Abstract
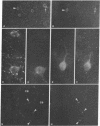
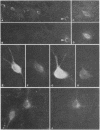
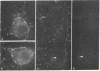
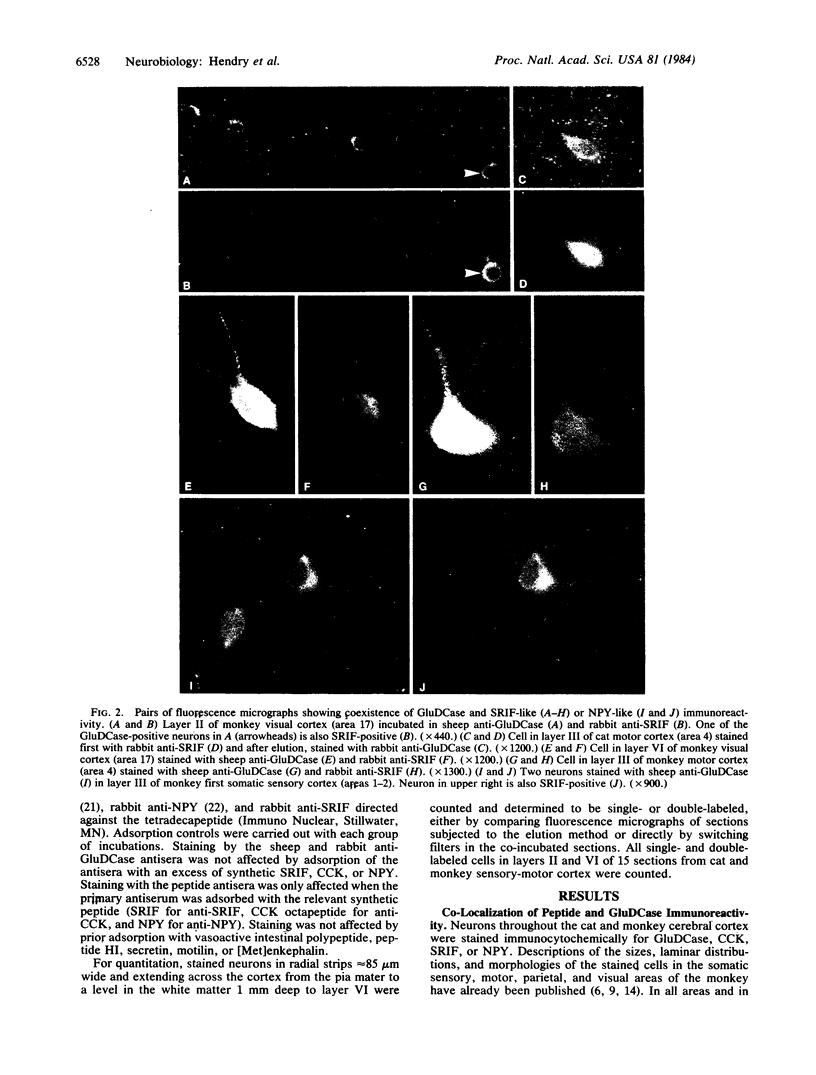
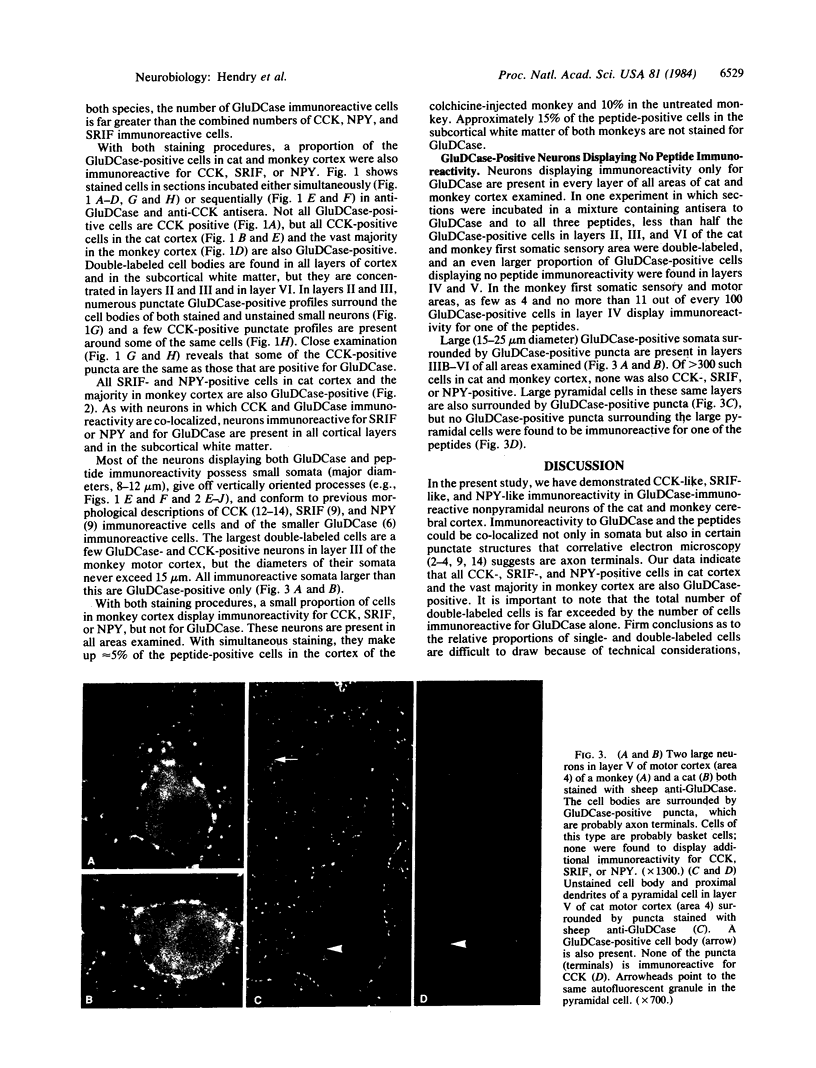
Neurons in the cat and monkey cerebral cortex were stained immunocytochemically for glutamic acid decarboxylase (GluDCase; L-glutamate 1-carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.15), somatostatin (SRIF), neuropeptide Y (NPY), and cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK). In all areas of cortex examined (somatic sensory, motor, parietal and visual areas), neurons displaying immunoreactivity for each of these molecules were nonpyramidal cells. Co-localization of GluDCase immunoreactivity with peptide immunoreactivity in the same cells was demonstrated by (i) the antibody elution method, staining the same cells by immunofluorescence, first for a peptide and then for GluDCase; (ii) double staining of the same sections with sheep anti-GluDCase and rabbit anti-peptide antisera, the bound antibodies being localized by rhodamine-conjugated donkey anti-sheep and fluorescein-conjugated swine anti-rabbit secondary antisera. With both procedures, cell bodies immunoreactive for GluDCase and for each of the peptides were found in all areas of cortex examined. With double labeling on single sections, it was found that all CCK-, SRIF-, and NPY-immunoreactive cells in cat cortex and 90%-95% in monkey cortex are also GluDCase positive. Many more cells, however, are immunoreactive for GluDCase alone. GluDCase was co-localized with CCK, SRIF, or NPY not only in cell somata, but also in small punctate structures, which are likely to be axon terminals. From the data gained in previous electron microscopic studies, we postulate that neurons displaying GluDCase- and CCK-like immunoreactivity are a class separate from those displaying GluDCase- and SRIF-like immunoreactivity. NPY, however, is co-localized with SRIF immunoreactivity. These results imply that classes of cortical interneuron contain a conventional neurotransmitter (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and a neuromodulator (one of the peptides).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beinfeld M. C., Meyer D. K., Eskay R. L., Jensen R. T., Brownstein M. J. The distribution of cholecystokinin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat as determined by radioimmunoassay. Brain Res. 1981 May 11;212(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalán R. E., Martínez A. M., Aragonés M. D. Inhibition of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by somatostatin in slices of mouse brain: dependence on extracellular calcium. Neuropharmacology. 1983 May;22(5):641–645. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfs J. R., Dichter M. A. Effects of somatostatin on mammalian cortical neurons in culture: physiological actions and unusual dose response characteristics. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1176–1188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01176.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dokas L. A., Zwiers H., Coy D. H., Gispen W. H. Somatostatin and analogs inhibit endogenous synaptic plasma membrane protein phosphorylation in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 25;88(2-3):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Hunt S. P., Rehfeld J. F., Golterman N., Fahrenkrug J. Cholecystokinin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the mammalian CNS: distribution and possible physiological roles. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1980;22:63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Lee C. M., Rehfeld J. F. Cholecystokinin octapeptide: vesicular localization and calcium dependent release from rat brain in vitro. Life Sci. 1980 Jun 23;26(25):2157–2163. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90603-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Lindvall O. Distribution of putative neurotransmitters in the neocortex. Neuroscience. 1979;4(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Martin K. A., Smith A. D., Somogyi P. Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Dec 10;221(3):263–278. doi: 10.1002/cne.902210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson A. E., Hunt S. P., Wu J. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase in monkey striate cortex. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):605–607. doi: 10.1038/292605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., Beinfeld M. C. Cholecystokinin-immunoreactive neurons in rat and monkey cerebral cortex make symmetric synapses and have intimate associations with blood vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Crawford G. D., Barber R. P., Salvaterra P. M., Vaughn J. E. Organization and morphological characteristics of cholinergic neurons: an immunocytochemical study with a monoclonal antibody to choline acetyltransferase. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 25;266(1):97–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., Vaughn J. E. Morphological diversity of immunocytochemically identified GABA neurons in the monkey sensory-motor cortex. J Neurocytol. 1983 Aug;12(4):617–638. doi: 10.1007/BF01181527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Iversen S. D., Bloom F., Douglas C., Brown M., Vale W. Calcium-dependent release of somatostatin and neurotensin from rat brain in vitro. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):161–163. doi: 10.1038/273161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G. Varieties and distribution of non-pyramidal cells in the somatic sensory cortex of the squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Mar 15;160(2):205–267. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S. Electrophysiology of peptides in the central nervous system. Br Med Bull. 1982 Sep;38(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Padilla M. Origin of the pericellular baskets of the pyramidal cells of the human motor cortex: a Golgi study. Brain Res. 1969 Aug;14(3):633–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Parnavelas J. G., Karamanlidis A. N., Brecha N. The morphology and distribution of peptide-containing neurons in the adult and developing visual cortex of the rat. II. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. J Neurocytol. 1982 Oct;11(5):825–837. doi: 10.1007/BF01153521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Parnavelas J. G., Karamanlidis A. N., Rosenquist G., Brecha N. The morphology and distribution of peptide-containing neurons in the adult and developing visual cortex of the rat. III. Cholecystokinin. J Neurocytol. 1982 Dec;11(6):881–895. doi: 10.1007/BF01148306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel W. H., Schmechel D. E., Tappaz M. L., Kopin I. J. Production of a specific antiserum to rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase by injection of an antigen-antibody complex. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2689–2700. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A., Miller M., Kimerer L. M. Cholecystokinin-like immunoreactive neurons in rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience. 1983 Mar;8(3):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A., Proskauer C. C., Ribak C. E. Chandelier cells in rat visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Apr 20;206(4):397–416. doi: 10.1002/cne.902060408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Kirkpatrick J. R. The actions of motilin, luteinizing hormone releasing hormone, cholecystokinin, somatostatin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and other peptides on rat cerebral cortical neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;58(6):612–623. doi: 10.1139/y80-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E. Aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate neurons in the visual cortex of rats contain glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurocytol. 1978 Aug;7(4):461–478. doi: 10.1007/BF01173991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Moghimzadeh E., Håkanson R., Ekelund M., Emson P. Nerve fibers in the gut and pancreas of the rat displaying neuropeptide-Y immunoreactivity. Intrinsic and extrinsic origin. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;230(3):487–493. doi: 10.1007/BF00216194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramu G., Pillez A., Leonardelli J. An efficient method of antibody elution for the successive or simultaneous localization of two antigens by immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Apr;26(4):322–324. doi: 10.1177/26.4.207771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Johansson O., Hökfelt T., Meyerson B., Sachs C., Elde R. P., Terenius L., Kimmel J. Neuropeptide coexistence in human cortical neurones. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):65–67. doi: 10.1038/298065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Skirboll L., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Lundberg J. M., Elde R. P., Terenius L., Kimmel J. Coexistence of somatostatin- and avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP)-like immunoreactivity in some forebrain neurons. Neuroscience. 1982 Feb;7(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]