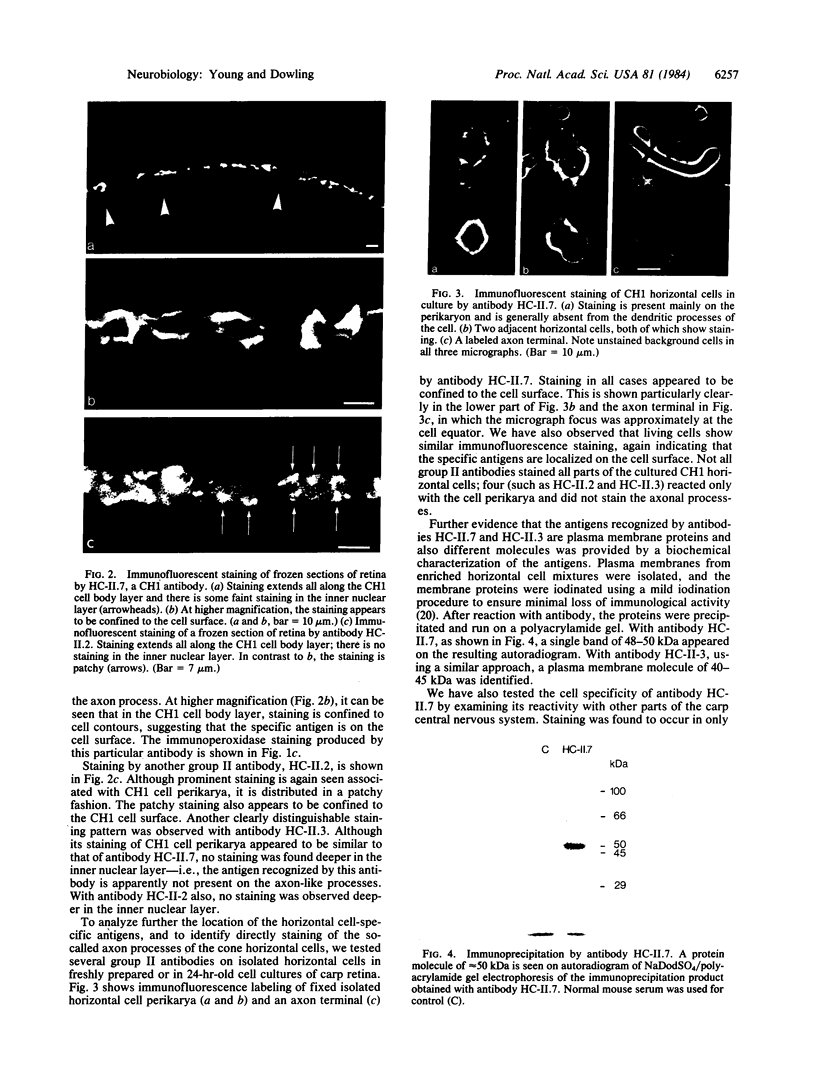
Abstract
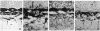
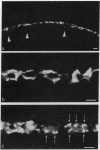
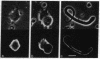
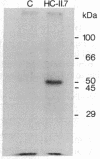
Sixteen hybridomas have been identified that secrete antibodies specific to horizontal cells in the carp retina. The hybridomas have been classified into three groups based on their antibody staining patterns: group I, staining associated with all horizontal cells; group II, staining associated with the most abundant subtype of horizontal cell (CH1); and group III, staining associated with other subtypes of horizontal cells. Most of the hybridomas fall in group II; some of these antibodies stain the entire horizontal cell, but others are specific only to the cell perikarya and do not stain axonal processes. Our results suggest that there are surface molecules specific (i) to all retinal horizontal cells, (ii) to individual subtypes of horizontal cells, and (iii) to portions of horizontal cells. Furthermore, a group II antibody, which recognizes a 48- to 50-kDa membrane protein, has been found to provide a substrate selective for horizontal cell growth. Horizontal cells plated on coverslips coated with this antibody remain healthy in culture and extend long and elaborate processes for at least 3 weeks.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J. Monoclonal antibodies which recognize different cell types in the rat retina. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):231–235. doi: 10.1038/286231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Selvendran S. Y. A neuronal cell-surface antigen is found in the CNS but not in peripheral neurones. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):421–423. doi: 10.1038/291421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Monoclonal antibody to a plasma membrane antigen of neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S. C., Zipursky S. L., Benzer S., Ferrús A., Shotwell S. L. Monoclonal antibodies against the Drosophila nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7929–7933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Margulies D. H., Scharff M. D. A simple method for polyethylene glycol-promoted hybridization of mouse myeloma cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Mar;3(2):231–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01551818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Matus A. Monoclonal antibodies identify novel neural antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2410–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockfield S., McKay R. D. A surface antigen expressed by a subset of neurons in the vertebrate central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5758–5761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A. Electrical connexions between horizontal cells in the dogfish retina. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):95–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam D. M., Steinman L. The uptake of ( - 3 H) aminobutyric acid in the goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2777–2781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E. Carp horizontal cells in culture respond selectively to L-glutamate and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leifer D., Lipton S. A., Barnstable C. J., Masland R. H. Monoclonal antibody to Thy-1 enhances regeneration of processes by rat retinal ganglion cells in culture. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):303–306. doi: 10.1126/science.6143400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon V., Gottlieb D. I. Monoclonal antibodies selective for the inner portion of the chick retina. J Neurosci. 1982 May;2(5):531–535. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-05-00531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACNICHOL E. J., SVAETICHIN G. Electric responses from the isolated retinas of fishes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;46(3 Pt 2):26–46. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeish P. R., Barnstable C. J., Townes-Anderson E. Use of a monoclonal antibody as a substrate for mature neurons in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):7014–7018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.7014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Stell W. K., Bok D., Lam D. M. GABA-ergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):221–244. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka K. I. The horizontal cells. Vision Res. 1972 Apr;12(4):573–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(72)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka K. Functional organization of catfish retina. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Jan;40(1):26–43. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K. Horizontal cell axons and axon terminals in goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Feb 15;159(4):503–520. doi: 10.1002/cne.901590405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K., Lightfoot D. O. Color-specific interconnections of cones and horizontal cells in the retina of the goldfish. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Feb 15;159(4):473–502. doi: 10.1002/cne.901590404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K. The structure and relationships of horizontal cells and photoreceptor-bipolar synaptic complexes in goldfish retina. Am J Anat. 1967 Sep;121(2):401–423. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Membrane properties of solitary horizontal cells isolated from goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:141–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Electrophysiological study of the mechanisms subserving color coding in the fish retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:559–566. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trisler G. D., Schneider M. D., Nirenberg M. A topographic gradient of molecules in retina can be used to identify neuron position. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Buskirk R., Dowling J. E. Isolated horizontal cells from carp retina demonstrate dopamine-dependent accumulation of cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7825–7829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliamy T., Rattray S., Mirsky R. Cell-surface antigen distinguishes sensory and autonomic peripheral neurones from central neurones. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):418–420. doi: 10.1038/291418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S., Dowling J. E. Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. II. Intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):339–355. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Hudson L., Jessell T. M., Yamamoto M. A monoclonal antibody defining antigenic determinants on subpopulations of mammalian neurones and Trypanosoma cruzi parasites. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):34–38. doi: 10.1038/296034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada E., Ishikawa T. The fine structure of the horizontal cells in some vertebrate retinae. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:383–392. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. A., Ling L., English L., Cantley L. Phosphorylation of the (Na,K)-ATPase by a plasma membrane-bound protein kinase in friend erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6567–6574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser B., McKay R. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish identifiable neurones in the leech. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):549–554. doi: 10.1038/289549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]