Abstract
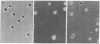
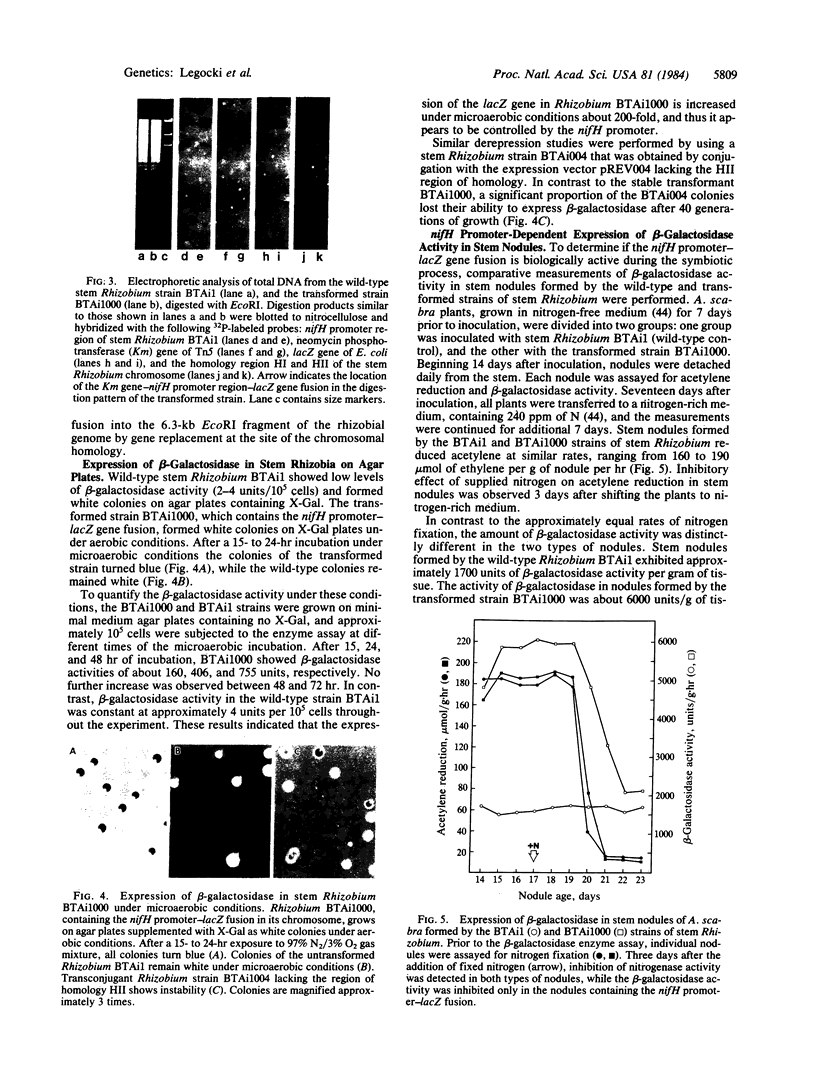
A 365-base-pair (bp) DNA fragment, containing the promoter region of the nitrogenase reductase (nifH) gene from stem Rhizobium BTAi1, has been isolated and sequenced. The transcription initiation sites were localized at positions 152 (major initiation) and 114 (minor initiation) nucleotides upstream of the translation initiation codon. The 200-bp nucleotide sequence upstream of the nifH structural gene shows substantial homology to the corresponding nifH regions of cowpea Rhizobium (100%), Parasponia Rhizobium (89%), and Rhizobium japonicum (88%). The nifH promoter region of stem Rhizobium BTAi1 was fused to the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. The fusion and a 1.6-kilobase DNA specifying neomycin phosphotransferase were inserted into a 3,4-kilobase fragment of stem Rhizobium chromosome, and the resulting construct was placed on a mobilizable vector, pREV1000. Stem Rhizobium transconjugants resistant to kanamycin were found to contain the nifH promoter region-lacZ fusion linked to the neomycin phosphotransferase gene at the site of chromosomal homology. Analysis of the DNA from stable transconjugants showed integration of a single copy of these sequences into the chromosome by a double-reciprocal crossover event. The transconjugants formed nitrogen-fixing nodules, indicating that the insertion occurred in a “nonessential” region of the stem Rhizobium chromosome. Transconjugant strain BTAi1000 grows on β-galactosidase indicator plates under aerobic conditions as white colonies, whereas under microaerobic conditions (97% N2/3% O2), which derepress nitrogenase, the colonies turn blue within 15-24 hr. β-Galactosidase activity in derepressed cultures of BTAi1000 showed a 200-fold increase in comparison to the wild-type strain, whereas stem nodules formed by BTAi1000 exhibited 15- to 20-fold higher β-galactosidase values than wild-type nodules. Nitrogenase promoter-dependent expression of β-galactosidase in stem nodules was inhibited by fixed nitrogen, suggesting that the nifH promoter-lacZ fusion is controlled coordinately in trans with the native nif region.
Keywords: expression vector, gene fusion, nitrogen fixation, stem nodulation
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. H., Chelm B. K. The nifH and nifDK promoter regions from Rhizobium japonicum share structural homologies with each other and with nitrogen-regulated promoters from other organisms. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(4):392–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avissar Y. J., Nadler K. D. Stimulation of tetrapyrrole formation in Rhizobium japonicum by restricted aeration. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):782–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.782-789.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Better M., Lewis B., Corbin D., Ditta G., Helinski D. R. Structural relationships among Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic promoters. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon J., Cannon M., Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon F. The nif promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae have a characteristic primary structure. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90399-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullerjahn G. S., Benzinger R. H. Genetic transformation of Rhizobium leguminosarum by plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):421–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.421-424.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin D., Barran L., Ditta G. Organization and expression of Rhizobium meliloti nitrogen fixation genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., De Greve H., Decraemer H., Schell J., Van Montagu M. Rapid mapping of transposon insertion and deletion mutations in the large Ti-plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1837–1849. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann M., Hennecke H. Rhizobium japonicum nitrogenase Fe protein gene (nifH). J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1005–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1005-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. W., Holsten R. D., Jackson E. K., Burns R. C. The acetylene-ethylene assay for n(2) fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1185–1207. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyneker H. L., Shine J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J., Dickerson R. E., Narang S. A., Itakura K., Lin S., Riggs A. D. Synthetic lac operator DNA is functional in vivo. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):748–752. doi: 10.1038/263748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss G. B., Kálmán Z. Transformation of Rhizobium meliloti 41 with plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):465–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.465-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. A nodule-specific plant protein (nodulin-35) from soybean. Science. 1979 Jul 13;205(4402):190–193. doi: 10.1126/science.205.4402.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Identification of "nodule-specific" host proteins (nodoulins) involved in the development of rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Brill W. J. Ineffective and non-nodulating mutant strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):763–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.763-769.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marians K. J., Wu R., Stawinski J., Hozumi T., Narang S. A. Cloned synthetic lac operator DNA is biologically active. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):744–748. doi: 10.1038/263744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Sundaresan V., Rothstein D. M., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Promoters regulated by the glnG (ntrC) and nifA gene products share a heptameric consensus sequence in the -15 region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2524–2528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. Interspecies homology of nitrogenase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):191–195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. F., Rolfe B. G., Shine J. Nitrogenase structural genes are unlinked in the nonlegume symbiont Parasponia rhizobium. DNA. 1983;2(2):141–148. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj G., Iyer V. N. Genetic transformation of Rhizobium meliloti by plasmid DNA. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjepkema J., Evans H. J. Nitrogen fixation by free-living Rhizobium in a defined liquid medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):625–628. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]