Abstract
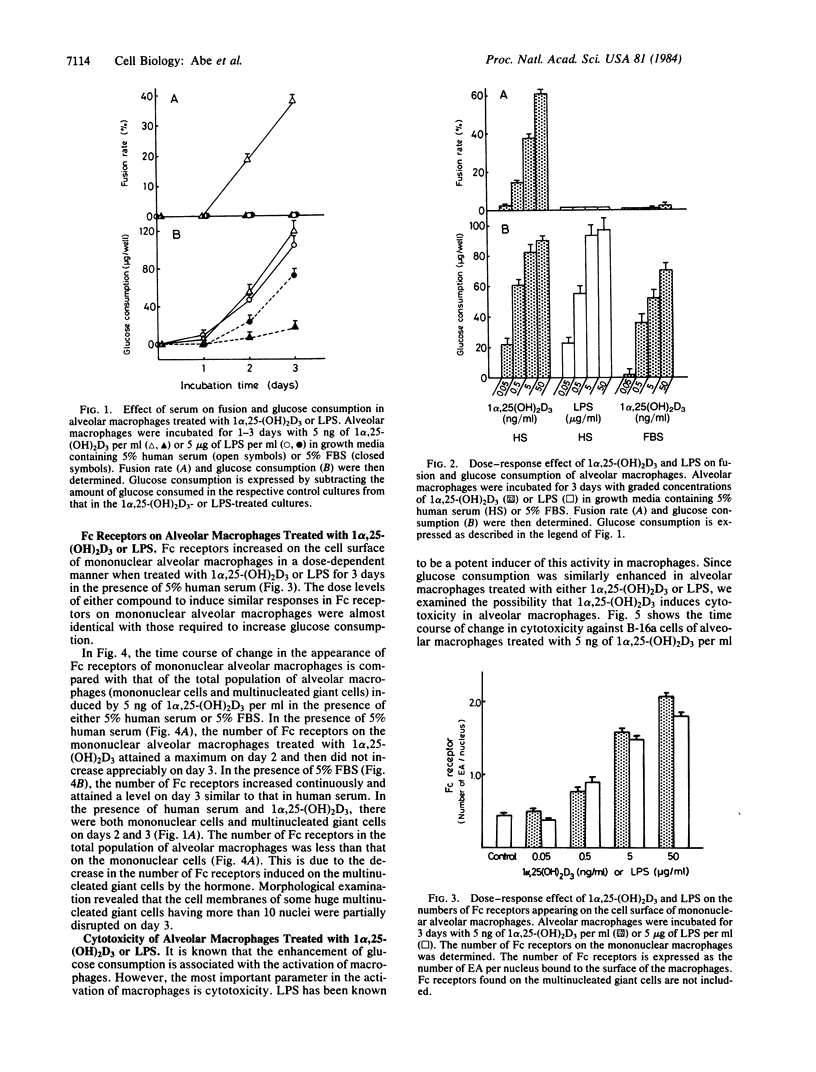
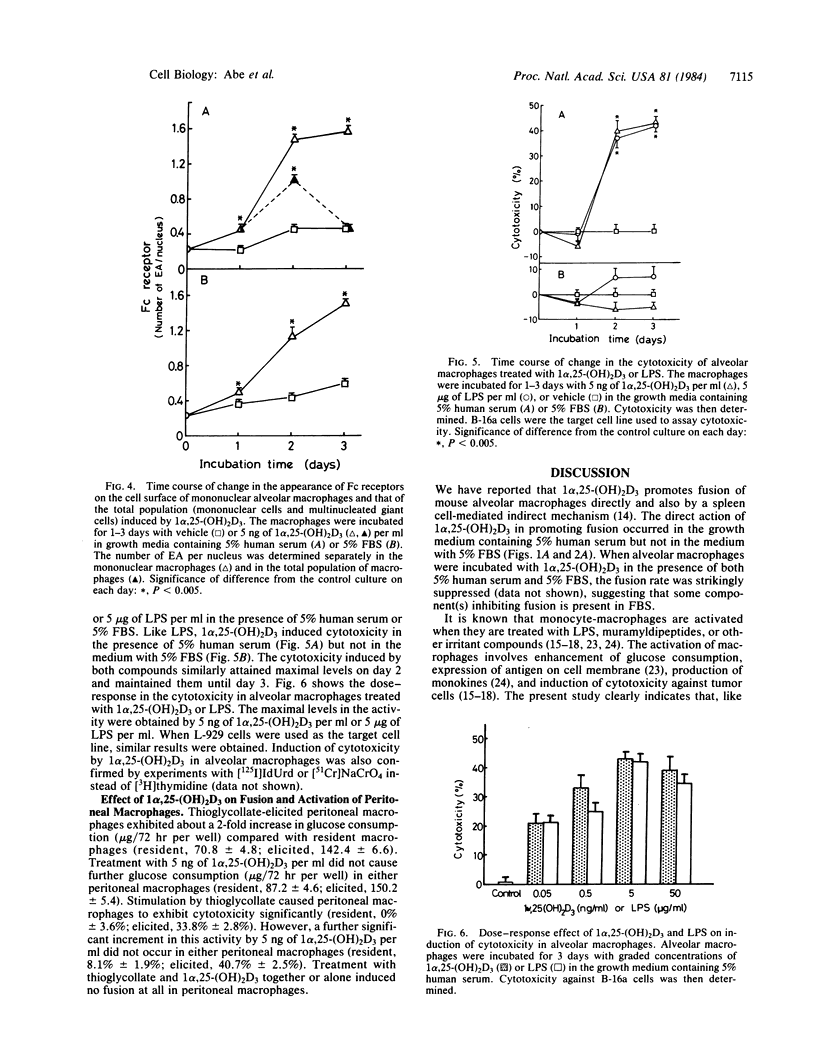
1 alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1 alpha,25-(OH)2D3] induces fusion of murine alveolar macrophages. This effect was observed in growth medium containing 5% human serum but not in the medium with 5% fetal bovine serum. Unlike 1 alpha,25-(OH)2D3, bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS) did not induce fusion of alveolar macrophages. However, both 1 alpha,25-(OH)2D3 and LPS activated alveolar macrophages, as measured by glucose consumption, increase in Fc receptors, and induction of cytotoxicity. The number of Fc receptors on the surface of multinucleated giant cells induced by 1 alpha,25-(OH)2D3 was much smaller than that on the surface of mononuclear macrophages treated with the hormone. These results indicate that 1 alpha,25-(OH)2D3 induces both fusion and activation of alveolar macrophages, whereas LPS elicits activation only.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe E., Miyaura C., Sakagami H., Takeda M., Konno K., Yamazaki T., Yoshiki S., Suda T. Differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells induced by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe E., Miyaura C., Tanaka H., Shiina Y., Kuribayashi T., Suda S., Nishii Y., DeLuca H. F., Suda T. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes fusion of mouse alveolar macrophages both by a direct mechanism and by a spleen cell-mediated indirect mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5583–5587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Teitelbaum S. L., Reitsma P., Hall A., Pegg L. E., Trial J., Kahn A. J. Induction of monocytic differentiation and bone resorption by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5907–5911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh P. F., Haussler M. R. 1 Alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in intestine. II. Temperature-dependent transfer of the hormone to chromatin via a specific cytosol receptor. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1258–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Schnoes H. K. Metabolism and mechanism of action of vitamin D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:631–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd R. C., Cohen M. S., Newman S. L., Gray T. K. Vitamin D metabolites change the phenotype of monoblastic U937 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7538–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe W. F., Henson P. M. Macrophage stimulation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. I. Cytolytic effect on tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):544–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drysdale B. E., Zacharchuk C. M., Shin H. S. Mechanism of macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity: production of a soluble cytotoxic factor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2362–2367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Fuller-Farrar J., Farrar W. L., Hilfiker M. L. Macrophage-independent activation of helper T cells. I. Production of Interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowen M., Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., McGuire M. K., Russell R. G. An interleukin 1 like factor stimulates bone resorption in vitro. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):378–380. doi: 10.1038/306378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowen M., Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., Meats J. E., Russell R. G. Stimulation by human interleukin 1 of cartilage breakdown and production of collagenase and proteoglycanase by human chondrocytes but not by human osteoblasts in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 14;797(2):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi J., Hosoi J., Abe E., Suda T., Kuroki T. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured mouse epidermal cells by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):1950–1957. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kream B. E., Jose M., Yamada S., DeLuca H. F. A specific high-affinity binding macromolecule for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in fetal bone. Science. 1977 Sep 9;197(4308):1086–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.887939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Characterization of macrophage activation factor, a lymphokine that causes macrophages to become cytotoxic for tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Dec;41(2):347–357. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Induction of specific changes in the surface membrane of myeloid leukemic cells by steroid hormones. Int J Cancer. 1975 May 15;15(5):731–740. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Koeffler H. P., Donaldson C. A., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation in a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60): receptor-mediated maturation to macrophage-like cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):391–398. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. M., San Miguel J. F., Freake H. C., Green P. M., Zola H., Catovsky D., Goldman J. M. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits proliferation of human promyelocytic leukaemia (HL60) cells and induces monocyte-macrophage differentiation in HL60 and normal human bone marrow cells. Leuk Res. 1983;7(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(83)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murao S., Gemmell M. A., Callaham M. F., Anderson N. L., Huberman E. Control of macrophage cell differentiation in human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1983 Oct;43(10):4989–4996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Rosenfeld M. G. Regulation of pituitary function and prolactin production in the GH4 cell line by vitamin D. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4050–4053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Gullberg U., Ivhed I., Nilsson K. Induction of differentiation of the human histiocytic lymphoma cell line U-937 by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):5862–5867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1863–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Fidler I. J. Tumor cytotoxicity of rat alveolar macrophages activated in vitro by endotoxin. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Mar;27(3):269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Poste G., Fidler I. J. Rat alveolar macrophages are susceptible to activation by free and liposome-encapsulated lymphokines. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2197–2202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Abe E., Miyaura C., Shiina Y., Suda T. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60) into monocyte-macrophages, but not into granulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91544-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama T., Tokunaga T. Monoclonal antibodies directed against mouse macrophages in different stages of activation for tumor cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):1032–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Riethmüller G. A rapid assay for cytotoxicity of unstimulated human monocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Jan;72(1):23–29. doi: 10.1093/jnci/72.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik A., Vatter A., Hayes R. L., Blumenthal E., Crowle A. J. Mouse pleural macrophages: characterization and comparison with mouse alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Mar;31(3):207–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



