Abstract
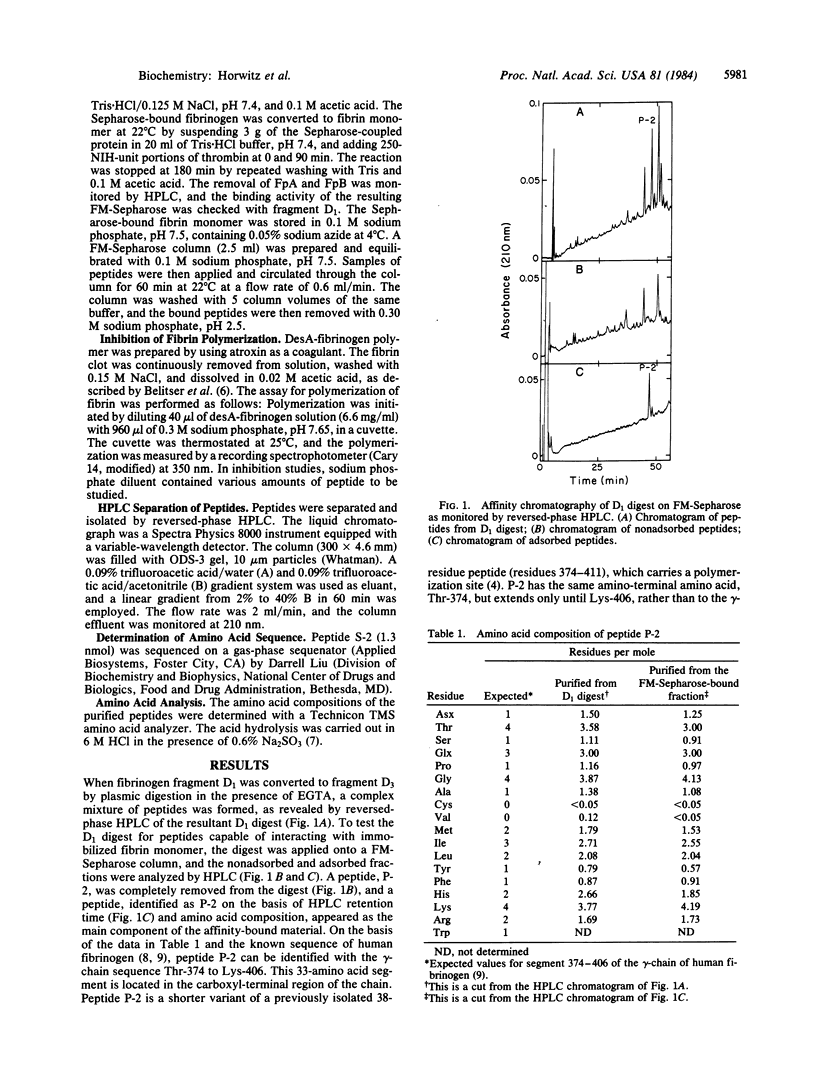
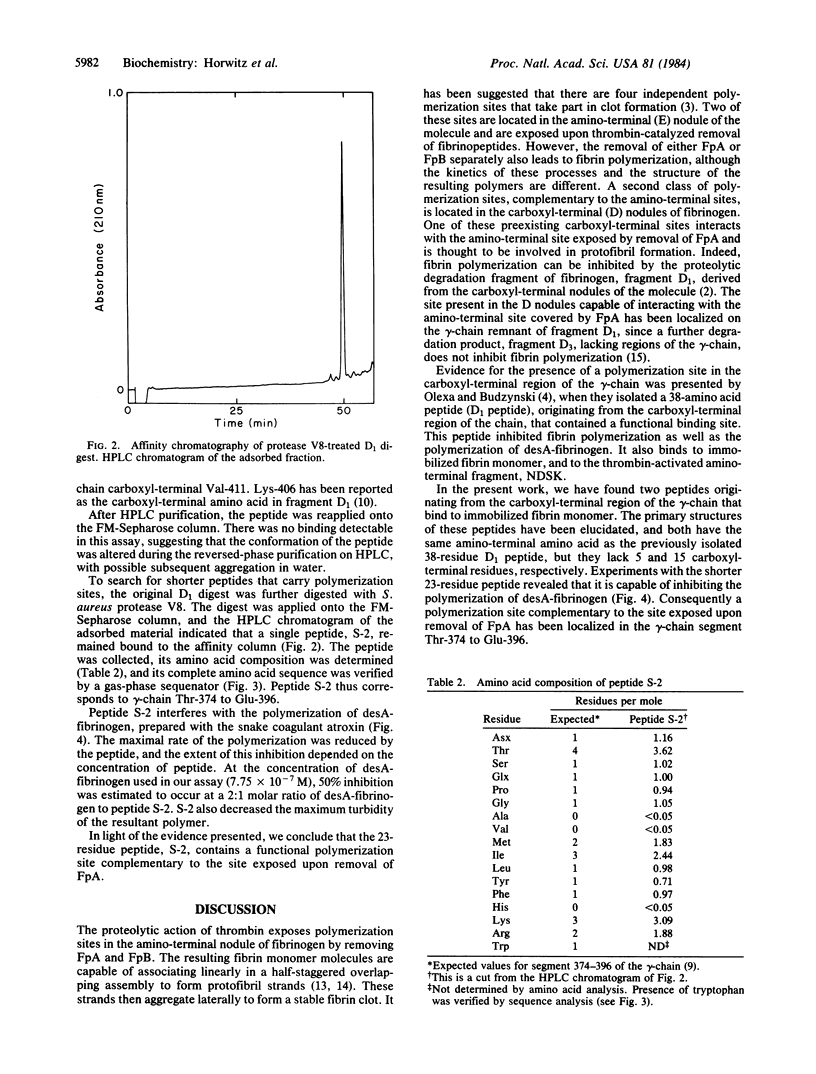
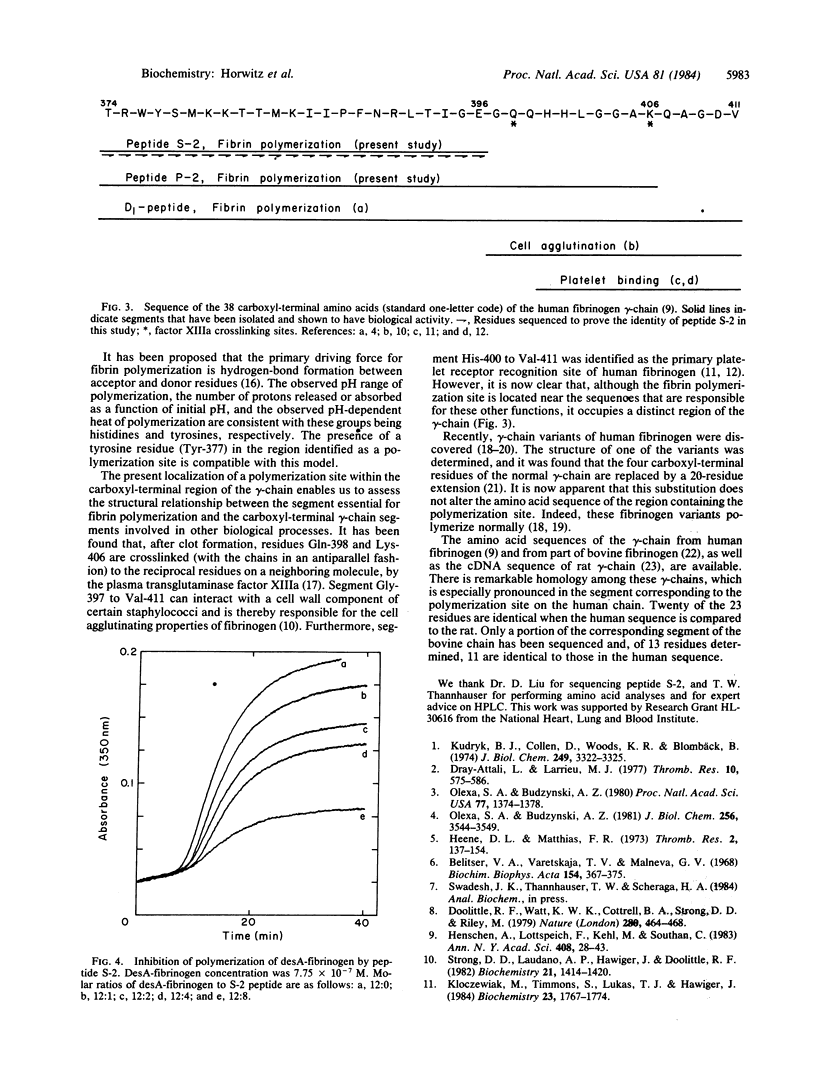
Fibrinogen fragment D1 was converted to fragment D3 by plasmic digestion. This conversion eliminates the ability of the fragment to interact with thrombin-exposed sites on fibrin monomer. Peptides released during this plasmic digestion were assayed for the presence of a polymerization site by affinity chromatography on fibrin monomer-Sepharose. We found that a 33-residue peptide, corresponding to gamma-chain Thr-374 to Lys-406, binds to immobilized fibrin monomer. This peptide is a shorter variant of a previously isolated 38-residue peptide (gamma-chain Thr-374 to Val-411) that contains a polymerization site [Olexa, S. A. & Budzynski, A. Z. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 3544-3549]. The peptide mixture derived from fragment D1 was digested further with Staphylococcus aureus protease V8, and a 23-residue peptide, gamma-chain Thr-374 to Glu-396, carrying a polymerization site, was isolated by affinity chromatography. This 23-residue peptide inhibits the polymerization of desA-fibrinogen. We conclude that a polymerization site complementary to the site exposed by removal of fibrinopeptide A is present in this segment. The localization of the polymerization site within the gamma-chain segment 374-396 implies that the polymerization site does not overlap with segments of the gamma-chain that are responsible for platelet aggregation and for Staphylococcus clumping (residues 400-411 and 397-411, respectively) or with the residues involved in factor XIIIa-catalyzed fibrin crosslinking (Gln-398 and Lys-406).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belitser V. A., Varetskaja T. V., Malneva G. V. Fibrinogen-fibrin interaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 19;154(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Organization of the rat gamma-fibrinogen gene: alternative mRNA splice patterns produce the gamma A and gamma B (gamma ') chains of fibrinogen. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray-Attali L., Larrieu M. J. Fragments d - correlation between structure and biological activity. Thromb Res. 1977 Apr;10(4):575–586. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Kraus D. H., Marder V. J. Structural and chromatographic heterogeneity of normal plasma fibrinogen associated with the presence of three gamma-chain types with distinct molecular weights. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 28;744(2):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. W., Marder V. J., Martin S. E. Demonstration of a large molecular weight variant of the gamma chain of normal human plasma fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5599–5604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkate F., Timan G., Nieuwenhuizen W. Anticlotting properties of fragments D from human fibrinogen and fibrin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;9(4):253–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Lottspeich F., Kehl M., Southan C. Covalent structure of fibrinogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 27;408:28–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb23232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Lukas T. J., Hawiger J. Platelet receptor recognition site on human fibrinogen. Synthesis and structure-function relationship of peptides corresponding to the carboxy-terminal segment of the gamma chain. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow W., Endres G. F., Siegel B. M., Scheraga H. A. An electron microscopic investigation of the polymerization of bovine fibrin monomer. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryk B. J., Collen D., Woods K. R., Blombäck B. Evidence for localization of polymerization sites in fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3322–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Evidence for four different polymerization sites involved in human fibrin formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Localization of a fibrin polymerization site. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3544–3549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Srouji A. H., Meyer D., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Evidence that three adhesive proteins interact with a common recognition site on activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5388–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. J., Cassman K. G., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence of the carboxy-terminal cyanogen bromide fragment from bovine and human fibrinogen gamma-chains. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):334–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80517-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong D. D., Laudano A. P., Hawiger J., Doolittle R. F. Isolation, characterization, and synthesis of peptides from human fibrinogen that block the staphylococcal clumping reaction and construction of a synthetic clumping particle. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1414–1420. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Mosesson M. W. Carboxy-terminal amino acid sequence of a human fibrinogen gamma-chain variant (gamma'). Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6146–6149. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenstein-Todel C., Mosesson M. W. Human plasma fibrinogen heterogeneity: evidence for an extended carboxyl-terminal sequence in a normal gamma chain variant (gamma'). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


