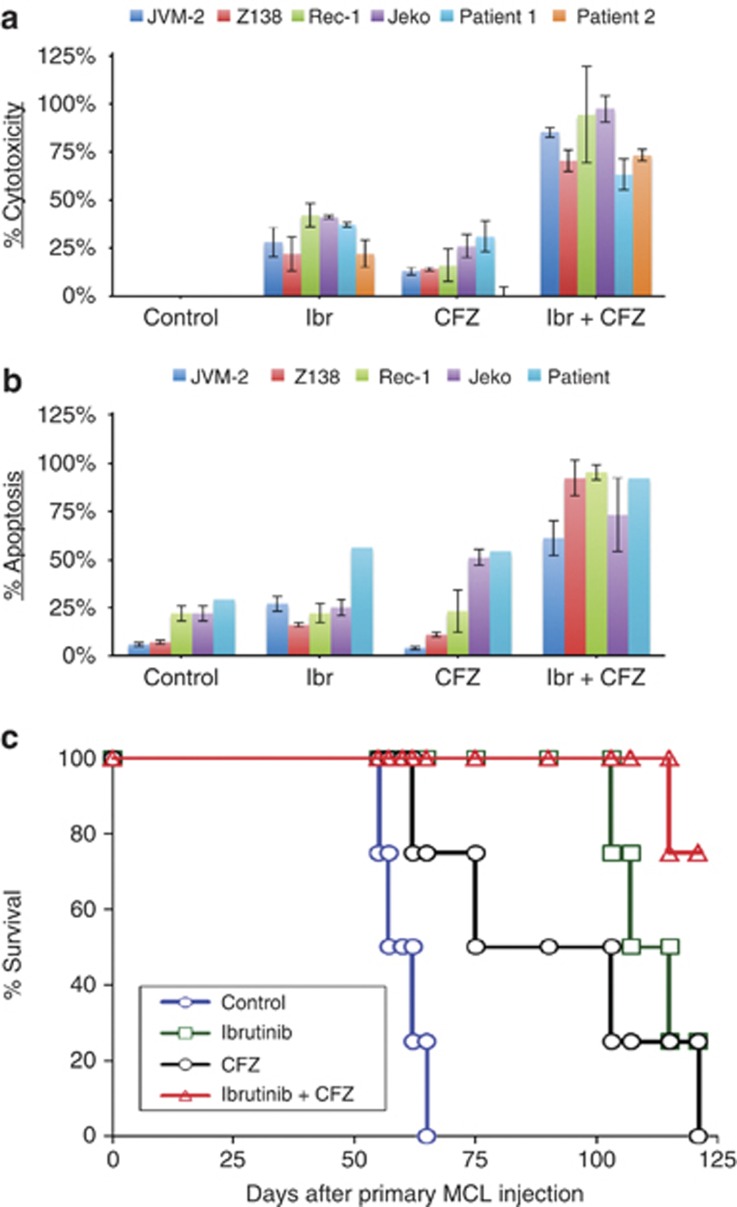
Figure 2.
The combination of ibrutinib (Ibr) and carfilzomib results in synergistic cytotoxicity, apoptosis and enhances survival in MCL models. The cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of Ibr and carfilzomib as single agents and in combination were assessed in MCL cell lines and primary patient samples. Cells were treated for 48 h (Rec-1, Jeko and patient samples) or 72 h (JVM-2 and Z138) with the indicated drugs. Ibr concentrations ranged between 1.5 and 21 μM. Carfilzomib concentrations ranged between 2.6 and 20 nM. (a) Cytotoxicity was assayed using tetrazolium (MTS) (Rec-1, Jeko and patient samples) or alamarBlue (JVM-2 and Z138). (b) Apoptosis was assayed using Annexin V/propidium iodide staining (Rec-1, Jeko and patient samples) or cleaved Poly ADP Ribose Polymerase (PARP) staining (JVM-2 and Z138). (c) Primary patient MCL cells injected into human fetal bone chips, which had been subcutaneously implanted in SCID-hu mice. When human β2m was detectable in mouse serum, mice (five per group) were given Ibr 25 mg/kg, daily oral gavage and/or CFZ 5 mg/kg, intravenously twice a week for 5 weeks. Mice were killed once tumor burden reached 1.5 cm diameter (tumor burden equals mass diameter minus bone chip diameter in the long dimension). Kaplan–Meier survival curves of primary MCL-bearing SCID-hu mice were analyzed (Ibr plus CFZ versus Ibr/CFZ alone: P<0.01).