–203. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis is encoded in a small family of genes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Wyler T., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Size, complexity and abundance of a specific poly(A)-containing RNA of liver from male Xenopus induced to vitellogenin synthesis by estrogen. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 15;66(3):457–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Knowland J. An estrogen receptor from Xenopus laevis liver possibly connected with vitellogenin synthesis. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., Wyler T., Ryffel G., Weber R. Xenopus laevis serum albumins are encoded in two closely related genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3557–3574. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Wright S. C., Knowland J. Partial purification of estradiol receptor from Xenopus laevis liver and levels of receptor in relation to estradiol concentration. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):973–977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Gurdon J. B., Price J. Nuclear localisation of an oocyte component required for the stability of injected DNA. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):150–152. doi: 10.1038/268150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]