Abstract
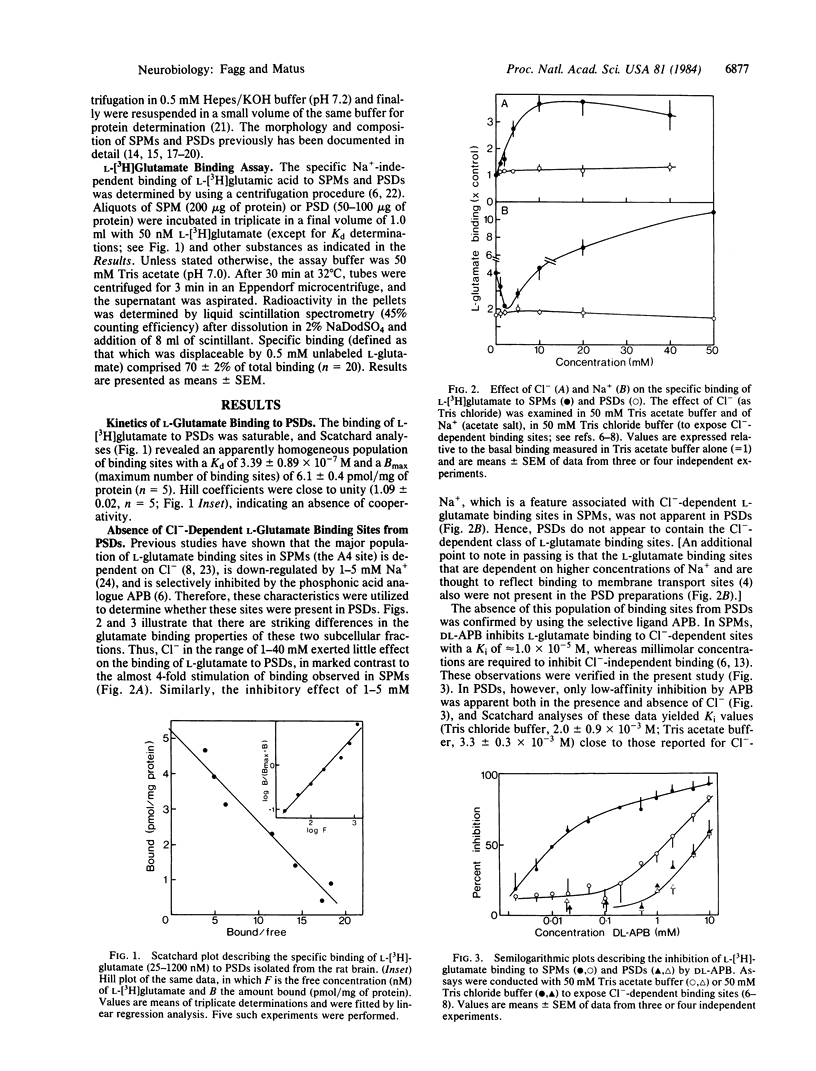
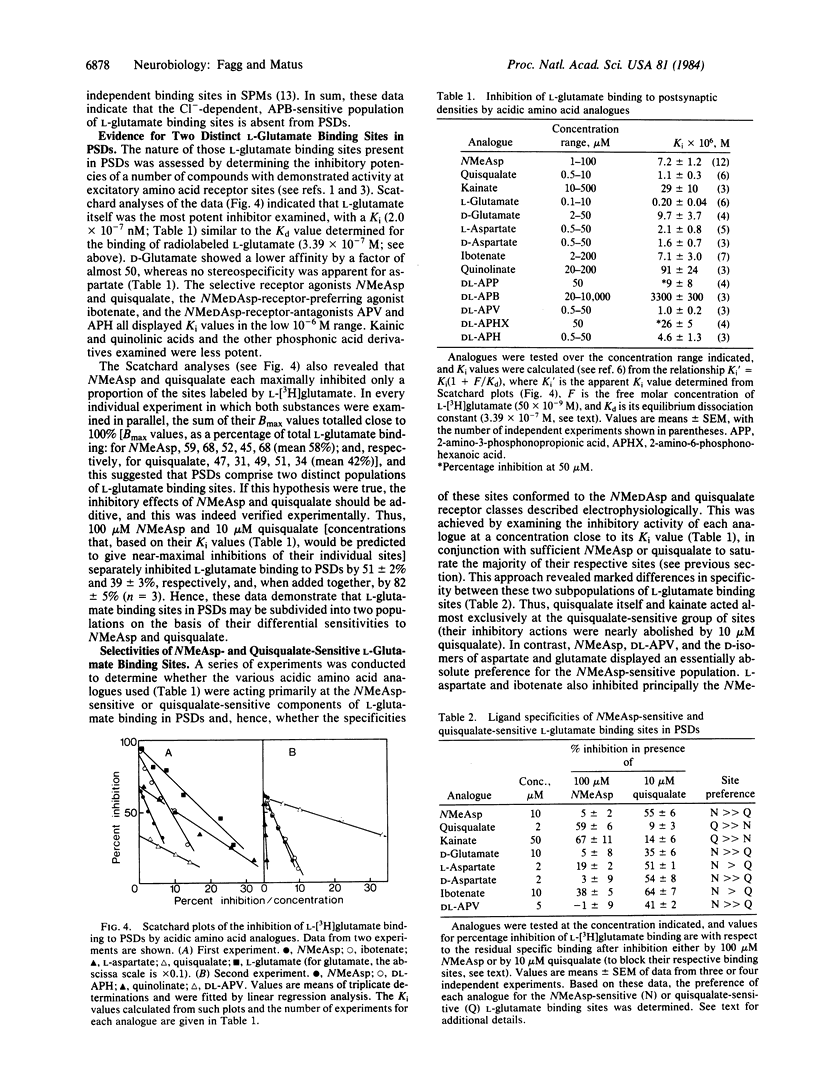
Recognition sites for the excitatory neurotransmitter, L-glutamate, were studied in synaptic plasma membranes and postsynaptic densities (PSDs) isolated from rat brains. The results demonstrate (i) that L-glutamate binding sites may be resolved into three distinct subtypes (categories A1, A2, and A4), each corresponding to an electrophysiologically identified receptor class, and (ii) that the N-methyl aspartate (A1) and quisqualate (A2) receptor types are selectively associated with PSDs. L-[3H]Glutamate bound to an apparently homogeneous population of sites in PSDs with a Kd of 3.39 X 10(-7) M and a Bmax (maximum number of binding sites) of 6.1 pmol/mg of protein. Inhibition studies demonstrated that these sites could be resolved into two distinct subtypes. N-Methyl aspartate maximally inhibited 58% of PSD-located L-glutamate binding sites with a Ki of 7.2 X 10(-6) M (the A1 site), and quisqualate inhibited 42% with a Ki of 1.1 X 10(-6) M (the A2 site); the effects of both substances were additive. Experiments with a range of acidic amino acid analogues indicated that the ligand selectivities of these two binding sites conformed to those of the N-methyl D-aspartate and quisqualate receptor classes defined electrophysiologically. The Cl--dependent population of L-glutamate binding sites (the A4 site), which predominates in synaptic membranes, was absent from isolated PSDs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charles A. K., Chang Y. F. Effect of D- and L-alpha-aminoadipate on the efflux of L-aspartate, L-glutamate and gamma-aminobutyrate from superfused rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1983 Jan 24;259(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Blomberg F., Berzins K., Siekevitz P. The structure of postsynaptic densities isolated from dog cerebral cortex. I. Overall morphology and protein composition. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):181–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G., Anson J., Surtees L. Presynaptic kainate and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors regulate excitatory amino acid release in the olfactory cortex. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 11;265(1):157–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins G. G. Some effects of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists on synaptic transmission in the rat olfactory cortex slice. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 29;244(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Kelly J. S. Blockade of amino acid-induced depolarizations and inhibition of excitatory post-synaptic potentials in rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:627–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usherwood P. N. Two populations of L-glutamate receptors on locust muscle fibres. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):62–64. doi: 10.1038/newbio246062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Role of excitatory amino acid receptors in mono- and polysynaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1983;49(2):280–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00238587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C. Amino acid neurotransmitters and their pathways in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):701–719. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C., Mena E. E., Cotman C. W. Chloride and calcium ions separate L-glutamate receptor populations in synaptic membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 18;88(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90397-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Mena E. E., Cotman C. W. L-glutamate receptor populations in synaptic membranes: effects of ions and pharmacological characteristics. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1983;37:199–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Mena E. E., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Freezing eliminates a specific population of L-glutamate receptors in synaptic membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jul 29;38(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Riederer B., Matus A. Sodium ions regulate a specific population of acidic amino acid receptors in synaptic membranes. Life Sci. 1984 Apr 30;34(18):1739–1745. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90573-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferkany J. W., Zaczek R., Coyle J. T. Kainic acid stimulates excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter release at presynaptic receptors. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):757–759. doi: 10.1038/298757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Acidic amino acid binding sites in mammalian neuronal membranes: their characteristics and relationship to synaptic receptors. Brain Res. 1984 May;319(2):103–164. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Mena E. E., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Synaptic localization of kainic acid binding sites. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):73–75. doi: 10.1038/289073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Roberts P. J. High affinity l-[3h]glutamate binding to postsynaptic receptor sites on rat cerebellar membranes. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1467–1477. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. G. Electron microscopy of excitatory and inhibitory synapses: a brief review. Prog Brain Res. 1969;31:141–155. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Cotman C. W. Effects of acidic amino acid antagonists on paired-pulse potentiation at the lateral perforant path. Exp Brain Res. 1983;52(3):455–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00238039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Lauridsen J., Krogsgaard-Larsen P. The binding of [3H]AMPA, a structural analogue of glutamic acid, to rat brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1982 Jan;38(1):173–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb10868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Matus A. I. Isolation of synaptic plasma membrane from brain by combined flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner J. F., Cotman C. W. Micromolar L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid selectively inhibits perforant path synapses from lateral entorhinal cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 6;216(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A. I., Taff-Jones D. H. Morphology and molecular composition of isolated postsynaptic junctional structures. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Dec 4;203(1151):135–151. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Pehling G., Wilkinson D. gamma-Aminobutyric acid receptors in brain postsynaptic densities. J Neurobiol. 1981 Jan;12(1):67–73. doi: 10.1002/neu.480120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBean G. J., Roberts P. J. Glutamate-preferring receptors regulate the release of D-[3H]aspartate from rat hippocampal slices. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):593–594. doi: 10.1038/291593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H. Receptors for the excitatory amino acids in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;20(3-4):251–271. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena E. E., Fagg G. E., Cotman C. W. Chloride ions enhance L-glutamate binding to rat brain synaptic membranes. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 15;243(2):378–381. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Holets V. R., Toy D. W., Cotman C. W. Anatomical distributions of four pharmacologically distinct 3H-L-glutamate binding sites. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):176–179. doi: 10.1038/306176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal M. J., Cunningham J. R., James T. A., Joseph M., Collins J. F. The effect of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (APB) on acetylcholine release from the rabbit retina: evidence for on-channel input to cholinergic amacrine cells. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Nov 4;26(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth E. F., Jackson H., Parks T. N. Pharmacologic evidence for synaptic transmission mediated by non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the avian cochlear nucleus. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Sep 19;40(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W., Collins J. F., Curry K. Phosphonate analogues of carboxylic acids as aminoacid antagonists on rat cortical neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1981 May 29;23(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bennett J. P., Jr Neurotransmitter receptors in the brain: biochemical identification. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:153–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Quinolinic acid: a potent endogenous excitant at amino acid receptors in CNS. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):411–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



