Abstract
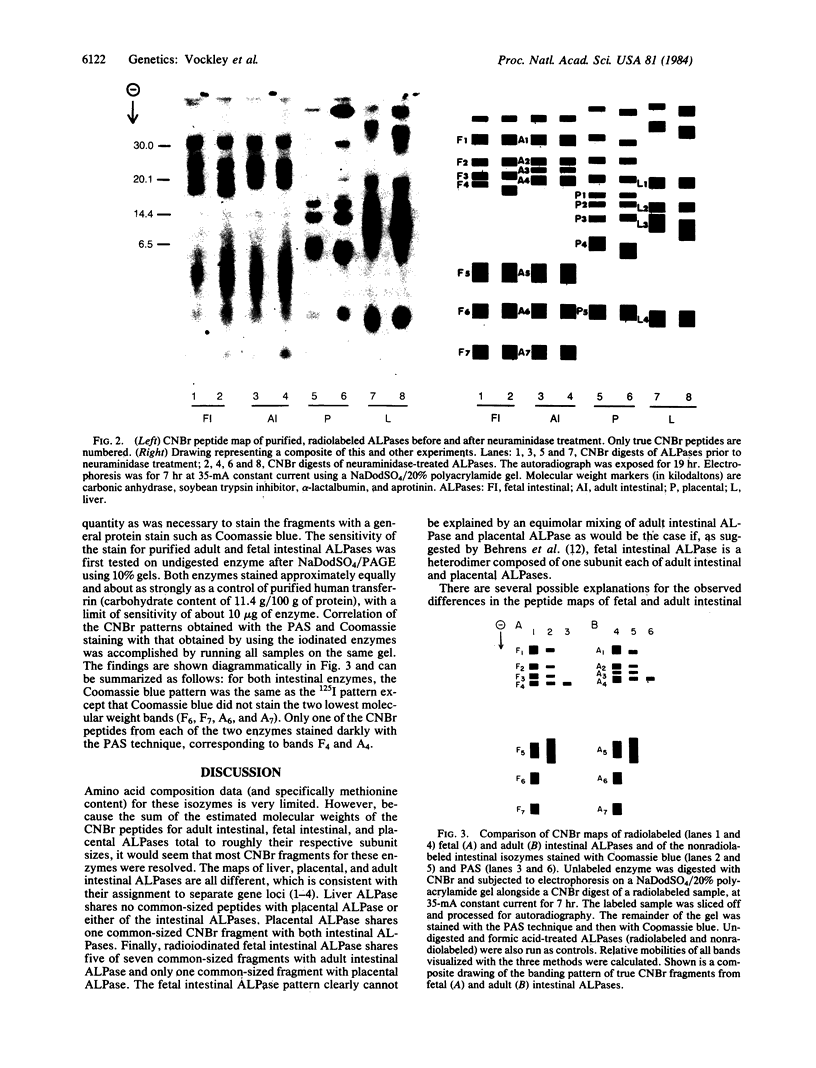
The adult and fetal forms of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase (ALPase; orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.3.1) are indistinguishable by a variety of analytical procedures. However, they differ electrophoretically and can be differentiated by binding studies with monoclonal antibodies. In this report, these two enzymes along with placental and liver ALPases are compared by the technique of CNBr peptide mapping, and the role of carbohydrate in generating these patterns is investigated. NaDodSO4/PAGE of CNBr digests of radiolabeled ALPases from fetal and adult intestine shows that these two isozymes share five of seven common-sized CNBr fragments. Placental ALPase shares only one common-sized fragment with either intestinal enzyme. Liver ALPase has no CNBr fragments in common with any of the others. These data indicate that fetal intestinal ALPase is not a heterodimer of one subunit each of intestinal ALPase and placental ALPase as has been postulated. CNBr digests of neuraminidase-treated enzymes reveal a change of mobility of only one CNBr band in each of fetal intestinal, placental, and liver ALPases, indicating the presence of sialic acid residues in these fragments. Periodic acid/Schiff reagent staining (specific for carbohydrate) of CNBr digests of fetal and adult intestinal ALPases reacts with only one band in each enzyme, which is the same band from the fetal enzyme shown to contain sialic acid. However, fetal and adult intestinal ALPases each contain at least one CNBr fragment of unique size that is apparently nonglycosylated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behrens C. M., Enns C. A., Sussman H. H. Characterization of human foetal intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Comparison with the isoenzymes from the adult intestine and human tumour cell lines. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):553–558. doi: 10.1042/bj2110553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogolin K. J., Wray L. K., Slaughter C. A., Harris H. A monoclonal antibody that reacts with nonallelic enzyme glycoproteins. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):59–61. doi: 10.1126/science.6175022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Lindstrom J. M. Structural similarities between acetylcholine receptors from fish electric organs and mammalian muscle. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4563–4569. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. Multilocus enzyme systems and the evolution of gene expression: the alkaline phosphatases as a model example. Harvey Lect. 1980;76:95–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano K., Iiizumi Y., Sugiura M., Miyazaki J., Miki K., Iino S., Suzuki H., Oda T. Characterization of human tissue-specific alkaline phosphatase. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1982 Apr;30(4):1387–1392. doi: 10.1248/cpb.30.1387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoda T., Sakagishi Y., Sekine T. Multiple forms of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase: chemical and enzymatic properties, and circulating clearances of the fast- and slow-moving enzymes. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Dec 9;117(2):167–187. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. J., Hamilton T. A., Sussman H. H. Comparison of human alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Structural evidence for three protein classes. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):67–73. doi: 10.1042/bj1810067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer L. J., Lafferty M. A., Raducha M. G., Foster C. J., Gogolin K. J., Harris H. Production of a monoclonal antibody to human liver alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Dec 9;126(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Hannig V. L., Harris H. Developmental change in human intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3909–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Plotkin L. I., Harris H. Differential inhibition of the products of the human alkaline phosphatase loci. Ann Hum Genet. 1978 Jul;42(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1978.tb00927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson E. B., Harris H. Genetics of the alkaline phosphatase polymorphism of the human placenta. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1257–1259. doi: 10.1038/2071257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seargeant L. E., Stinson R. A. Evidence that three structural genes code for human alkaline phosphatases. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):152–154. doi: 10.1038/281152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter C. A., Gogolin K. J., Coseo M. C., Meyer L. J., Lesko J., Harris H. Discrimination of human placental alkaline phosphatase allelic variants by monoclonal antibodies. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jan;35(1):1–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson R. A., Seargeant L. E. Comparative studies of pure alkaline phosphatases from five human tissues. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Mar 5;110(2-3):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Hirano K., Iiizumi Y., Miyazaki J., Miki K., Iino S., Suzuki H., Oda T. Purification and properties of human alkaline phosphatase from meconium. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1981 Dec;29(12):3660–3666. doi: 10.1248/cpb.29.3660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vockley J., Harris H. Purification of human adult and foetal intestinal alkaline phosphatases by monoclonal antibody immunoaffinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):535–541. doi: 10.1042/bj2170535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. K., Harris H. Monoclonal antibodies to an ectopically expressed alkaline phosphatase in a human malignant cell line. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):758–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]