Abstract
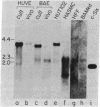
Recognition that the sis gene codes for a protein homologous with at least one of the two chains of platelet-derived growth factor has made it possible to directly assess transcriptional expression of platelet-derived growth factor both in cultured cells and in tissue obtained in vivo. We have found that a 3.7-kilobase RNA homologous to the sis gene is expressed at moderate levels in cultured human and bovine endothelial cells, at low levels in in vivo endothelium from human umbilical vein, and at very low levels in bovine aortic endothelium in vivo. This RNA migrates at the same rate as the previously reported sis band in the HUT 102 human T-cell lymphoma line. This band is not found in RNA extracted from freshly obtained bovine aortic media or from human foreskin fibroblasts or cultured fetal human aortic smooth muscle cells. Our in vitro results suggest that the sis gene is responsible for at least part of the platelet-derived growth factor-like mitogenic activity secreted by cultured endothelial cells and indicate that the sis gene is readily activated in endothelial cells during the transition from in vivo conditions to in vitro growth as a monolayer on plastic. Expression of the sis gene by endothelium in vivo raises the possibility that platelet-derived growth factor has a role in the development of the vascular system in the young animal and in the maintenance of the normal vascular system in the adult.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Vogel A., Ross R. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules and reduced expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptors accompany transformation by a wide spectrum of agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCorleto P. E., Bowen-Pope D. F. Cultured endothelial cells produce a platelet-derived growth factor-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCorleto P. E., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., Ross R. Biochemical properties of the endothelium-derived growth factor: comparison to other growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Mar;114(3):339–345. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Devare S. G., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A., Antoniades H. N. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.6304883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eva A., Robbins K. C., Andersen P. R., Srinivasan A., Tronick S. R., Reddy E. P., Ellmore N. W., Galen A. T., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Cellular genes analogous to retroviral onc genes are transcribed in human tumour cells. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):116–119. doi: 10.1038/295116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M. Technique for cloning bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1983 May;19(5):394–402. doi: 10.1007/BF02619556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek C., DiCorleto P., Ross R., Schwartz S. M. An endothelial cell-derived growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):467–472. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Chang T., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor is a chemoattractant for vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Nov;113(2):261–266. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Specific receptors for platelet-derived growth factor on cells derived from connective tissue and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs S. F., Guo C., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F. Human-proto-oncogene nucleotide sequences corresponding to the transforming region of simian sarcoma virus. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.6318322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan R. M., Moss N. S., Benditt E. P. Human arterial wall cells and tissues in culture. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21A:153–166. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60764-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M. Selection and characterization of bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1978 Dec;14(12):966–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02616210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H., Grotendorst G., Seppä S., Schiffmann E., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor in chemotactic for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):584–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Scrace G. T., Whittle N., Stroobant P., Johnsson A., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):35–39. doi: 10.1038/304035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]