Abstract
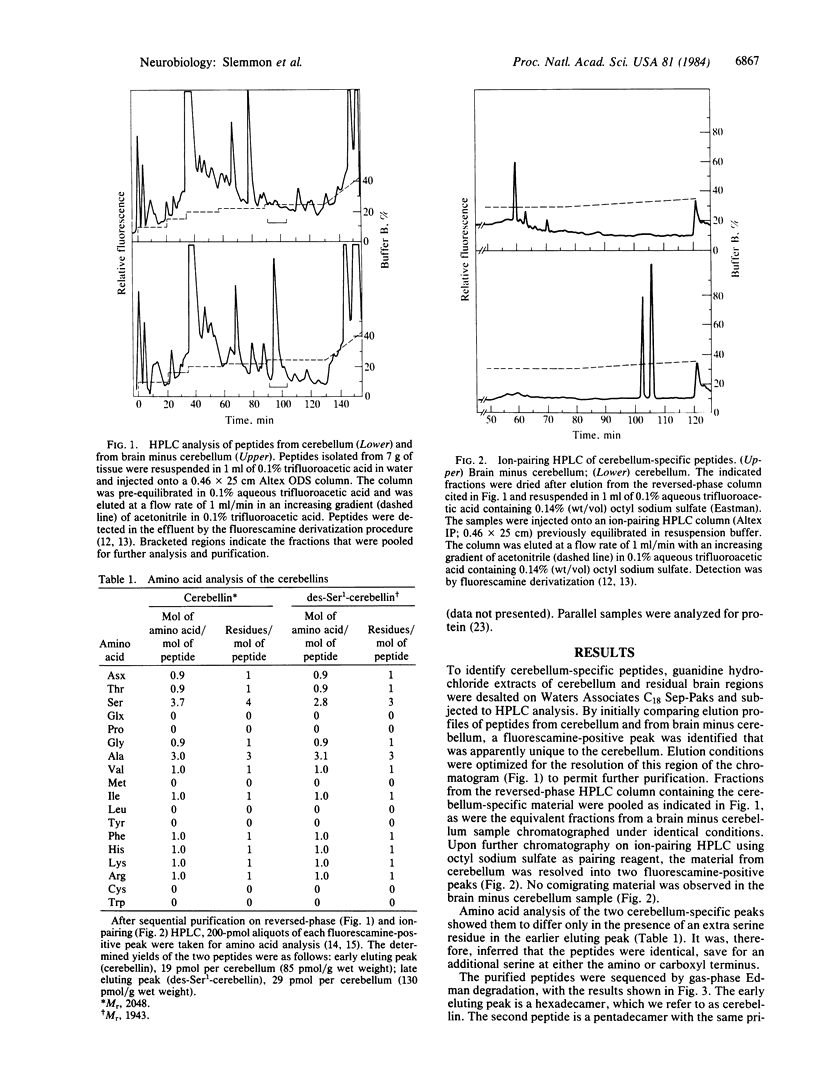
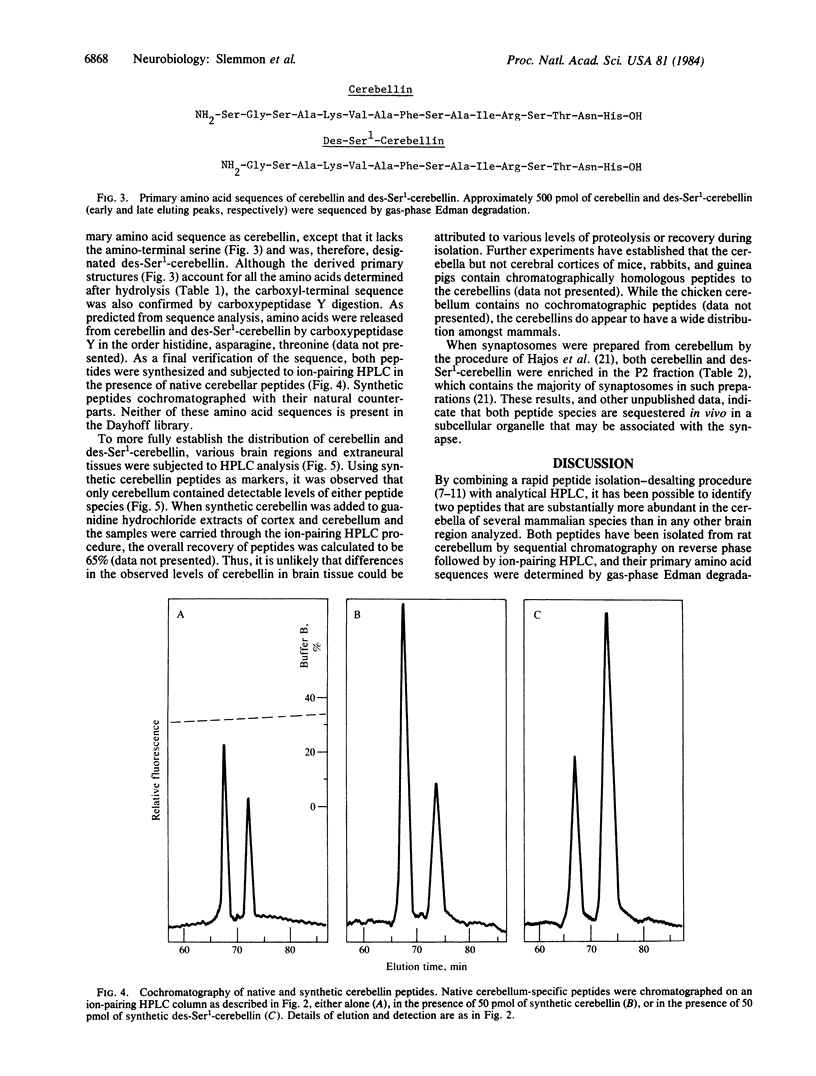
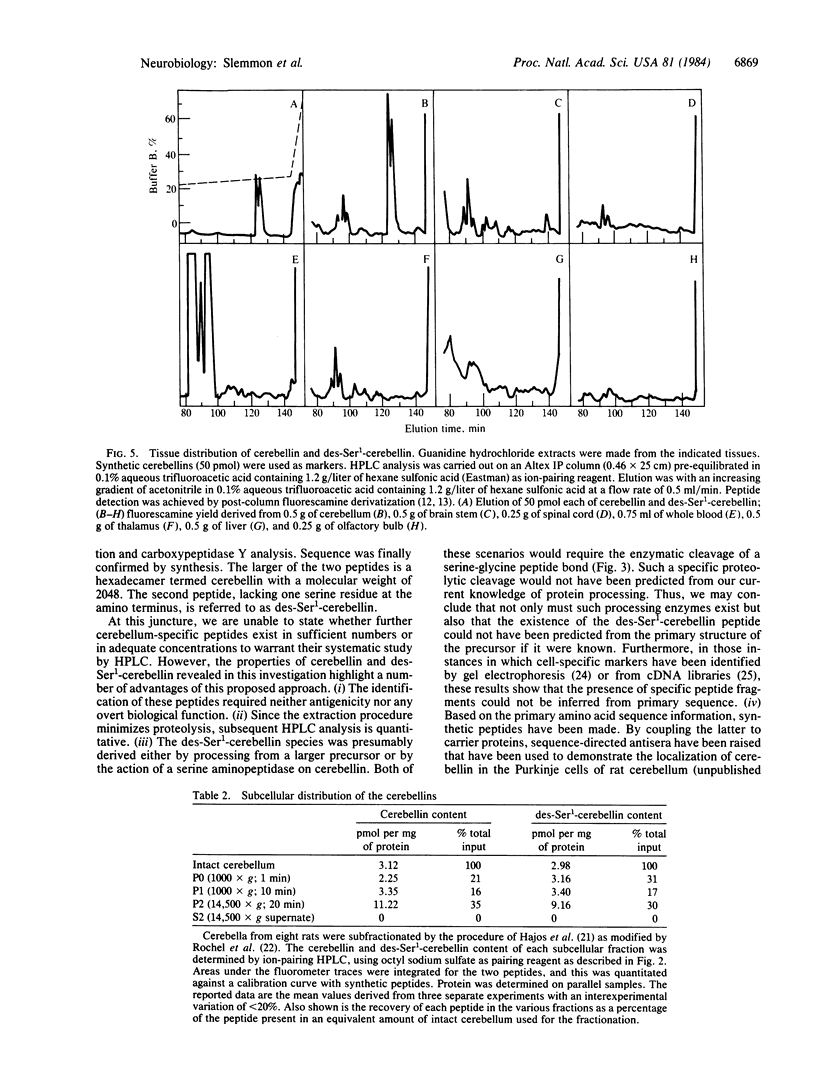
By comparing the HPLC elution profiles of peptides isolated from different brain regions, two cerebellum-specific species have been identified. The peptides were isolated by sequential chromatography on reverse phase, followed by ion-pairing HPLC using alkane sulfates as pairing reagents. The sequences of both peptides have been determined by gasphase Edman degradation and carboxypeptidase Y analysis and were confirmed by synthesis. The larger peptide, termed cerebellin, is a hexadecamer of primary amino acid sequence NH2-Ser-Gly-Ser-Ala-Lys-Val-Ala-Phe-Ser-Ala-Ile-Arg-Ser-Thr-Asn-His- OH. The second peptide is a pentadecamer with a primary sequence identical to residues 2-16 of cerebellin, the nomenclature of which is des-Ser1-cerebellin. Subcellular fractionation of cerebellum followed by ion-pairing HPLC analysis shows that both cerebellin and des-Ser1-cerebellin are enriched between 2.5- and 4-fold in the P2 crude synaptosomal fraction, suggesting their sequestration in some subcellular particle in vivo.
Keywords: endogenous peptide analysis, neural markers, synaptosomes
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J. Monoclonal antibodies which recognize different cell types in the rat retina. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):231–235. doi: 10.1038/286231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Stone J., Udenfriend S. Automatic Monitoring of primary amines in preparative column effluents with fluorescamine. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):438–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Hempstead J. L., Morgan J. I. Production and characterization of antibodies to thymosin beta 4. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajós F., Tapia R., Wilkin G., Johnson A. L., Balázs R. Subcellular fractionation of rat cerebellum: an electron microscopic and biochemical investigation. I. Preservation of large fragments of the cerebellar glomeruli. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 19;70(2):261–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Davoust S., Horecker B. L. Isolation of peptides from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91969-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Davoust S., Horecker B. L. Thymosins beta 8 and beta 9: two new peptides isolated from calf thymus homologous to thymosin beta 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1708–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Xu G. J., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Thymosin beta 4: a ubiquitous peptide in rat and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D., Yuan P. M., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. II. Separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoin derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography on octadecylsilane supports. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Direct microsequence analysis of polypeptides using an improved sequenator, a nonprotein carrier (polybrene), and high pressure liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2124–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny C., Moschera J. A., Stein S. Purification of human fibroblast interferon produced in the absence of serum by Cibacron Blue F3GA-Agarose and high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):435–447. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)78154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis F. L. A brain protein unique to the olfactory bulb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1221–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D., Hockfield S. J. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish antigenically discrete neuronal types in the vertebrate central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6747–6751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Fields K. L., Hakomori S. I., Mirsky R., Pruss R. M., Winter J. Cell-type-specific markers for distinguishing and studying neurons and the major classes of glial cells in culture. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):283–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90851-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochel S., Lichtstein D., Blume A. J., Margolis F. L. Membrane potential of olfactory bulb synaptosomal fractions: characterization with the lipophilic cation tetraphenylphosphonium. J Neurosci. 1981 Oct;1(10):1180–1192. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-10-01180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Hawke D., Jones B. N. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. III. Artifacts and the effects of impurities on analysis. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):312–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Brink L. Amino acid analysis of proteins and peptides at the picomole level: the fluorescamine amino acid analyzer. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):20–25. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Böhlen P., Stone J., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Amino acid analysis with fluorescamine at the picomole level. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):202–212. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Milner R. J., Shinnick T. M., Bloom F. E. Identifying the protein products of brain-specific genes with antibodies to chemically synthesized peptides. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):671–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trisler G. D., Schneider M. D., Nirenberg M. A topographic gradient of molecules in retina can be used to identify neuron position. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. J., Hannappel E., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Synthesis of thymosin beta 4 by peritoneal macrophages and adherent spleen cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4006–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



