Abstract
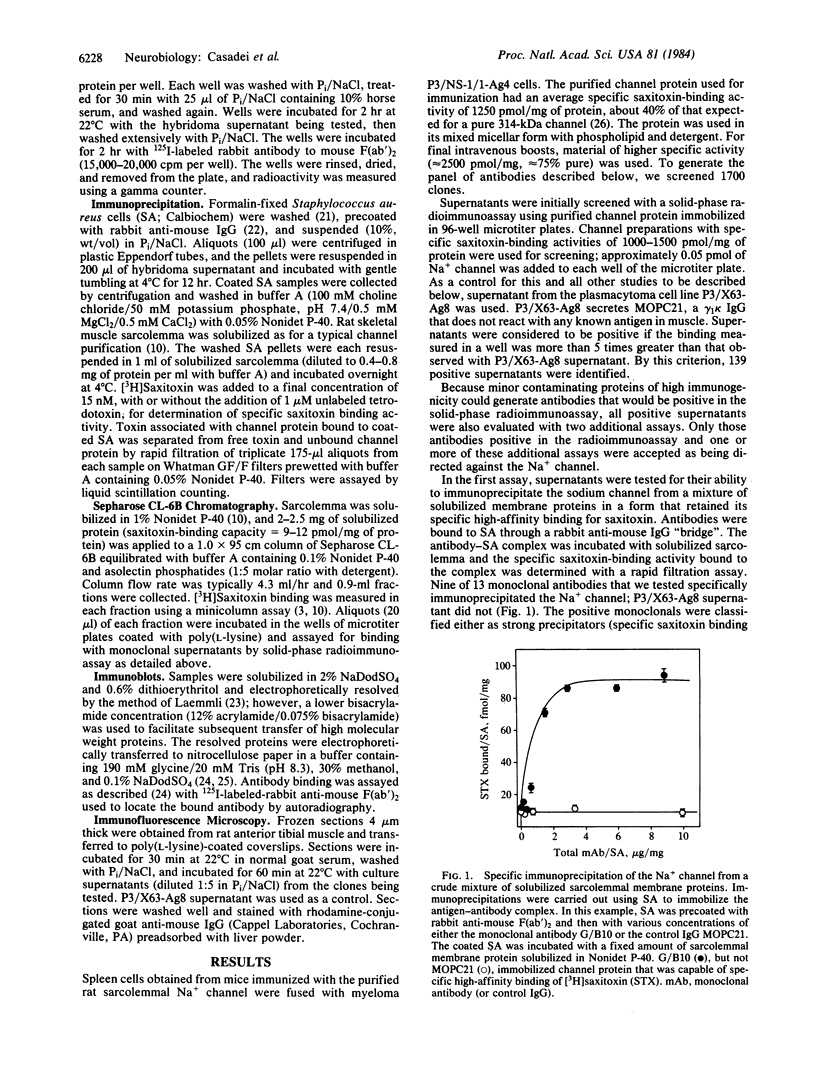
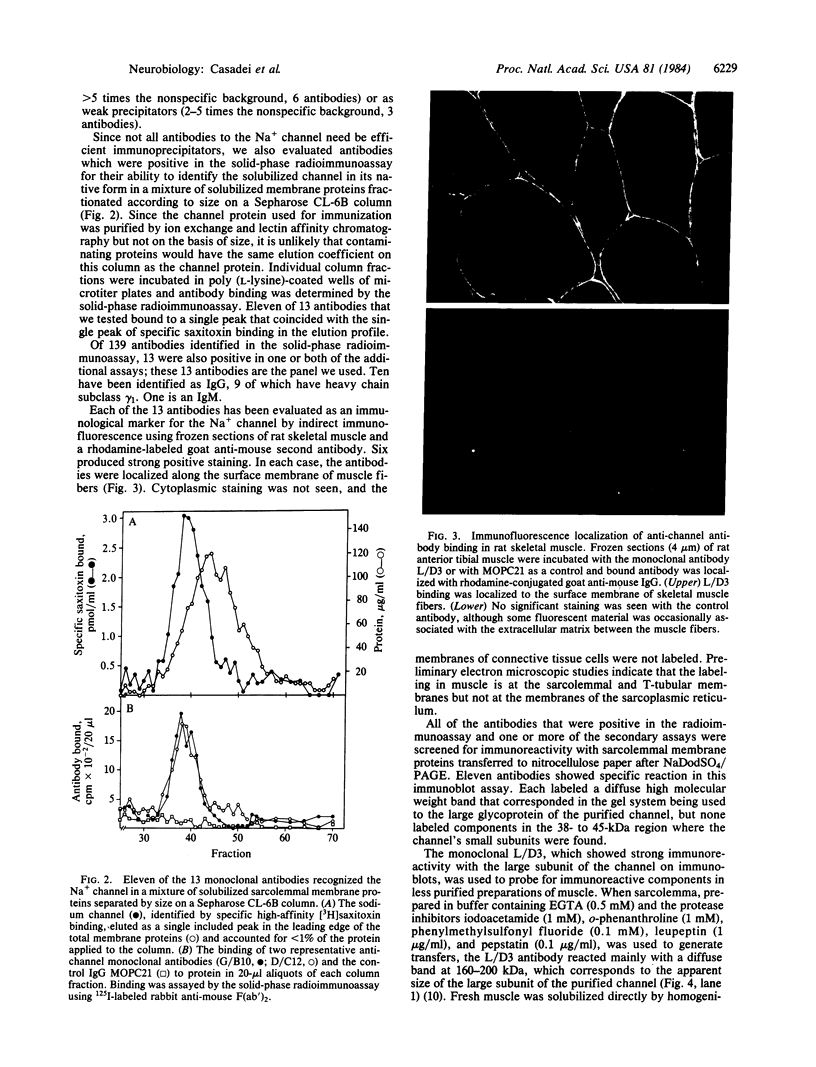
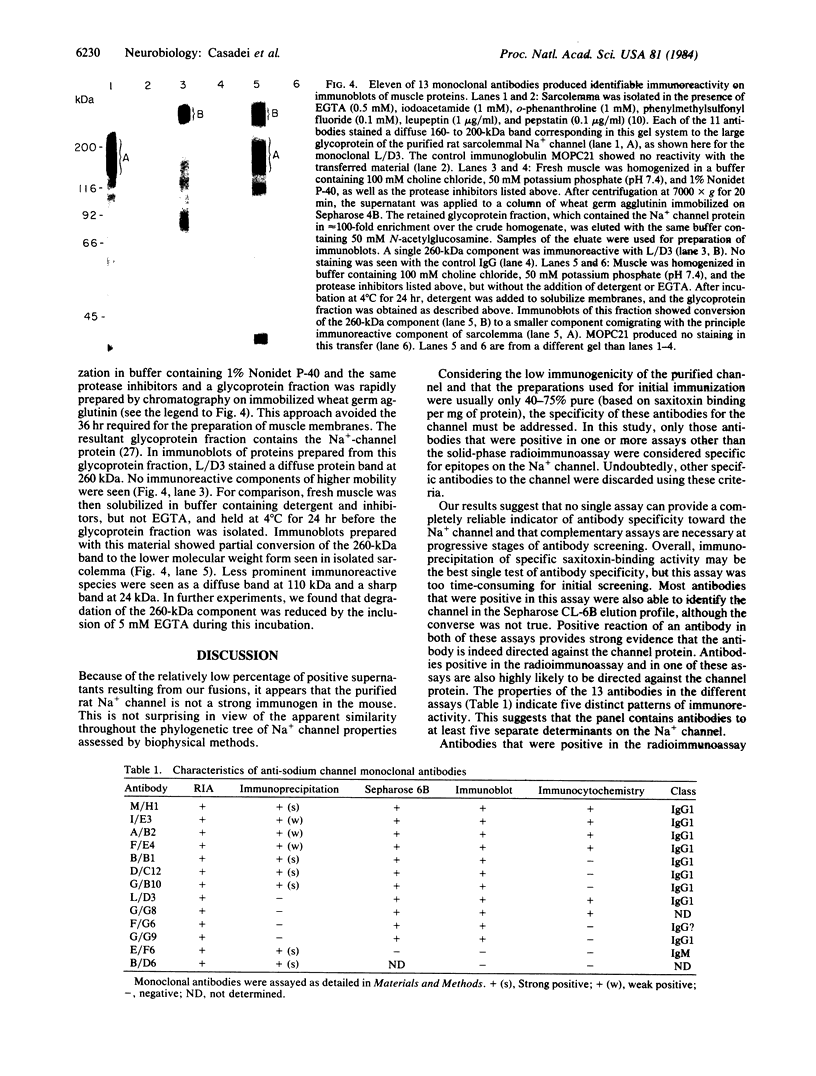
A panel of 13 monoclonal antibodies against the voltage-sensitive Na+ channel of rat skeletal muscle has been characterized. Each of these antibodies reacted with the purified Na+ channel protein in a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Nine antibodies specifically immunoprecipitated the Na+ channel in a form that retained its characteristic high affinity for saxitoxin, and 11 recognized the channel in a crude mixture of solubilized membrane proteins separated on a Sepharose CL-6B column. Six antibodies specifically labeled skeletal muscle in immunofluorescence techniques. In each case, antibody was localized only to the surface membrane of the muscle fibers. Eleven antibodies produced detectable reaction on immunoblot transfers of sarcolemmal membrane proteins; each of these bound to a diffuse 160- to 200-kDa band that comigrated with the large glycoprotein subunit of the purified Na+ channel. Further studies were carried out with one of these antibodies, L/D3. In immunoblots of a glycoprotein fraction prepared from muscle that had been homogenized rapidly in a solution containing detergent, EGTA, and protease inhibitors, L/D3 recognized only a single 260-kDa band. Incubation of solubilized muscle proteins at 4 degrees C for 24 hr without EGTA prior to isolation of the glycoprotein fraction resulted in partial conversion of this 260-kDa component to a smaller component between 160 and 200 kDa that comigrated with the principal immunoreactive component of sarcolemma. Based on its immunoreactivity with monoclonal antibodies, the large subunit of the rat skeletal muscle Na+ channel appears to be approximately equal to 260 kDa in its native state but may be sensitive to proteolysis during the isolation of sarcolemmal membranes.
Full text
PDF

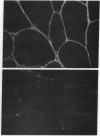
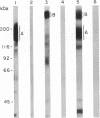
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R., Brabson J. S., Raftery M. A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Cohen S. A., Murphy L. E. Purification from rat sarcolemma of the saxitoxin-binding component of the excitable membrane sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1306–1310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Murphy L. E. Estimate of the molecular weight of the sarcolemmal sodium channel using H2O-D2O centrifugation. J Neurochem. 1981 Jun;36(6):2097–2100. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Protein components of the purified sodium channel from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1377–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Weigele J. B., Chalikian D. M., Murphy L. E. Muscle surface membranes: preparative methods affect apparent chemical properties and neurotoxin binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 5;550(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Barchi R. L. Glycoprotein characteristics of the sodium channel saxitoxin-binding component from mammalian sarcolemma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 20;645(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Levinson S. R. Immunocytochemical localization of sodium channel distributions in the excitable membranes of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6707–6711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz L. C., Brockes J. P. Immunochemical properties and cytochemical localization of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from the electroplax of the eel (Electrophorus electricus). J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2300–2309. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02300.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovich B., Bonilla E., Casadei J., Barchi R. Immunocytochemical localization of the mammalian voltage-dependent sodium channel using polyclonal antibodies against the purified protein. J Neurosci. 1984 Sep;4(9):2259–2268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-09-02259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. Purification of the saxitoxin receptor of the sodium channel from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H. Cell fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:345–359. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):462–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Fritz L. C., Raftery M. A., Brockes J. P. Isolation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against the saxitoxin-binding component from the electric organ of the eel Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1673–1677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama H., Withy R. M., Raftery M. A. Use of a monoclonal antibody to purify the tetrodotoxin binding component from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Strichartz G. R. A new method for labelling saxitoxin and its binding to non-myelinated fibres of the rabbit vagus, lobster walking leg, and garfish olfactory nerves. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):477–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Wrigley C. W., Baldo B. A. Detection of IgE- and IgG-binding proteins after electrophoretic transfer from polyacrylamide gels. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jul 30;52(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Talvenheimo J. A., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-activated ion flux and scorpion toxin binding from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1676–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J. C., Eccleston J. F., Barchi R. L. Cation selectivity characteristics of the reconstituted voltage-dependent sodium channel purified from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7519–7526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigele J. B., Barchi R. L. Functional reconstitution of the purified sodium channel protein from rat sarcolemma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]