Abstract
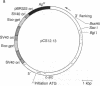
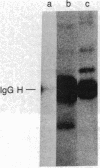
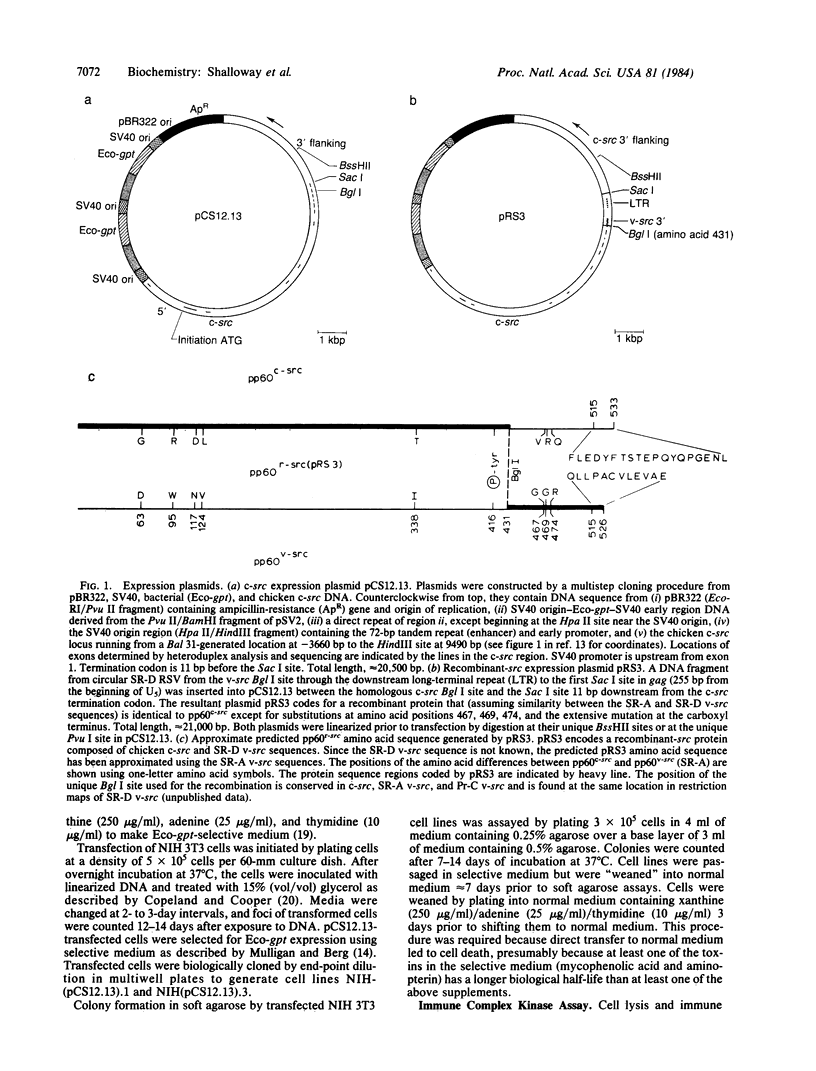
NIH 3T3 mouse cells were transfected with plasmids that induce efficient expression of either (i) the Rous sarcoma virus v-src gene, (ii) the chicken c-src gene, or (iii) a recombinant gene combining the 5' portion of c-src with the 3' end of v-src. Focus formation in tissue culture and formation of large colonies in soft agar did not occur in cells transfected with c-src. Cells transfected with c-src expression plasmids did not form foci but were isolated using a coselectable biological marker. They display morphological and substrate-independent growth characteristics intermediate between those of normal and v-src-transformed mouse cells, and lysates from these cells have enhanced in vitro tyrosine kinase activity. Transfection with the c-src-v-src recombinant induced focus formation with an efficiency similar to that obtained with a v-src expression plasmid. These results imply that v-src-induced transformation does not result just from overexpression of an essentially normal cellular protein but, at least in part, depends on the mutations distinguishing the cellular and viral proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Cooper G. M. Transfection by exogenous and endogenous murine retrovirus DNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. Corrections to the nucleotide sequence of the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):736–738. doi: 10.1038/301736b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Retroviral transforming genes in normal cells? Nature. 1983 Jul 21;304(5923):219–226. doi: 10.1038/304219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Cook R., Miller G. J., Erikson R. L. The same normal cell protein is phosphorylated after transformation by avian sarcoma viruses with unrelated transforming genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):43–50. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. I., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F., Brugge J. S. Protein phosphorylation mediated by partially purified avian sarcoma virus transforming-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):907–917. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein phosphorylated by the RSV transforming function. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90539-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Cellular homologue (c-src) of the transforming gene of Rous sarcoma virus: isolation, mapping, and transcriptional analysis of c-src and flanking regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Zelenetz A. D., Cooper G. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the chicken gene homologous to the transforming gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):531–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Feldman R. A., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. 1. Complete nucleotide sequence of an EcoRI fragment of recovered avian sarcoma virus which codes for gp37 and pp60src. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.1-11.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. DNA sequence of the viral and cellular src gene of chickens. II. Comparison of the src genes of two strains of avian sarcoma virus and of the cellular homolog. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.12-18.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H., Junghans R. P., Ju G., Skalka A. M. Comparison between the viral transforming gene (src) of recovered avian sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1024–1037. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Curran T., Müller R., Verma I. M. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1241–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]