Abstract
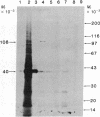
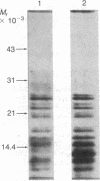
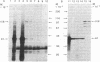
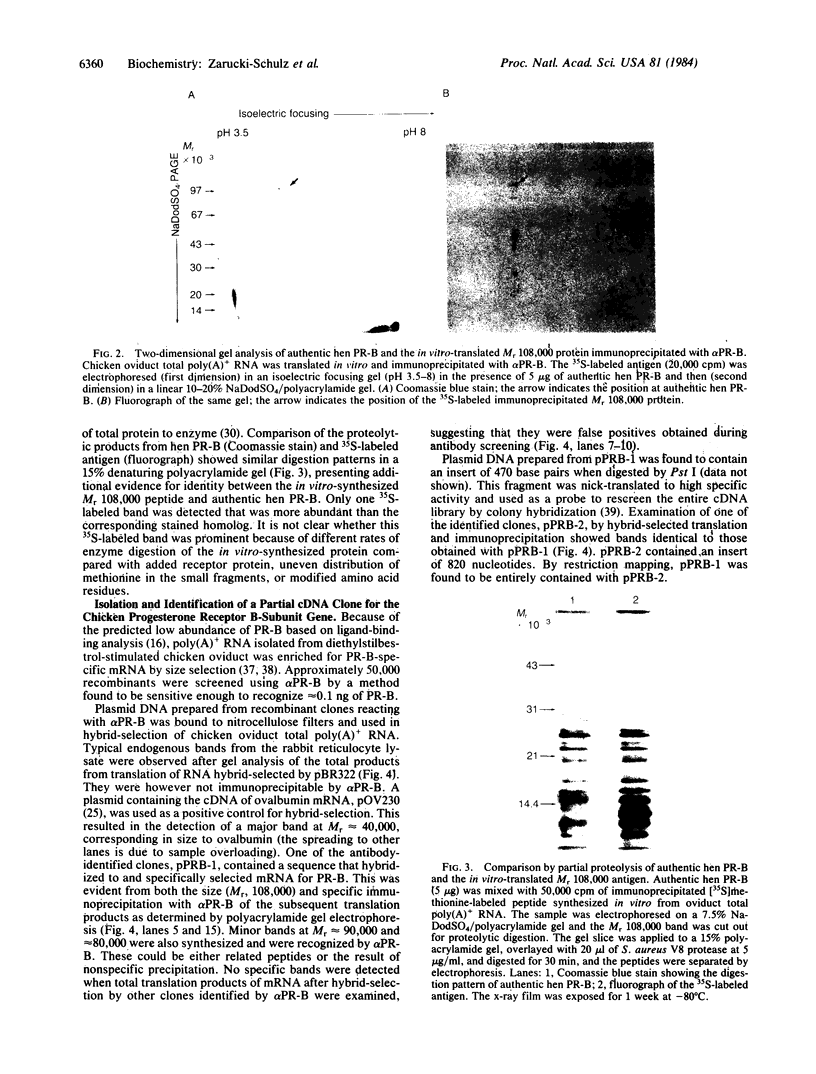
A cDNA for the chicken progesterone receptor B subunit antigen (Mr, 108,000) has been isolated from a cDNA library prepared from size-selected chicken oviduct poly(A)+RNA. A specific monoclonal antibody raised against hen progesterone receptor B subunit (alpha PR-B) was used to screen the library. Recombinant clones reacting with the antibody by virtue of antigen expression were used in hybrid-selected translation. A single clone, pPRB-1, hybridized specifically to a mRNA that yielded a Mr 108,000 protein when translated in vitro and which was immunoprecipitable by the alpha PR-B antibody. This cDNA represents a 470-base-pair portion of the PR-B nucleotide sequence. Additional clones have been subsequently isolated from the recombinant library using the insert from pPRB-1 as a specific probe. A mRNA size of approximately 3000 nucleotides was determined for the chicken progesterone receptor B subunit by formaldehyde/agarose gel electrophoresis and blot hybridization using pPRB-1 as a probe. Preliminary studies show that withdrawal of hormone from chickens treated chronically with estrogen leads to a dramatic decrease in the cellular RNA concentration of receptor B, indicating that target tissue levels of receptor B RNA are under hormonal control.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Newby R. F., Huet M. Glucorticoid resistance in murine lymphoma and thymoma lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4279–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd-Leinen P. A., Fournier D., Spelsberg T. C. Nonfunctioning progesterone receptors in the developed oviducts from estrogen-withdrawn immature chicks and in aged nonlaying hens. Endocrinology. 1982 Jul;111(1):30–36. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. DNA sequence preference of the progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A 5'-flanking sequence essential for progesterone regulation of an ovalbumin fusion gene. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):551–554. doi: 10.1038/305551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenette G., Dube J. Y., Tremblay R. R. Effect of hormone injections on levels of cytosolic receptors for estrogen, androgen and progesterone in dog prostate. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 Sep;17(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H., Pongs O. Localization of ecdysterone on polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2108–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Direct immunoassay for detecting Escherichia coli colonies that contain polypeptides encoded by cloned DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4520–4524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom E., Thi L., Atger M., Baulieu E. E. Mechanisms regulating the concentration and the conformation of progesterone receptor(s) in the uterus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6366–6374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. J., Harris S. E., Woo S. L., Robberson D. L., O'Malley B. W. The synthesis and properties of the complete complementary DNA transcript of ovalbumin mRNA. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 13;15(1):223–233. doi: 10.1021/bi00646a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. Chicken oviduct progesterone receptor: location of specific regions of high-affinity binding in cloned DNA fragments of hormone-responsive genes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K. L., Mauron A., Raese J., Barchas J. D., Kedes L. Genes for catecholamine biosynthesis: cloning by expression and identification of the cDNA for rat dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2161–2165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pageaux J. F., Laugier C., Pal D., Pacheco H. Analysis of progesterone receptor in the quail oviduct. Correlation between plasmatic estradiol and cytoplasmic progesterone receptor concentrations. J Steroid Biochem. 1983 Feb;18(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(83)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzio M. A., Pearson A. M. Improved resolution of myofibrillar proteins with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Woo S. L., Holder J. W., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Preparation and preliminary characterization of purified ovalbumin messenger RNA from the hen oviduct. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):69–78. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader W. T., Birnbaumer M. E., Hughes M. R., Weigel N. L., Grody W. W., O'Malley B. W. Studies on the structure and function of the chicken progesterone receptor. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1981;37:583–633. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571137-1.50017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley C. H., Tomkins G. M. Mechanisms of steroid resistance. Cell. 1974 Aug;2(4):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft D., O'Malley B. W. Target tissue receptors for progesterone: the influence of estrogen treatment. Endocrinology. 1972 Apr;90(4):1041–1045. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-4-1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel N. L., Tash J. S., Means A. R., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Phosphorylation of hen progesterone receptor by cAMP dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle D. J., Kilburn D. G., Warren R. A., Miller R. C., Jr Molecular cloning of a Cellulomonas fimi cellulose gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]