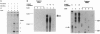Abstract
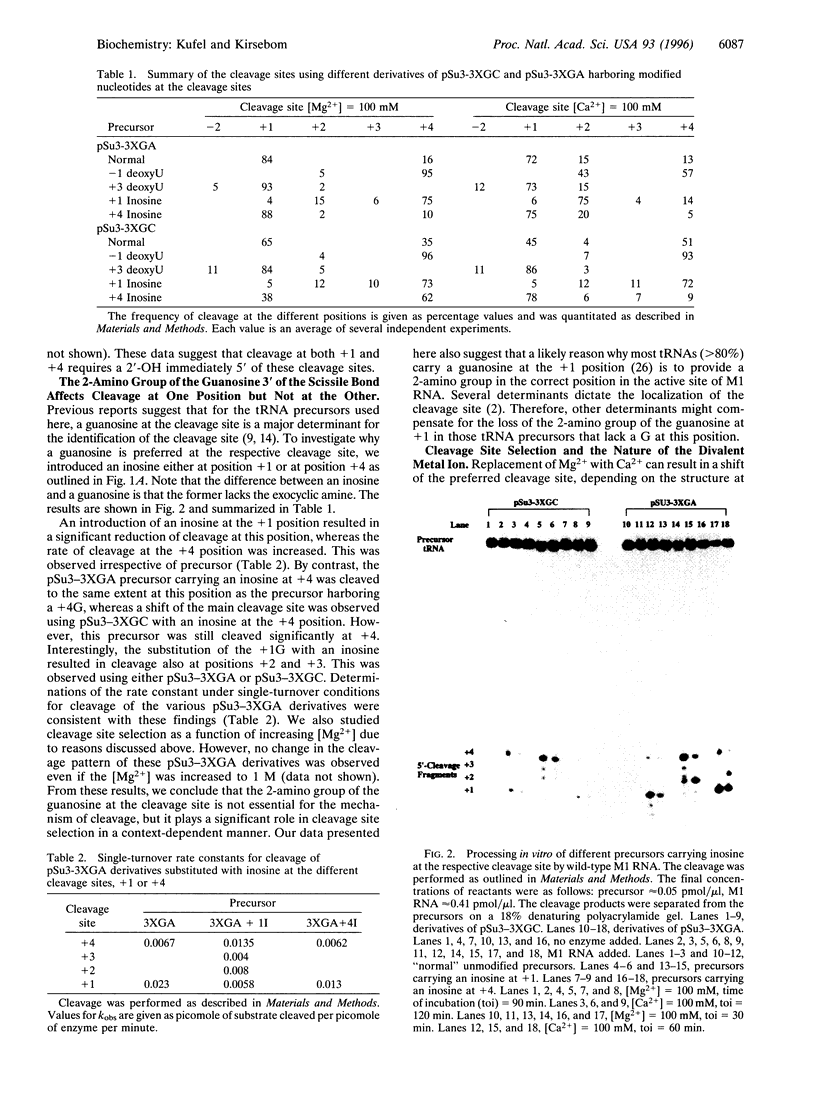
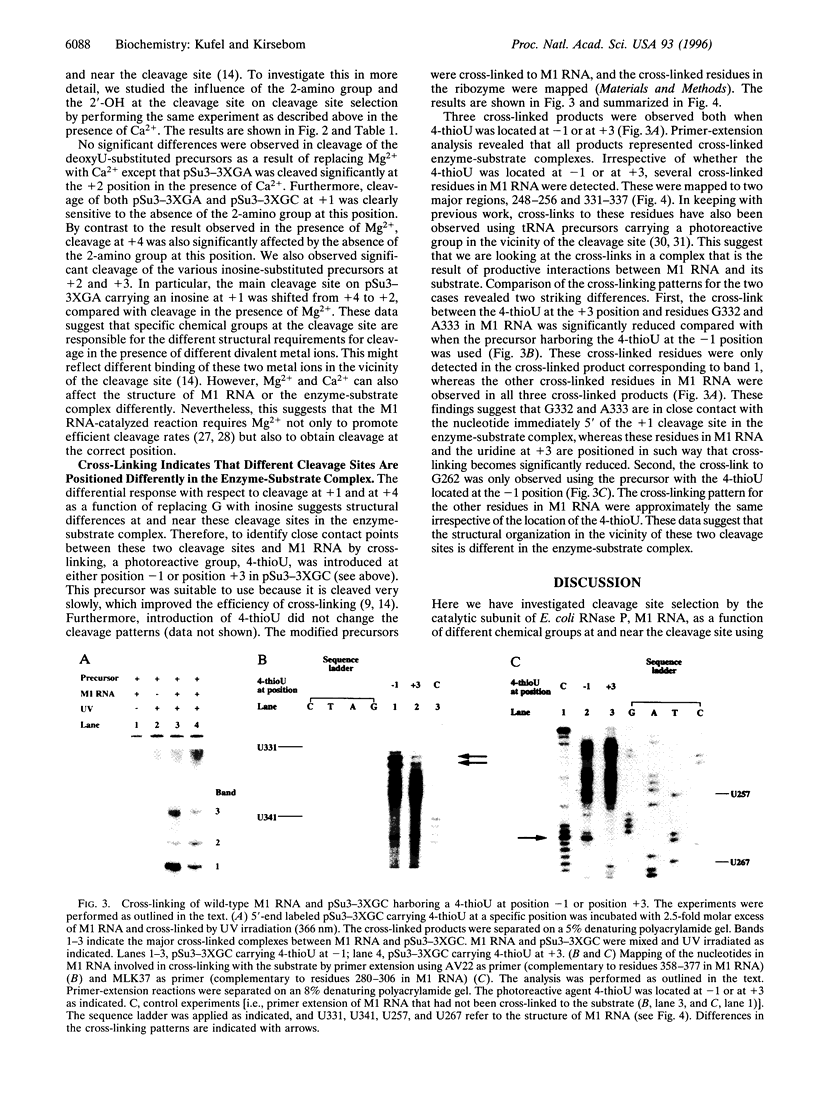
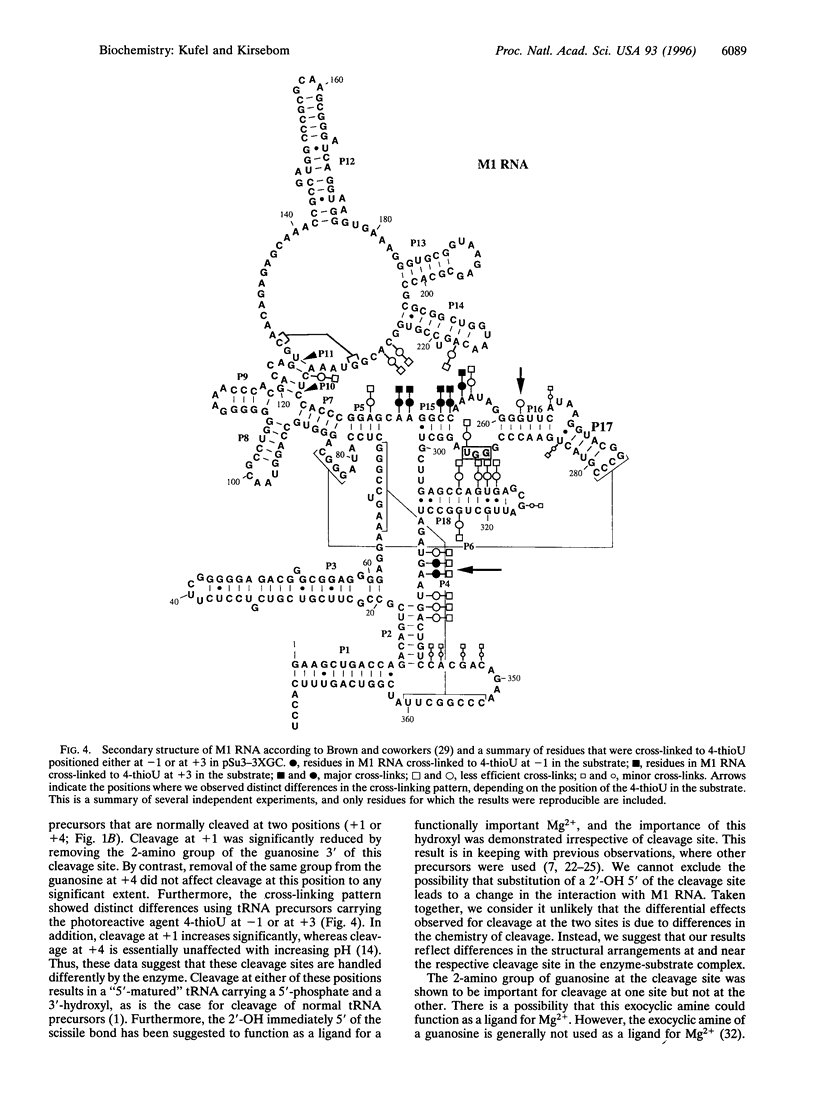
We have studied RNase P RNA (M1 RNA) cleavage of model tRNA precursors that are cleaved at two independent positions. Here we present data demonstrating that cleavage at both sites depends on the 2'-OH immediately 5' of the respective cleavage site. However, we show that the 2-amino group of a guanosine at the cleavage site plays a significant role in cleavage at one of these sites but not at the other. These data suggest that these two cleavage sites are handled differently by the ribozyme. This theory is supported by our finding that the cross-linking pattern between Ml RNA and tRNA precursors carrying 4-thioU showed distinct differences, depending on the location of the 4-thioU relative to the respective cleavage site. These findings lead us to suggest that different cleavage sites are aligned differently in the active site, possibly as a result of different binding modes of a substrate to M1 RNA. We discuss a model in which the interaction between the 3'-terminal "RCCA" motif (first three residues interact) of a tRNA precursor and M1 RNA plays a significant role in this process.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer M. F., Reilly R. M., McCorkle G. M., Hai T. Y., Altman S., RajBhandary U. L. The recognition by RNase P of precursor tRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2344–2351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Haas E. S., Gilbert D. G., Pace N. R. The Ribonuclease P database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep;22(17):3660–3662. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.17.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgin A. B., Pace N. R. Mapping the active site of ribonuclease P RNA using a substrate containing a photoaffinity agent. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4111–4118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Altman S. External guide sequences for an RNA enzyme. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):783–786. doi: 10.1126/science.1697102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur R. K., Krupp G. Modification interference approach to detect ribose moieties important for the optimal activity of a ribozyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):21–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. A physical assay for and kinetic analysis of the interactions between M1 RNA and tRNA precursor substrates. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 20;32(28):7152–7161. doi: 10.1021/bi00079a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Lumelsky N., Altman S. Specific interactions in RNA enzyme-substrate complexes. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1578–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2480641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
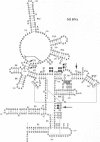
- Harris M. E., Nolan J. M., Malhotra A., Brown J. W., Harvey S. C., Pace N. R. Use of photoaffinity crosslinking and molecular modeling to analyze the global architecture of ribonuclease P RNA. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):3953–3963. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov S., Altman S. Site-specific cleavage by metal ion cofactors and inhibitors of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A. RNase P--a 'Scarlet Pimpernel'. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Aug;17(3):411–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_17030411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Svärd S. G. Base pairing between Escherichia coli RNase P RNA and its substrate. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4870–4876. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Svärd S. G. Identification of a region within M1 RNA of Escherichia coli RNase P important for the location of the cleavage site on a wild-type tRNA precursor. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 5;231(3):594–604. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsebom L. A., Svärd S. G. The kinetics and specificity of cleavage by RNase P is mainly dependent on the structure of the amino acid acceptor stem. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):425–432. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleineidam R. G., Pitulle C., Sproat B., Krupp G. Efficient cleavage of pre-tRNAs by E. coli RNAse P RNA requires the 2'-hydroxyl of the ribose at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1097–1101. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komine Y., Adachi T., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H. Genomic organization and physical mapping of the transfer RNA genes in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):579–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90224-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
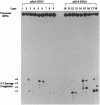
- Kufel J., Kirsebom L. A. Cleavage site selection by M1 RNA the catalytic subunit of Escherichia coli RNase P, is influenced by pH. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 16;244(5):511–521. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGrandeur T. E., Hüttenhofer A., Noller H. F., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic comparative chemical footprint analysis of the interaction between ribonuclease P RNA and tRNA. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):3945–3952. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. J., Sharp P. A. Site-specific modification of pre-mRNA: the 2'-hydroxyl groups at the splice sites. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):992–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1589782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh B. K., Pace N. R. Interaction of the 3'-end of tRNA with ribonuclease P RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4087–4094. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault J. P., Altman S. Important 2'-hydroxyl groups in model substrates for M1 RNA, the catalytic RNA subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 20;226(2):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90955-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Uhlenbeck O. C. Biochemical and physical characterization of an unmodified yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA transcribed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Burgin A. B., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Influence of metal ions on the ribonuclease P reaction. Distinguishing substrate binding from catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Pace N. R. Multiple magnesium ions in the ribonuclease P reaction mechanism. Biochemistry. 1993 May 25;32(20):5273–5281. doi: 10.1021/bi00071a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S., Misch A., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences and sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3011–3015. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svärd S. G., Kirsebom L. A. Determinants of Escherichia coli RNase P cleavage site selection: a detailed in vitro and in vivo analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):427–434. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svärd S. G., Kirsebom L. A. Several regions of a tRNA precursor determine the Escherichia coli RNase P cleavage site. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1019–1031. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90518-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vioque A., Arnez J., Altman S. Protein-RNA interactions in the RNase P holoenzyme from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):835–848. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90562-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altman S. Three-dimensional working model of M1 RNA, the catalytic RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5133–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]