Abstract
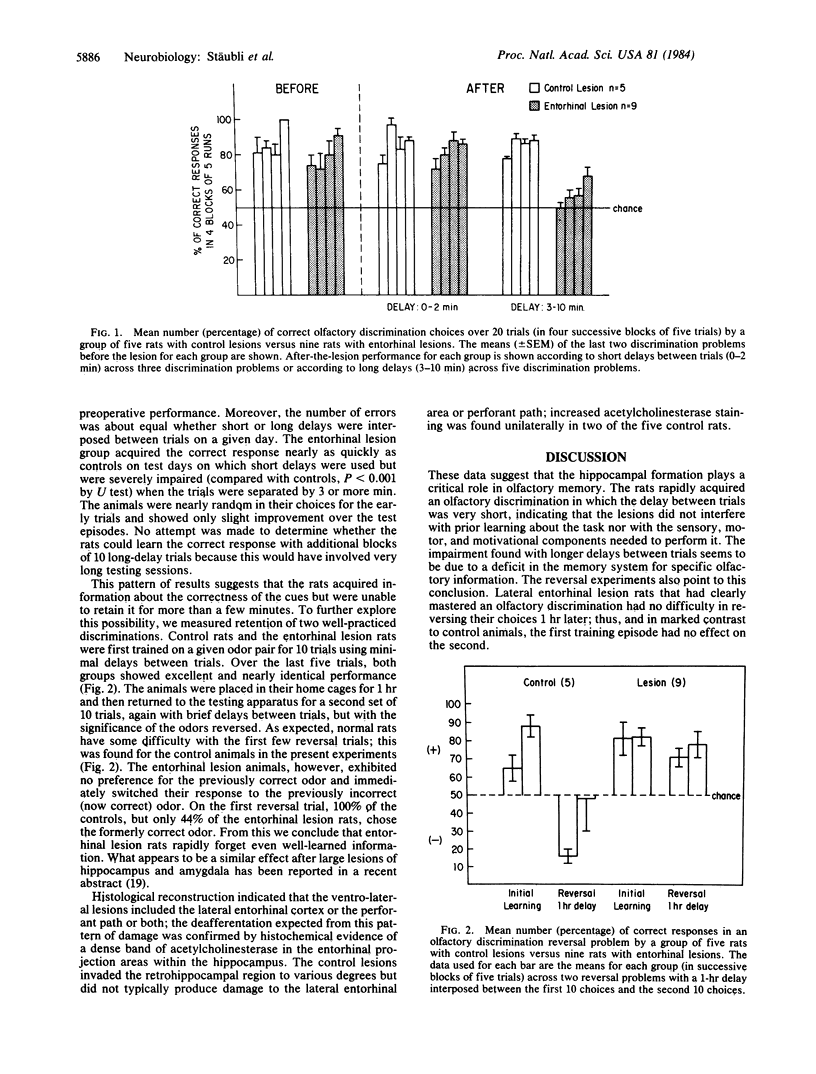
Rats were trained on a succession of two-odor discriminations for a water reward in a modified radial maze. A different odor pair was used each day. After three or four pairs, rats would learn to choose the correct odor in only 3-5 trials. Animals were then subjected to electrolytic lesions in the lateral entorhinal cortex, which is innervated by the lateral olfactory tract, or in the dorsal entorhinal cortex, which is not a target of the olfactory system. Lesions of the first type did not interfere with performance, provided a short interval (30 sec to 2 min) was used between trials. However, the rats were severely impaired when trials were separated by 3-10 min. Dorsal lesions had no effect on olfactory discrimination irrespective of length of delay. In additional experiments, the rats were trained for 10 trials with short inter-trial intervals and then tested 1 hr later with the significance of the cues reversed. Animals with dorsal lesions continued to respond to the formerly correct odor while those with lateral entorhinal damage immediately reversed their response choices. These results provide evidence that lesions to the hippocampal system produce a rapid forgetting syndrome in rats comparable with that reported for humans with temporal lobe damage or dysfunction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen N. J., Squire L. R. Preserved learning and retention of pattern-analyzing skill in amnesia: dissociation of knowing how and knowing that. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):207–210. doi: 10.1126/science.7414331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichenbaum H., Shedlack K. J., Eckmann K. W. Thalamocortical mechanisms in odor-guided behavior. I. Effects of lesions of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus and frontal cortex on olfactory discrimination in the rat. Brain Behav Evol. 1980;17(4):255–275. doi: 10.1159/000121803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth-Simonsen A., Jeune B. Origin and termination of the hippocampal perforant path in the rat studied by silver impregnation. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Feb;144(2):215–232. doi: 10.1002/cne.901440206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert F. A., Piercy M. Normal and abnormal forgetting in organic amnesia: effect of locus of lesion. Cortex. 1979 Sep;15(3):385–390. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(79)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosel K. C., Van Hoesen G. W., West J. R. Olfactory bulb projections to the parahippocampal area of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1981 May 20;198(3):467–482. doi: 10.1002/cne.901980307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch G., Matthews D. A., Mosko S., Parks T., Cotman C. Induced acetylcholinesterase-rich layer in rat dentate gyrus following entorhinal lesions. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 20;42(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90533-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner B. Disorders of learning and memory after temporal lobe lesions in man. Clin Neurosurg. 1972;19:421–446. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/19.cn_suppl_1.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigrosh B. J., Slotnick B. M., Nevin J. A. Olfactory discrimination, reversal learning, and stimulus control in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1975 Jun;89(4):285–294. doi: 10.1037/h0076821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOVILLE W. B., MILNER B. Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 Feb;20(1):11–21. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotnick B. M., Kaneko N. Role of mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in olfactory discrimination learning in rats. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):91–92. doi: 10.1126/science.7280684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire L. R. The neuropsychology of human memory. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:241–273. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. Rapid forgetting of a spatial habit in rats with hippocampal lesions. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):959–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6785882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. H., Gupta K. C., Mishkin M. The locus and cytoarchitecture of the projection areas of the olfactory bulb in Macaca mulatta. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Feb 1;177(3):381–396. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]