Abstract
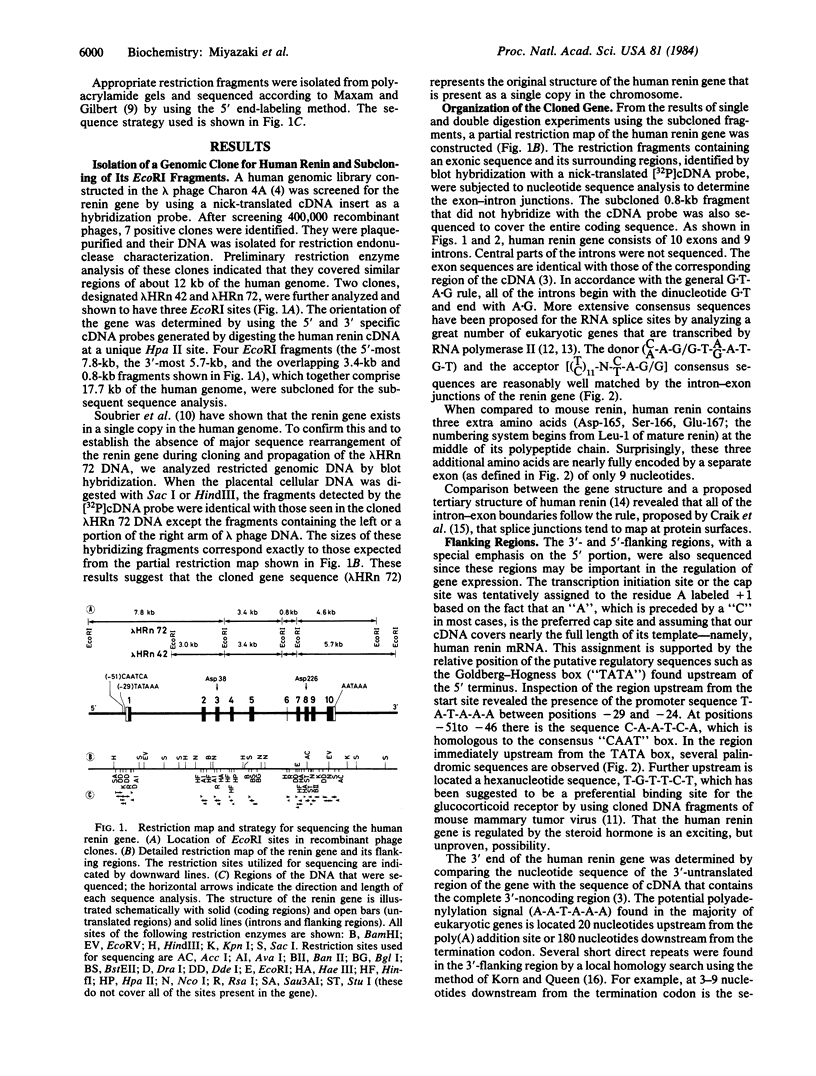
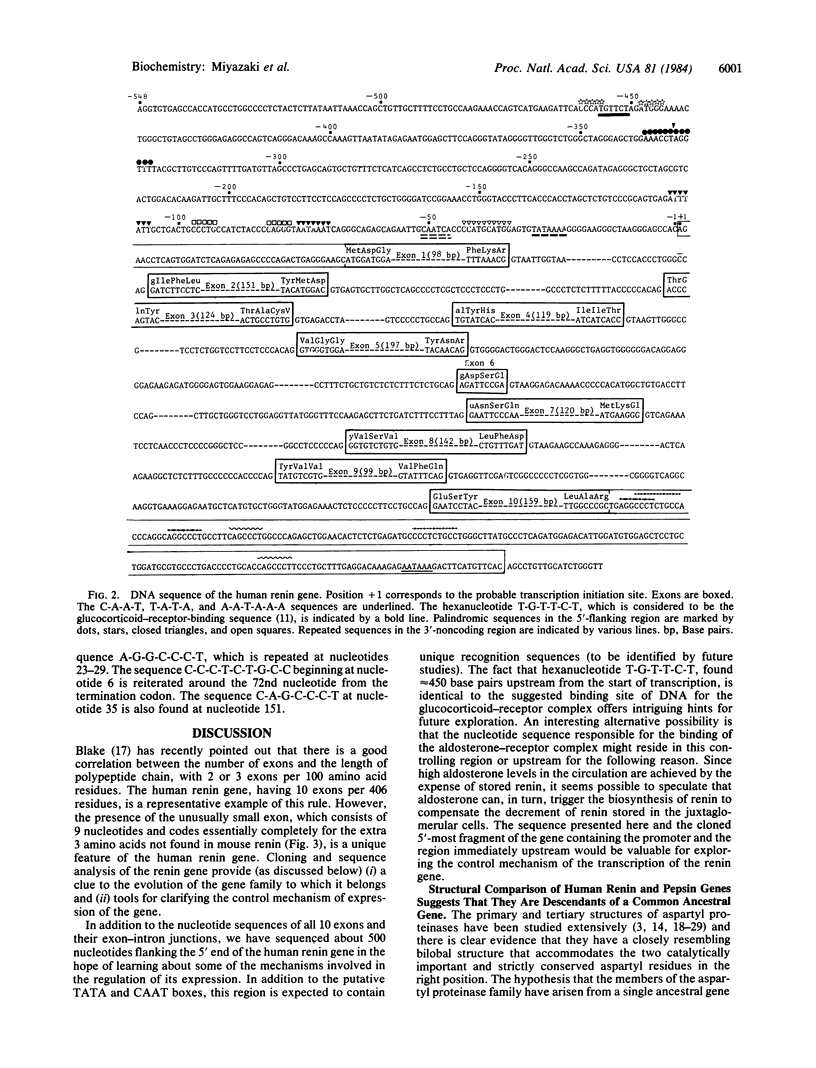
The human renin gene was isolated from a Charon 4A human genomic library and characterized. The gene spans about 11.7 kilobases and consists of 10 exons and 9 introns that map at points that could be variable surface loops of the enzyme. The complete coding regions, the 5'- and 3'-flanking regions, and the exon-intron boundaries were sequenced. The active site aspartyl residues Asp-38 and Asp-226 are encoded by the third and eighth exons, respectively. The extra three amino acids (Asp-165, Ser-166, Glu-167) that are not present in mouse renin are encoded by the separate sixth exon, an exon as small as 9 nucleotides. The positions of the introns are in remarkable agreement with those in the human pepsin gene, supporting the view that the genes coding for aspartyl proteinases have arisen as the result of duplication of a common ancestral gene. As in most eukaryotic genes, the putative T-A-T-A and C-A-A-T sequences, which may play a role in the initiation of gene transcription, are found in the vicinity of -29 and -51 nucleotides of the cap site. Further upstream, at nucleotides -456 to -451, is located the hexanucleotide T-G-T-T-C-T, which has recently been suggested as a binding site for the glucocorticoid receptor. In the 3'-flanking region, there is the conserved hexanucleotide sequence A-A-T-A-A-A, thought to be necessary for polyadenylylation. Blot-hybridization analyses of the isolated gene clone and the total cellular DNA after digestion with restriction enzymes revealed that human renin is encoded by a single gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreeva N. S., Gustchina A. E. On the supersecondary structure of acid proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):32–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91643-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. Exons--present from the beginning? Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):535–537. doi: 10.1038/306535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T., Sibanda B. L., Pearl L. Three-dimensional structure, specificity and catalytic mechanism of renin. Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):273–275. doi: 10.1038/304273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Rutter W. J., Fletterick R. Splice junctions: association with variation in protein structure. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6344214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Sprang S., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Intron-exon splice junctions map at protein surfaces. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):180–182. doi: 10.1038/299180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai T., Miyazaki H., Hirose S., Hori H., Hayashi T., Kageyama R., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Murakami K. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human renin precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A. R. Structure and refinement of penicillopepsin at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 15;163(2):299–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Queen C. L., Wegman M. N. Computer analysis of nucleic acid regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misono K. S., Chang J. J., Inagami T. Amino acid sequence of mouse submaxillary gland renin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4858–4862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S., Haber E. The renin-angiotensin system (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 22;291(8):389–401. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408222910805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Foote S., Chambraud B., Strosberg A. D., Corvol P., Rougeon F. Complete amino acid sequence and maturation of the mouse submaxillary gland renin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):90–92. doi: 10.1038/298090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. A., Morris B. J., Ganong W. F. The renin-angiotensin system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:377–410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Mizukami Y., Ichihara Y., Takahashi K. Primary structure of human pepsinogen gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5306–5311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soubrier F., Panthier J. J., Corvol P., Rougeon F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a human renin cDNA fragment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7181–7190. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian E., Swan I. D., Liu M., Davies D. R., Jenkins J. A., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L. Homology among acid proteases: comparison of crystal structures at 3A resolution of acid proteases from Rhizopus chinensis and Endothia parasitica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):556–559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Schmidt P. G., Tang J. Oligosaccharide units of lysosomal cathepsin D from porcine spleen. Amino acid sequence and carbohydrate structure of the glycopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2819–2830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Tang J. Amino acid sequence of porcine spleen cathepsin D light chain. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6435–6443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J. Evolution in the structure and function of carboxyl proteases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Jul 31;26(2):93–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00232887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., James M. N., Hsu I. N., Jenkins J. A., Blundell T. L. Structural evidence for gene duplication in the evolution of the acid proteases. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):618–621. doi: 10.1038/271618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


