Abstract
The Escherichia coli translational initiation factor IF3 is encoded by an mRNA that has an unusual ribosome binding site. We have explored a mechanism that may account for the translation of IF3 and that provides regulation of the quantity of IF3 relative to ribosomes.
Full text
PDF
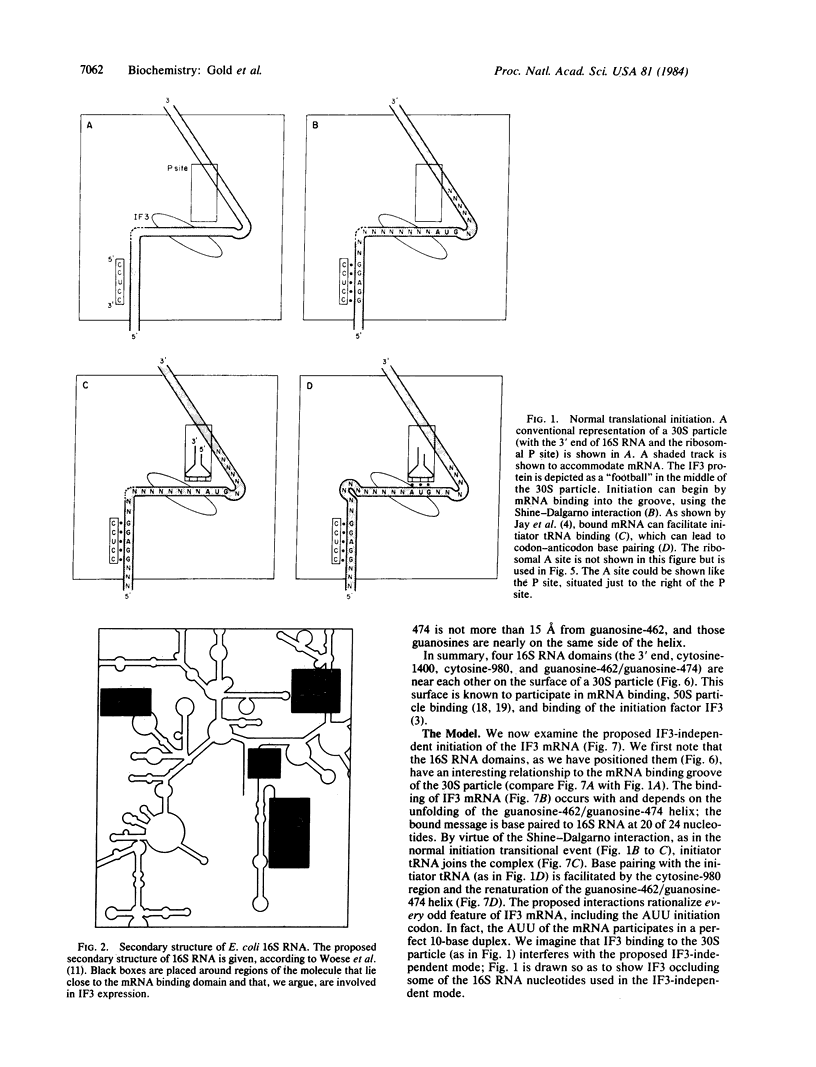
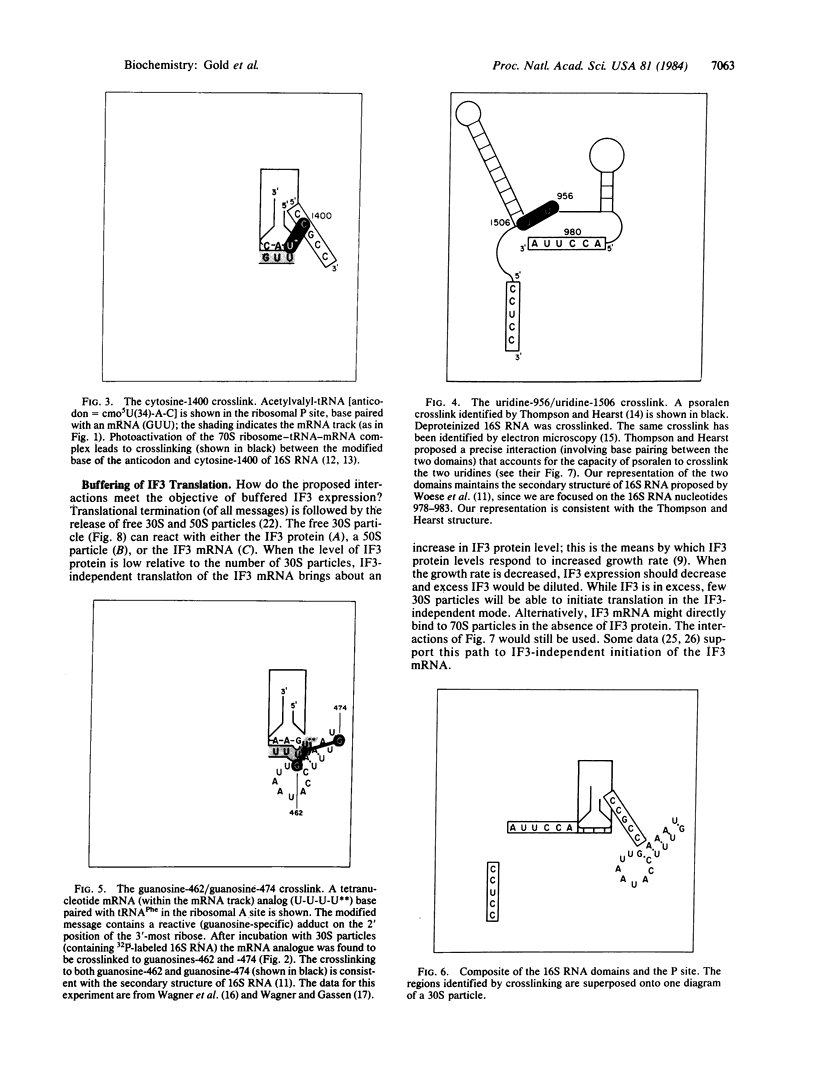

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brauer D., Wittmann-Liebold B. The primary structure of the initiation factor IF-3 from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80801-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaires J. B., Hawley D. A., Wahba A. J. Chain initiation factor 3 crosslinks to E. coli 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits and alters the UV absorbance spectrum of 70S ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5681–5693. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B., Millon R., Ebel J. P., Nurse K., Ofengand J. Cross-linking of the anticodon of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis acetylvalyl-tRNA to the ribosomal P site. Characterization of a unique site in both E. coli 16S and yeast 18S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):429–437. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss D. J., Parkhurst L. J., Wahba A. J. Kinetic studies on the interaction of chain initiation factor 3 with 70 S Escherichia coli ribosomes and subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10119–10127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Chapman N. M., Noller H. F. Mechanism of ribosomal subunit association: discrimination of specific sites in 16 S RNA essential for association activity. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 5;130(4):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Hershey J. W. Initiation factor and ribosome levels are coordinately controlled in Escherichia coli growing at different rates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1954–1959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Seth A. K., Jay G. Specific binding of a chemically synthesized prokaryotic ribosome recognition site. Prospect for molecular cloning and expression of eukaryotic genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3809–3812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lestienne P., Dondon J., Plumbridge J. A., Howe J. G., Mayaux J. F., Springer M., Blanquet S., Hershey J. W., Grunberg-Manago M. Expression of the gene for Escherichia coli initiation factor IE-3 in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):483–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Webster R. E. The in vitro translation of a terminating signal by a single Escherichia coli ribosome. The fate of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 25;250(20):8132–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince J. B., Taylor B. H., Thurlow D. L., Ofengand J., Zimmermann R. A. Covalent crosslinking of tRNA1Val to 16S RNA at the ribosomal P site: identification of crosslinked residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5450–5454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacerdot C., Fayat G., Dessen P., Springer M., Plumbridge J. A., Grunberg-Manago M., Blanquet S. Sequence of a 1.26-kb DNA fragment containing the structural gene for E.coli initiation factor IF3: presence of an AUU initiator codon. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):311–315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana T., Subramanian A. R. Separation of two forms of IF-3 in Escherichia coli by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80800-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Hearst J. E. Structure of E. coli 16S RNA elucidated by psoralen crosslinking. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1355–1365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Laken K., Bakker-Steeneveld H., Van Knippenberg P. Polyuridylic acid-dependent binding of fMet-tRNA to Escherichia coli ribosomes and incorporation of formylmethionine into polyphenylalanine. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):230–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilenko S. K., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. Topography of 16 S RNA in 30 S subunits and 70 S ribosomes accessibility to cobra venom ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):699–721. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Gassen H. G. Identification of a 16S rna sequence located in the decoding site of 30S ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 1;67(3):312–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80554-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Gassen H. G. On the covalent binding of mRNA models to the part of the 16 S RNA which is located in the mRNA binding site of the 30 S ribosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 22;65(2):519–529. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenzien P., Hearst J. E., Thammana P., Cantor C. R. Base-pairing between distant regions of the Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):255–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laken K., Bakker-Steeneveld H., Berkhout B., van Knippenberg P. H. The role of the codon and the initiation factor IF-2 in the selection of N-blocked aminoacyl-tRNA for initiation. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):19–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]