Abstract
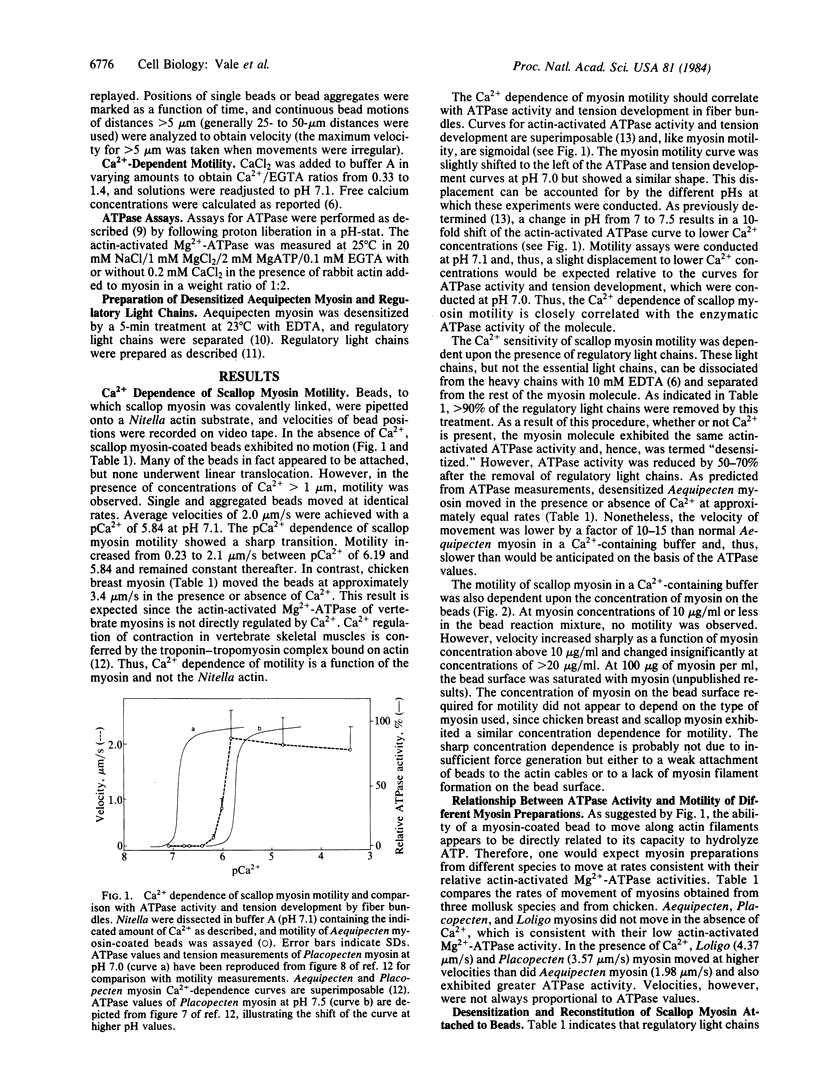
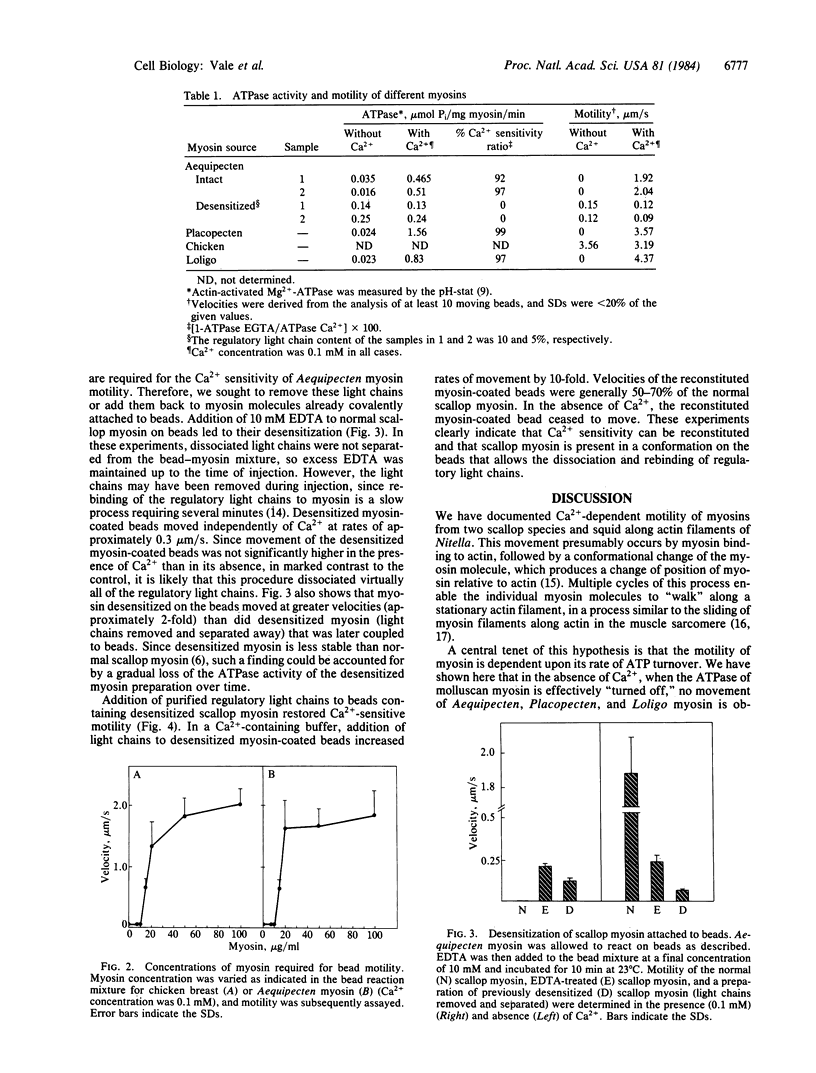
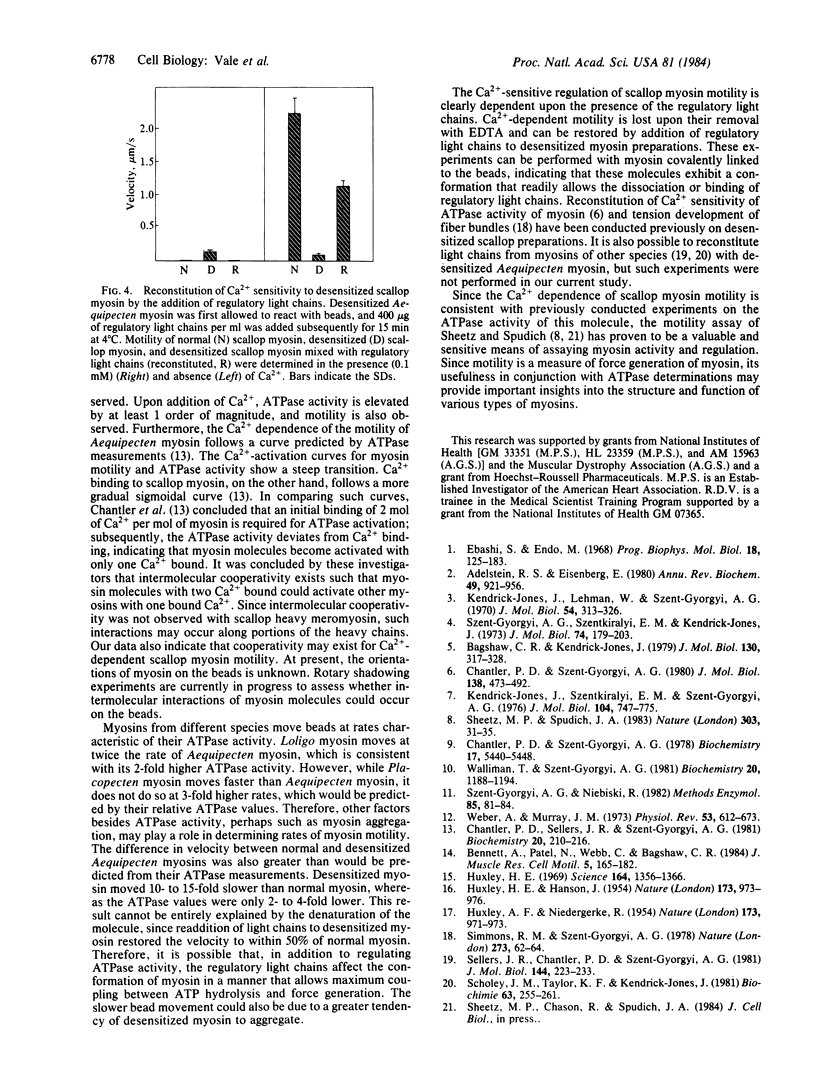
In order to determine if Ca2+ regulates scallop myosin movement on actin, we have measured motility of scallop myosin along actin filaments using a direct visual assay. This procedure consists of covalently linking myosin to 1-micron beads and pipetting them onto a parallel array of actin filaments located on the cytoplasmic face of a Nitella internodal cell. In the absence of Ca2+, scallop myosin-coated beads exhibit no directed motion; however, in the presence of pCa2+ of greater than 5.84, these beads undergo linear translocations with average velocities of 2.0 micron/s. This Ca2+ -sensitive motility requires the presence of regulatory light chains on the scallop myosin. Removal of regulatory light chains with 10 mM EDTA produces a "desensitized" myosin, no longer sensitive to Ca2+, which moves at rates of 0.09-0.3 micron in the presence or absence of Ca2+. Readdition of regulatory light chains to preparations of desensitized myosin once again confers Ca2+-sensitive motility. The Ca2+ dependence of scallop-myosin motility shows a sharp transition, consistent with the Ca2+ activation sensitivity of the actin-activated ATPase. Furthermore, relative rates of movement of calcium-regulated myosins from various molluscan species are consistent with their respective rates of ATP hydrolysis. Thus, myosin motility along actin filaments provides a sensitive and direct assay of myosin activity and is suitable for studying myosin regulation.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshaw C. R., Kendrick-Jones J. Characterization of homologous divalent metal ion binding sites of vertebrate and molluscan myosins using electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1979 May 25;130(3):317–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90544-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. J., Patel N., Wells C., Bagshaw C. R. 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulphonate, a fluorescent probe for the regulatory light chain binding site of scallop myosin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Apr;5(2):165–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00712154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler P. D., Sellers J. R., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Cooperativity in scallop myosin. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):210–216. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler P. D., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulatory light-chains and scallop myosin. Full dissociation, reversibility and co-operative effects. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):473–492. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler P. D., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Spectroscopic studies on invertebrate myosins and light chains. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5440–5448. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., NIEDERGERKE R. Structural changes in muscle during contraction; interference microscopy of living muscle fibres. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):971–973. doi: 10.1038/173971a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H., HANSON J. Changes in the cross-striations of muscle during contraction and stretch and their structural interpretation. Nature. 1954 May 22;173(4412):973–976. doi: 10.1038/173973a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J., Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulation in molluscan muscles. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J., Szentkiralyi E. M., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulatory light chains in myosins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 15;104(4):747–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholey J. M., Taylor K. A., Kendrick-Jones J. The role of myosin light chains in regulating actin-myosin interaction. Biochimie. 1981 Apr;63(4):255–271. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(81)80115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Chantler P. D., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Hybrid formation between scallop myofibrils and foreign regulatory light-chains. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):223–245. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Spudich J. A. Movement of myosin-coated fluorescent beads on actin cables in vitro. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):31–35. doi: 10.1038/303031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons R. M., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Reversible loss of calcium control of tension in scallop striated muscle associated with the removal of regulatory light chains. Nature. 1978 May 4;273(5657):62–64. doi: 10.1038/273062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Niebieski R. Preparation of light chains from scallop myosin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Szentkiralyi E. M., Kendrick-Jonas J. The light chains of scallop myosin as regulatory subunits. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):179–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallimann T., Szent-Györgyi A. G. An immunological approach to myosin light-chain function in thick filament linked regulation. 2. Effects of anti-scallop myosin light-chain antibodies. Possible regulatory role for the essential light chain. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1188–1197. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Murray J. M. Molecular control mechanisms in muscle contraction. Physiol Rev. 1973 Jul;53(3):612–673. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.3.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



