Abstract
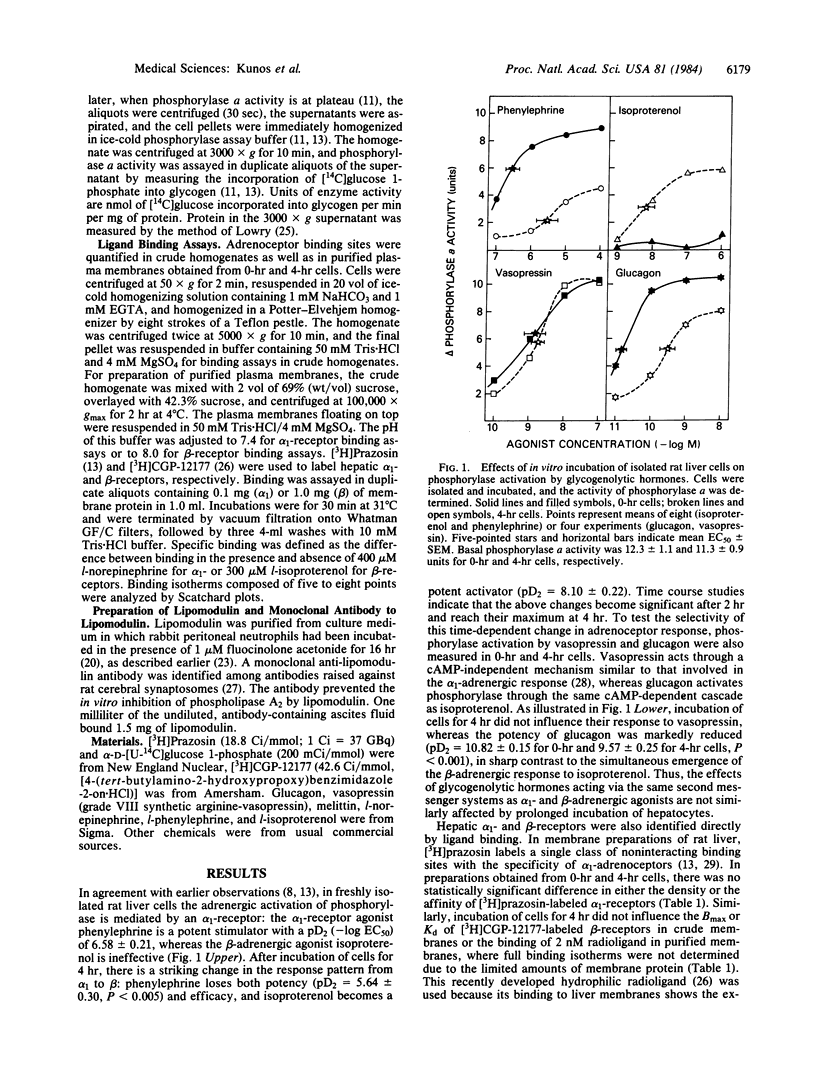
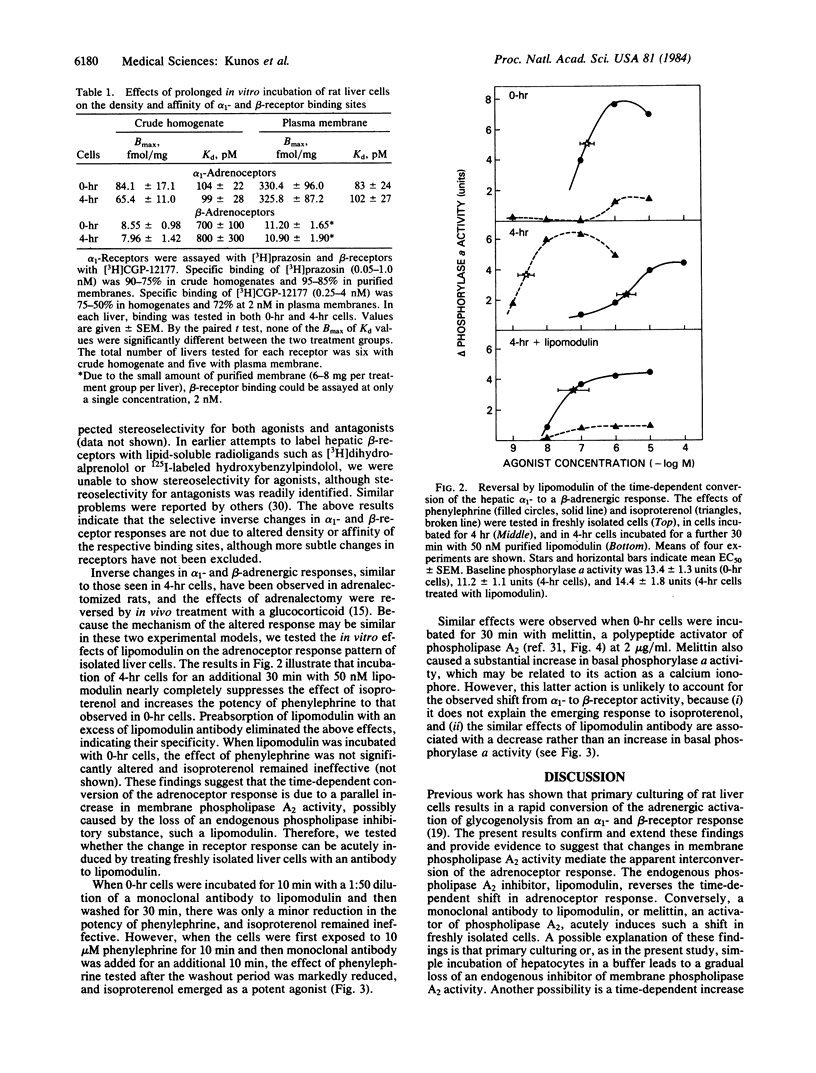
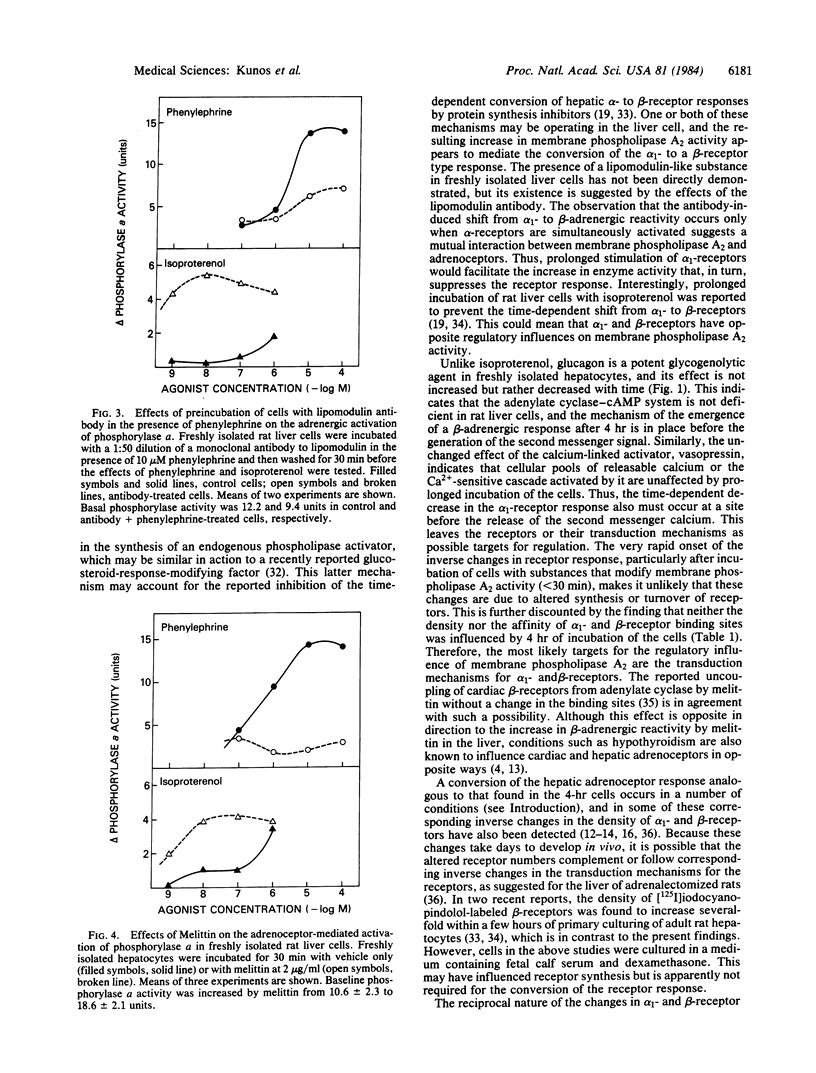
Incubation of isolated rat liver cells in a serum-free buffer leads to the reduction of the glycogenolytic effect of phenylephrine and the simultaneous emergence of a glycogenolytic response to isoproterenol within 4 hr. This conversion of the adrenergic activation of phosphorylase from an alpha 1- to a beta-adrenoceptor-mediated response is associated with no change in the glycogenolytic response to the calcium-linked activator vasopressin, and a reduction of the glycogenolytic response to the cAMP-linked activator glucagon. In vitro incubation of hepatocytes does not influence the density of affinity of [3H]prazosin-labeled alpha 1-receptors and [3H]CGP-12177-labeled beta-receptors. In cells preincubated for 4 hr, a further 30-min incubation with 50 nM lipomodulin, an endogenous inhibitor of membrane phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4), reverses the adrenergic activation of phosphorylase from a beta- to an alpha 1-receptor-mediated event, whereas in freshly isolated cells lipomodulin does not affect the predominant alpha-receptor response. Conversely, exposure of freshly isolated cells to a monoclonal antibody to lipomodulin in the presence of 10 microM phenylephrine, or to melittin, an activator of phospholipase A2, at 2 micrograms/ml, results in the suppression of the effect of phenylephrine and the emergence of a response to isoproterenol within 30 min. It is proposed that coupling of hepatic alpha 1- and beta-adrenoceptors to postreceptor pathways is regulated in an inverse reciprocal manner by changes in membrane phospholipase A2 activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck M., Ferry N., Zafrani E. S., Billon M. C., Barouki R., Hanoune J. Adrenergic regulation of glycogenolysis in rat liver after cholestasis. Modulation of the balance between alpha 1 and beta 2 receptors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):476–486. doi: 10.1172/JCI110792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. B., James M. E., Foster J. L. Adrenergic control of glucose output and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate levels in hepatocytes from juvenile and adult rats. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7579–7584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobik A., Campbell J., Snow P., Little P. J. The effects of endogenous phospholipase A2 activation on beta adrenoceptor function in cardiac cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1983 Nov;15(11):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(83)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. M., Blackmore P. F., Steiner K. E., Exton J. H. Effects of adrenalectomy on hormone action on hepatic glucose metabolism. Reciprocal change in alpha- and beta-adrenergic activation of hepatic glycogen phosphorylase and calcium mobilization in adrenalectomized rats. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2428–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corwin E. J., Cho K. W., Malvin R. L. Temperature-induced conversion of the renal adrenoreceptor: modulating renin release. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):F23–F28. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.1.F23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dax E. M., Partilla J. S., Gregerman R. I. Quantitation of beta adrenergic receptors in rat liver: confounding effect of displaceable but nonstereospecific antagonist binding. J Recept Res. 1981;2(3):267–283. doi: 10.3109/10799898109038804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild S. S., Shannon K., Kwan E., Mishell R. I. T cell-derived glucosteroid response-modifying factor (GRMFT): a unique lymphokine made by normal T lymphocytes and a T cell hybridoma. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):821–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C. M., Venter J. C., Kaliner M. Autonomic abnormalities and autoantibodies to beta-adrenergic receptors. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 12;305(20):1165–1170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111123052001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D. Involvement of guanine nucleotide-binding protein in the gating of Ca2+ by receptors. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):64–66. doi: 10.1038/306064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Ferry N., Geynet P., Hanoune J. Hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptors show agonist-specific regulation by guanine nucleotides. Loss of nucleotide effect after adrenalectomy. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11577–11583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Hoffman T., Hirata F. Differentiation of a histiocytic lymphoma cell line by lipomodulin, a phospholipase inhibitory protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Notsu Y., Iwata M., Parente L., DiRosa M., Flower R. J. Identification of several species of phospholipase inhibitory protein(s) by radioimmunoassay for lipomodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91588-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F. The regulation of lipomodulin, a phospholipase inhibitory protein, in rabbit neutrophils by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7730–7733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Brumley F. T., Assimacopoulos F. D., Harper S. C., Exton J. H. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. I. Studies on the alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase and gluconeogenesis and inactivation of glycogen synthase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5200–5208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Perfusion of the pancreas isolated from pertussis-sensitized rats: potentiation of insulin secretory responses due to beta-adrenergic stimulation. Endocrinology. 1977 Oct;101(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-4-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Kan W. H., Greguski R., Venter J. C. Selective affinity labeling and molecular characterization of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptors with [3H]phenoxybenzamine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):326–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Mucci L., Jaeger V. Interconversion of myocardial adrenoceptors: its relationship to adenylate cyclase activation. Life Sci. 1976 Nov 15;19(10):1597–1602. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Mucci L., O'Regan S. The influence of hormonal and neuronal factors on rat heart adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):371–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Szentivanyi M. Evidence favouring the existence of a single adrenergic receptor. Nature. 1968 Mar 16;217(5133):1077–1078. doi: 10.1038/2171077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Li S., Fain J. N. Hormonal activation of glycogen phosphorylase in hepatocytes from hypothyroid rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Li S., Fain J. N. Hormonal activation of glycogen phosphorylase in hepatocytes from hypothyroid rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson R. A., Laskin J. D., Fisher P. B., Weinstein I. B. Melittin shares certain cellular effects with phorbol ester tumour promoters. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):72–74. doi: 10.1038/280072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomomura A., Noda C., Shimoji M., Ichihara A. Acquisition of a beta-adrenergic response by adult rat hepatocytes during primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9283–9289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi A. Normal ontogeny of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor in rat liver is thyroid hormone dependent. Endocrinology. 1983 Aug;113(2):672–676. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-2-672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. Conversion of adrenergic regulation of glycogen phosphorylase and synthase from an alpha to a beta type during primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):658–668. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic W. J., Brown J. E., Adamson J. W. Modulation of in vitro erythropoiesis. Studies with euthyroid and hypothyroid dogs. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):56–61. doi: 10.1172/JCI109463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiksaitis H. G., Kan W. H., Kunos G. Decreased alpha 1-adrenoceptor responsiveness and density in liver cells of thyroidectomized rats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4321–4327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiksaitis H. G., Kunos G. Adrenoceptor-mediated activation of liver glycogen phosphorylase: effects of thyroid state. Life Sci. 1979 Jan 1;24(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refsnes M., Sandnes D., Melien O., Sand T. E., Jacobsen S., Christoffersen T. Mechanisms for the emergence of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase and beta-adrenergic receptors in cultured hepatocytes. Dependence on protein and RNA synthesis and suppression by isoproterenol. FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Simons P., Jaeggi K., Wigger N. CGP-12177. A hydrophilic beta-adrenergic receptor radioligand reveals high affinity binding of agonists to intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3496–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



