Abstract
NMR images of preselected chemically shifted species can be obtained by selective irradiation of the remainder of the NMR chemical shift spectrum prior to application of a conventional NMR imaging sequence. The chemical-selective irradiation consists of narrow-bandwidth pi/2 or saturation radio-frequency pulses applied in the absence of imaging gradients. The technique permits substantial reductions in scan and reconstruction times over standard three- and four-dimensional Fourier transform chemical-shift-imaging methods, when images of few spectral peaks are desired. It is also suitable for the elimination of chemical shift artifacts in conventional high-field NMR imaging. In vivo applications of the technique to the head and limbs in a 1.5-T magnetic field yield 1H H2O and -CH2-images, with little detectable -CH2- in muscle and brain.
Full text
PDF
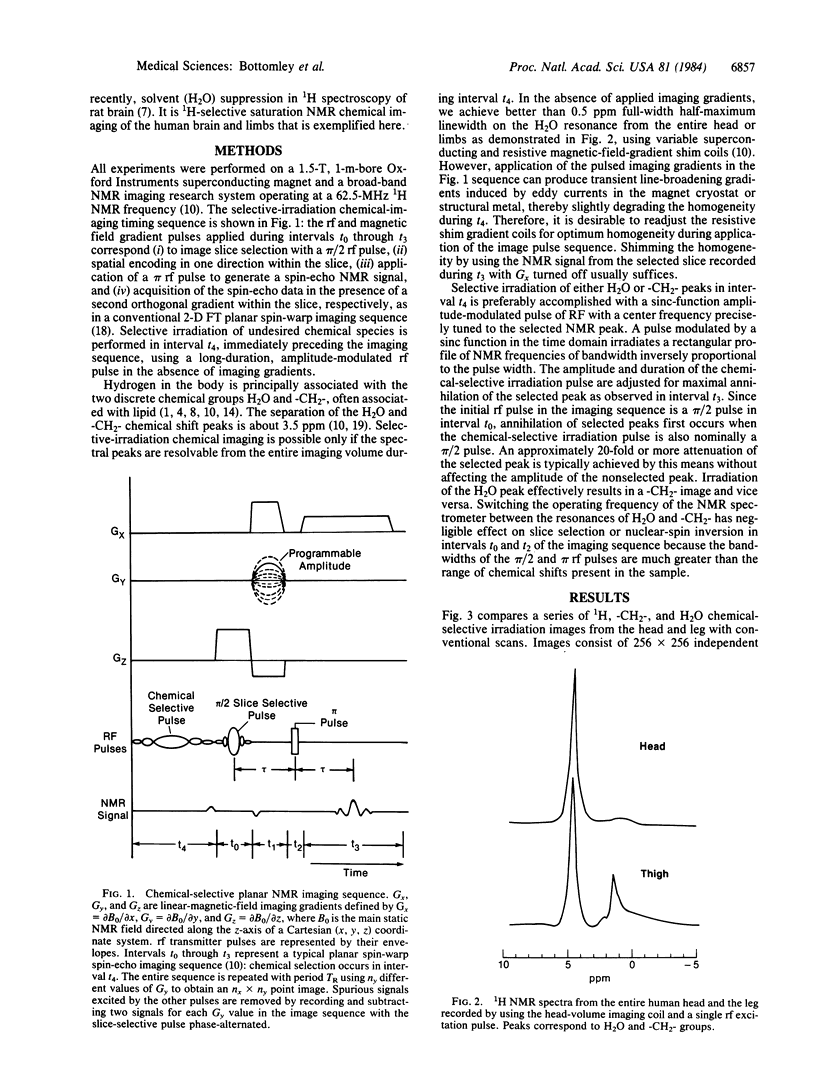


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behar K. L., den Hollander J. A., Stromski M. E., Ogino T., Shulman R. G., Petroff O. A., Prichard J. W. High-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of cerebral hypoxia in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4945–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Edelstein W. A., Hart H. R., Schenck J. F., Smith L. S. Spatial localization in 31P and 13C NMR spectroscopy in vivo using surface coils. Magn Reson Med. 1984 Sep;1(3):410–413. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910010311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Edelstein W. A. Power deposition in whole-body NMR imaging. Med Phys. 1981 Jul-Aug;8(4):510–512. doi: 10.1118/1.595000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Foster T. H., Argersinger R. E., Pfeifer L. M. A review of normal tissue hydrogen NMR relaxation times and relaxation mechanisms from 1-100 MHz: dependence on tissue type, NMR frequency, temperature, species, excision, and age. Med Phys. 1984 Jul-Aug;11(4):425–448. doi: 10.1118/1.595535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Hart H. R., Edelstein W. A., Schenck J. F., Smith L. S., Leue W. M., Mueller O. M., Redington R. W. NMR imaging/spectroscopy system to study both anatomy and metabolism. Lancet. 1983 Jul 30;2(8344):273–274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Hart H. R., Jr, Edelstein W. A., Schenck J. F., Smith L. S., Leue W. M., Mueller O. M., Redington R. W. Anatomy and metabolism of the normal human brain studied by magnetic resonance at 1.5 Tesla. Radiology. 1984 Feb;150(2):441–446. doi: 10.1148/radiology.150.2.6691099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A. In-vivo soft tissue NMR imaging of the rat thorax and abdomen. Experientia. 1981 Jul 15;37(7):768–770. doi: 10.1007/BF01967970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A. NMR imaging techniques and applications: a review. Rev Sci Instrum. 1982 Sep;53(9):1319–1337. doi: 10.1063/1.1137180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. R., Kincaid B. M., Ugurbil K. NMR chemical shift imaging in three dimensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3523–3526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cady E. B., Costello A. M., Dawson M. J., Delpy D. T., Hope P. L., Reynolds E. O., Tofts P. S., Wilkie D. R. Non-invasive investigation of cerebral metabolism in newborn infants by phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Lancet. 1983 May 14;1(8333):1059–1062. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91906-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein W. A., Bottomley P. A., Hart H. R., Smith L. S. Signal, noise, and contrast in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983 Jun;7(3):391–401. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198306000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Dawson M. J., Wilkie D. R., Gordon R. E., Shaw D. Clinical use of nuclear magnetic resonance in the investigation of myopathy. Lancet. 1982 Mar 27;1(8274):725–731. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92635-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurohr K. J., Barrett E. J., Shulman R. G. In vivo carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of heart metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally R. L., Hollis D. P. Adenosine triphosphate compartmentation in living hearts: a phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance saturation transfer study. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3642–3646. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard J. W., Alger J. R., Behar K. L., Petroff O. A., Shulman R. G. Cerebral metabolic studies in vivo by 31P NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2748–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykett I. L., Rosen B. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance: in vivo proton chemical shift imaging. Work in progress. Radiology. 1983 Oct;149(1):197–201. doi: 10.1148/radiology.149.1.6310682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radda G. K., Bore P. J., Gadian D. G., Ross B. D., Styles P., Taylor D. J., Morgan-Hughes J. 31P NMR examination of two patients with NADH-CoQ reductase deficiency. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):608–609. doi: 10.1038/295608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. D., Radda G. K., Gadian D. G., Rocker G., Esiri M., Falconer-Smith J. Examination of a case of suspected McArdle's syndrome by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. N Engl J Med. 1981 May 28;304(22):1338–1342. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198105283042206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]