Abstract
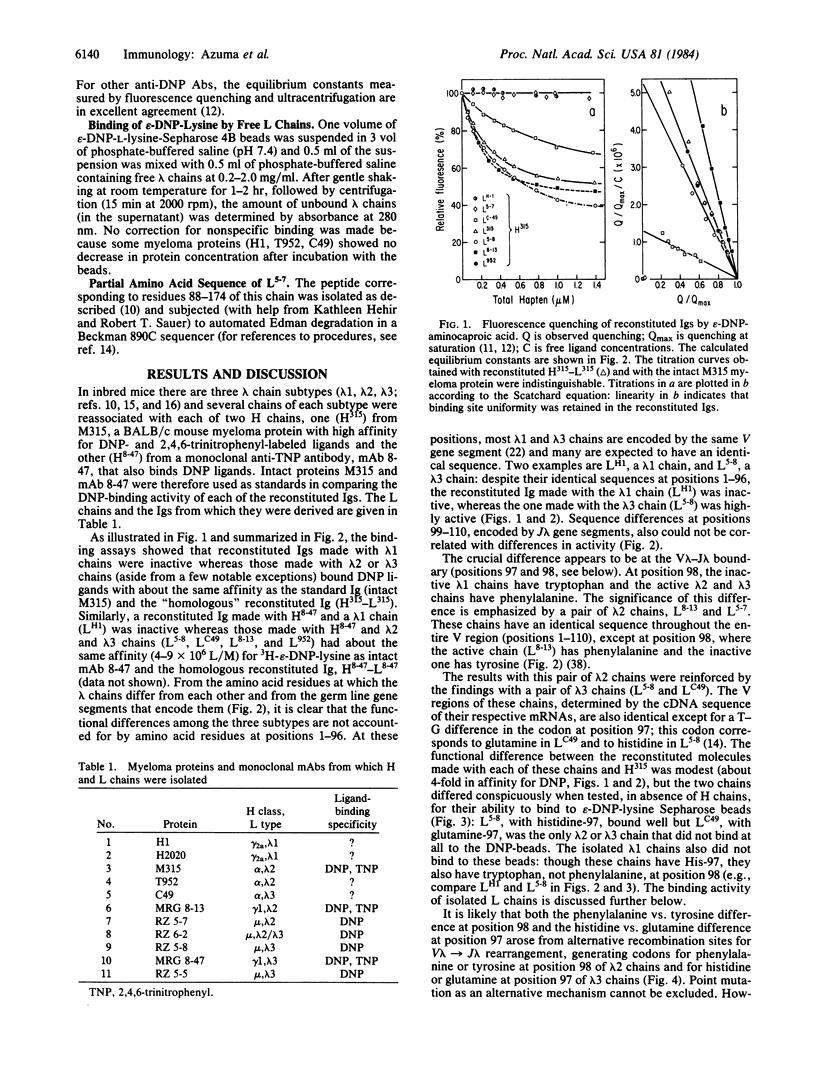
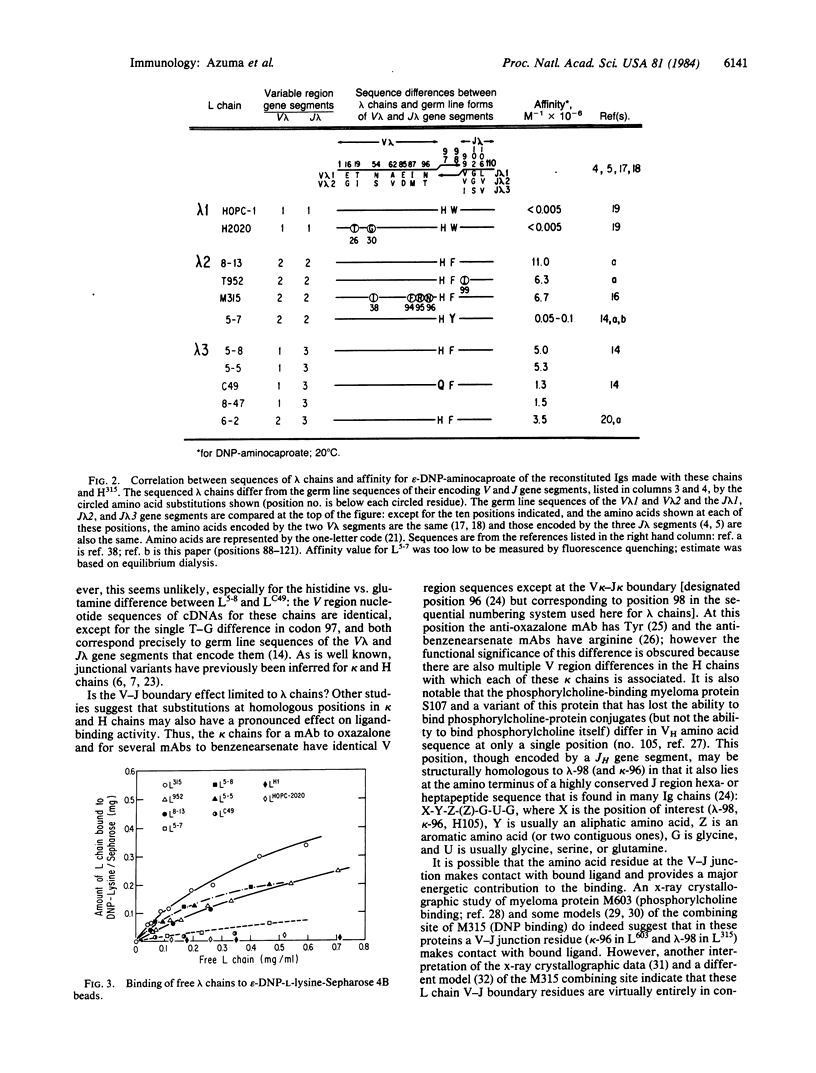
By recombining lambda light (L) chains having known variable (V) region amino acid or nucleotide sequences with a heavy (H) chain from a myeloma protein or a monoclonal antibody, we obtained reconstituted Igs that differed from each other in sequence by only one or a few amino acid substitutions at known L chain positions. Differences in affinity of the reconstituted Igs for 2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) ligands revealed a pronounced effect on Ig binding activity of amino acids at the V-J boundary of the lambda chains. In one instance, two reconstituted Igs that differed about 1000-fold in affinity for epsilon-DNP-aminocaproate differed in primary structure by only a single tyrosine-phenylalanine substitution at the V-J junction (position 98) of their lambda 2 chains--i.e., by only one out of approximately 660 amino acid residues (L + H chains). By focusing on affinity changes, chains with unusual V lambda-J lambda junctional residues were identified. It is possible that because of a critical effect on tertiary structure junctional amino acid variations arising from gene segment assembly (V/J and perhaps V/D/J) constitute an important source of ligand-binding diversity of antibodies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E. Amino acid sequences of two mouse immunoglobulin lambda chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma T., Steiner L. A., Eisen H. N. Identification of a third type of lambda light chain in mouse immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):569–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Sequences of mouse immunoglobulin light chain genes before and after somatic changes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk I., Tanford C. Recovery of native conformation of rabbit immunoglobulin G upon recombination of separately renatured heavy and light chains at near-neutral pH. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1289–1295. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B., Tonegawa S. DNA sequences of the joining regions of mouse lambda light chain immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):530–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges S. H., Little J. R. Recovery of binding activity in reconstituted mouse myeloma proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2525–2530. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Rudikoff S., Giusti A. M., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation in a cultured mouse myeloma cell affects antigen binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1240–1244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotner T., Blaser K., Kriedberg J., Potter M., Eisen H. N. Mouse myeloma proteins with lambda 2 and lambda 3 light chains. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):2150–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugan E. S., Bradshaw R. A., Simms E. S., Eisen H. N. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of a mouse myeloma protein (MOPC-315). Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 18;12(26):5400–5416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwek R. A., Wain-Hobson S., Dower S., Gettins P., Sutton B., Perkins S. J., Givol D. Structure of an antibody combining site by magnetic resonance. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):31–37. doi: 10.1038/266031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott B. W., Jr, Eisen H. N., Steiner L. A. Unusual association of V, J and C regions in a mouse immunoglobulin lambda chain. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):559–561. doi: 10.1038/299559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Metzger H. Affinity labeling of a mouse myeloma protein which binds nitrophenyl ligands. Kinetics of labeling and isolation of a labeled peptide. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 3;9(5):1267–1278. doi: 10.1021/bi00807a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne C., Klein M., Polidoulis I., Dorrington K. J. Noncovalent association of heavy and light chains of human immunoglobulins. III. Specific interactions between VH and VL. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):660–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett G. J., Yeh E., Schachman H. K. Protein-ligand binding studies with a table-top, air-driven high-speed centrifuge. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):808–819. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen M., Griffiths G. M., Markham A. F., Milstein C. mRNA sequences define an unusually restricted IgG response to 2-phenyloxazolone and its early diversification. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):320–324. doi: 10.1038/304320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., von Boehmer H., Haas W., Sakano H., Trauneker A., Tonegawa S. Identification of D segments of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes and their rearrangement in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):565–570. doi: 10.1038/290565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Selsing E., Storb U. Structural alterations in J regions of mouse immunoglobulin lambda genes are associated with differential gene expression. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):428–430. doi: 10.1038/295428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Bruccoleri R., Newell J., Murphy D., Haber E., Karplus M. Molecular anatomy of the antibody binding site. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14433–14437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A., Davies D. R., Pecht I., Givol D., Wright C. Model-building studies of antigen-binding sites: the hapten-binding site of mopc-315. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):627–637. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly E. B., Blomberg B., Imanishi-Kari T., Tonegawa S., Eisen H. N. Restricted association of V and J-C gene segments for mouse lambda chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2484–2488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly E. B., Reilly R. M., Breyer R. M., Sauer R. T., Eisen H. N. Amino acid and nucleotide sequences of variable regions of mouse immunoglobulin light chains of the lambda 3-subtype. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):471–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell J. D., Gearhart P. J., Karush F. Restriction in IgM expression. IV. Affinity analysis of monoclonal anti-phosphorylcholine antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Rao D. N., Glaudemans C. P., Potter M. kappa Chain joining segments and structural diversity of antibody combining sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4270–4274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakato N., Semma M., Eisen H. N., Azuma T. A small hypervariable segment in the variable domain of an immunoglobulin light chain stimulates formation of anti-idiotypic suppressor T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5396–5400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Ziv E. Binding of 2,4-dinitrophenyl derivatives by the light chain dimer obtained from immunoglobulin A produced by MOPC-315 mouse myeloma. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2785–2790. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Davies D. R. The three-dimensional structure of a phosphorylcholine-binding mouse immunoglobulin Fab and the nature of the antigen binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequence of light chain variable regions derived from five monoclonal anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies differing with respect to a crossreactive idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7679–7683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. M., Wu T. T. A predictive method for determining possible three-dimensional foldings of immunoglobulin backbones around antibody combining sites. J Theor Biol. 1981 Feb 7;88(3):421–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens F. J., Westholm F. A., Solomon A., Schiffer M. Self-association of human immunoglobulin kappa I light chains: role of the third hypervariable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1144–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zidovetski R., Licht A., Pecht I. Effect of interchain disulfide bond on hapten binding properties of light chain dimer of protein 315. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5848–5852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



