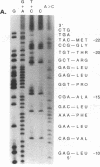
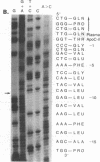
Abstract
Apolipoprotein (apo) C-II is a cofactor for lipoprotein lipase, the enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of triglycerides on plasma triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. The complete coding sequence of apoC-II mRNA has been determined from an apoC-II clone isolated from a human liver cDNA library. A 17-base-long synthetic oligonucleotide based on amino acid residues 5-10 of apoC-II was utilized as a hybridization probe to select recombinant plasmids containing the apoC-II sequence. Two thousand four hundred clones were screened and one apoC-II cDNA clone containing 500 bases was identified. DNA sequence analysis of this clone revealed a 101 amino acid C-II apolipoprotein containing a 22 amino acid signal peptide attached to the amino terminus of the 79 amino acid residue plasma apoC-II. The amino acid sequence of apoC-II determined by nucleic acid analysis is in agreement with the recently determined sequence of plasma apoC-II isolated from normal subjects. The determination of the complete cDNA sequence of apoC-II and the availability of a cDNA probe of apoC-II will facilitate our analysis of the biosynthesis and processing as well as the genomic organization of apoC-II in normal subjects and patients with dyslipoproteinemias characterized by hypertriglyceridemia.
Full text
PDF
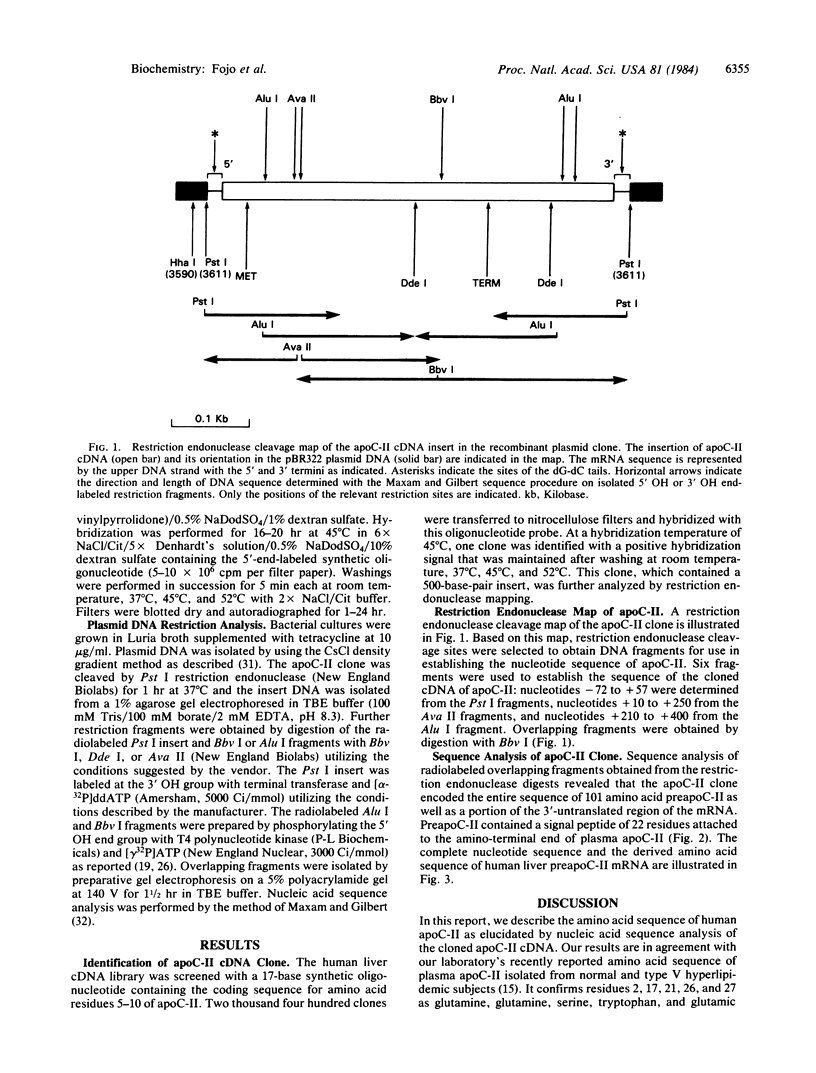


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austen B. M. Predicted secondary structures of amino-terminal extension sequences of secreted proteins. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaufuss M. C., Gordon J. I., Schonfeld G., Strauss A. W., Alpers D. H. Biosynthesis of apolipoprotein C-III in rat liver and small intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2452–2456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanovski D., Gregg R. E., Brewer H. B., Jr Tangier disease. In vitro conversion of proapo-A-ITangier to mature APO-A-ITangier. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6049–6051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge W. C., Little J. A., Steiner G., Chow A., Poapst M. Hypertriglyceridemia associated with deficiency of apolipoprotein C-II. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 8;298(23):1265–1273. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806082982301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catapano A. L., Mills G. L., Roma P., La Rosa M., Capurso A. Plasma lipids, lipoproteins and apoproteins in a case of apo C-II deficiency. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jun 15;130(3):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein C., Gordon J. I., Toscas K., Sims H. F., Strauss A. W., Scanu A. M. In vitro conversion of proapoprotein A-I to apoprotein A-I. Partial characterization of an extracellular enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11430–11433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T. On the metabolic conversion of human plasma very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):361–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo S. S., Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr, Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. The localization of the gene for apolipoprotein C-II to chromosome 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):687–693. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Assignment of the human gene for the low density lipoprotein receptor to chromosome 19: synteny of a receptor, a ligand, and a genetic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2826–2830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Bisgaier C. L., Sims H. F., Sachdev O. P., Glickman R. M., Strauss A. W. Biosynthesis of human preapolipoprotein A-IV. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):468–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Budelier K. A., Sims H. F., Edelstein C., Scanu A. M., Strauss A. W. Biosynthesis of human preproapolipoprotein A-II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14054–14059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Shore V. G., Shore B., Bier D. M. Role of specific glycopeptides of human serum lipoproteins in the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(4):595–600. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hospattankar A. V., Fairwell T., Ronan R., Brewer H. B., Jr Amino acid sequence of human plasma apolipoprotein C-II from normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):318–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Bruns G. A., Breslow J. L. Isolation and sequence of a human apolipoprotein CII cDNA clone and its use to isolate and map to human chromosome 19 the gene for apolipoprotein CII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2945–2949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Baker H. N., Gilliam E. B., Gotto A. M., Jr Primary structure of very low density apolipoprotein C-II of human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1942–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Herbert P., Lux S. E., Fredrickson D. S. A specific apoprotein activator for lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Brewer H. B., Jr Nucleotide sequence and the encoded amino acids of human apolipoprotein A-I mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):66–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Gray G., Brewer H. B., Jr cDNA cloning of human apoA-I: amino acid sequence of preproapoA-I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91824-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. E., Rao S. N., Alaupovic P., Noble N., Slack J., Brunzell J. D., Lewis B. Familial apolipoprotein CII deficiency: plasma lipoproteins and apolipoproteins in heterozygous and homozygous subjects and the effects of plasma infusion. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;11(1):69–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb01768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang S. A., Brousseau R., Hsiung H. M., Michniewicz J. J. Chemical synthesis of deoxyoligonucleotides by the modified triester method. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):610–620. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaisen B., Teisberg P., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr The locus for apolipoprotein E (apoE) is linked to the complement component C3 (C3) locus on chromosome 19 in man. Hum Genet. 1982;62(3):233–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00333526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Brewer H. B., Jr The plasma lipoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:253–337. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. C., Pownall H. J., Gotto A. M., Jr The plasma lipoproteins: structure and metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:751–757. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.003535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalenhoef A. F., Casparie A. F., Demacker P. N., Stouten J. T., Lutterman J. A., van 't Laar A. Combined deficiency of apolipoprotein C-II and lipoprotein lipase in familial hyperchylomicronemia. Metabolism. 1981 Sep;30(9):919–926. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura T., Sudo H., Ishikawa K., Yamamoto A. Familial type I hyperlipoproteinemia caused by apolipoprotein C-II deficiency. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Sep;34(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Karathanasis S. K., Keutmann H. T., Goldberger G., Breslow J. L. Intracellular and extracellular processing of human apolipoprotein A-I: secreted apolipoprotein A-I isoprotein 2 is a propeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Sande J. H., Kleppe K., Khorana H. G. Reversal of bacteriophage T4 induced polynucleotide kinase action. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5050–5055. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]