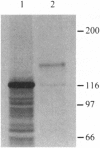
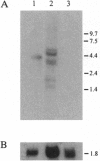
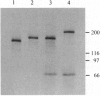
Abstract
The eukaryotic convertase family plays an important role in posttranslational proteolytic processing and activation of many pro- and polypeptides that have at their cleavage sites the paired basic motif, RX(K/R)R. Recent studies have revealed that the cleavage site of insect pro-vitellogenins (pro-Vg) also contains this motif. To identify and characterize the insect pro-Vg processing enzyme, Vg convertase (VC), its cDNA was cloned from a vitellogenic female fat body cDNA library of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. The 3735-bp-long VC cDNA has an open reading frame encoding a 115-kDa protein. In vitro transcription/translation of VC cDNA revealed that this 115-kDa protein becomes 140 kDa after co- and posttranslational modifications. The VC deduced amino acid sequence has high similarity to and a domain structure characteristic of furin-like convertases. Northern blot analysis showed that a single 4.2-kb transcript was expressed in the fat body during the first 18 hr of the Vg synthetic period. Coexpression of VC cDNA with mosquito Vg cDNA resulted in correct cleavage of pro-Vg. Thus, this newly identified convertase is, indeed, a functional fat body-specific enzyme for pro-Vg cleavage.
Full text
PDF


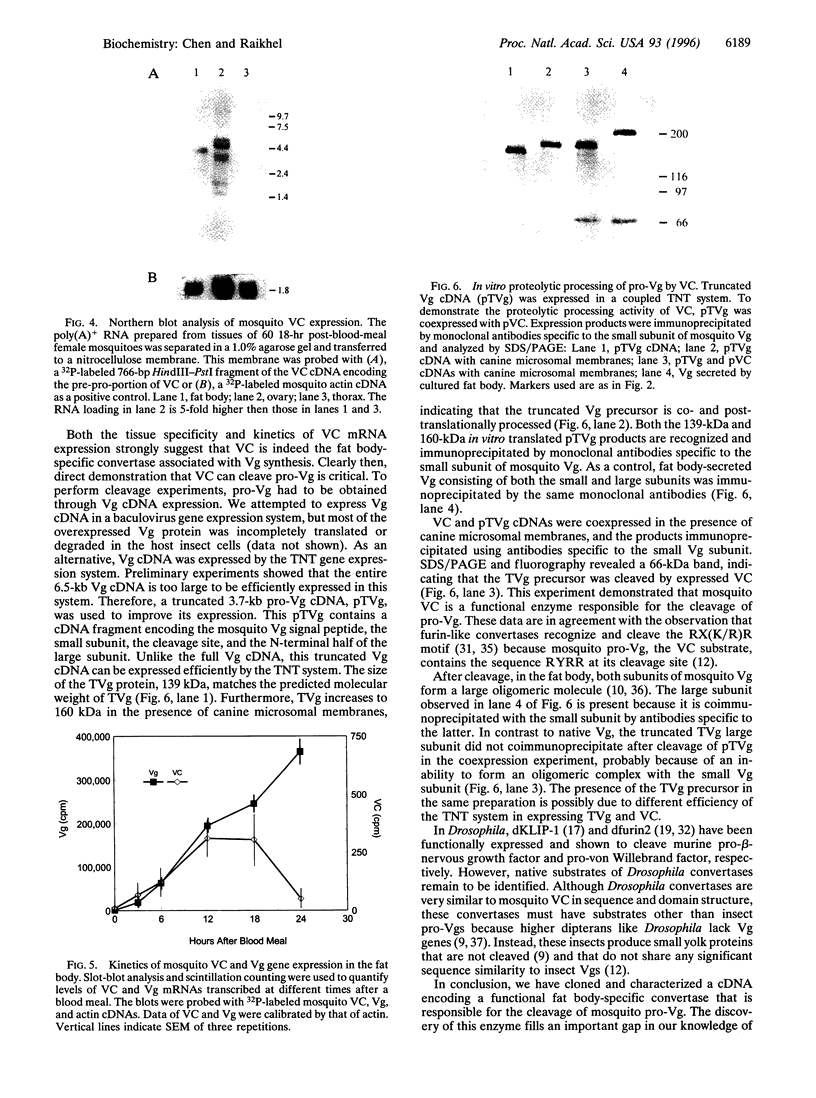

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakch N., Boussetta H., Rholam M., Cohen P. Processing endoprotease recognizes a structural feature at the cleavage site of peptide prohormones. The pro-ocytocin/neurophysin model. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15912–15916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brakch N., Rholam M., Boussetta H., Cohen P. Role of beta-turn in proteolytic processing of peptide hormone precursors at dibasic sites. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4925–4930. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne B. M., Gruber M., Ab G. The evolution of egg yolk proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;53(1):33–69. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Cho W. L., Raikhel A. S. Analysis of mosquito vitellogenin cDNA. Similarity with vertebrate phosvitins and arthropod serum proteins. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):641–647. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho W. L., Raikhel A. S. Cloning of cDNA for mosquito lysosomal aspartic protease. Sequence analysis of an insect lysosomal enzyme similar to cathepsins D and E. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21823–21829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitsch K. W., Chen J. S., Raikhel A. S. Indirect control of yolk protein genes by 20-hydroxyecdysone in the fat body of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1995 Apr;25(4):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(94)00082-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhadialla T. S., Raikhel A. S. Biosynthesis of mosquito vitellogenin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9924–9933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Molecular and enzymatic properties of furin, a Kex2-like endoprotease involved in precursor cleavage at Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg sites. J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):296–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick J. S., Wolfgang W. J., Forte M. A., Thomas G. A unique Kex2-like endoprotease from Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in the central nervous system during early embryogenesis. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):705–717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00705.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann L. J., Trewitt P. M., Kumaran A. K. Proteolytic processing of the vitellogenin precursor in the boll weevil, Anthonomus grandis. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1993;23(3):125–134. doi: 10.1002/arch.940230304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkin P. G., Fallon A. M. Ribosome metabolism during the vitellogenic cycle of the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 19;924(2):352–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Thomas L., VanSlyke J. K., Stenberg P. E., Thomas G. Intracellular trafficking and activation of the furin proprotein convertase: localization to the TGN and recycling from the cell surface. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):18–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Identification of an isoform with an extremely large Cys-rich region of PC6, a Kex2-like processing endoprotease. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 26;327(2):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80163-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raikhel A. S., Dhadialla T. S. Accumulation of yolk proteins in insect oocytes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1992;37:217–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raikhel A. S., Lea A. O. Control of follicular epithelium development and vitelline envelope formation in the mosquito; role of juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone. Tissue Cell. 1991;23(4):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(91)90015-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Ayoubi T. A., Creemers J. W., Pauli I. G., Van de Ven W. J. The Dfur2 gene of Drosophila melanogaster: genetic organization, expression during embryogenesis, and pro-protein processing activity of its translational product Dfurin2. DNA Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;14(3):223–234. doi: 10.1089/dna.1995.14.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Creemers J. W., Pauli I. G., Kurzik-Dumke U., Rentrop M., Gateff E. A., Leunissen J. A., Van de Ven W. J. Cloning and functional expression of Dfurin2, a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme of Drosophila melanogaster with multiple repeats of a cysteine motif. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17208–17215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Pauli I. G., Zhang Y., van de Ven W. J. cDNA sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster gene, Dfur1, encoding a protein structurally related to the subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme furin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81052-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siezen R. J., Creemers J. W., Van de Ven W. J. Homology modelling of the catalytic domain of human furin. A model for the eukaryotic subtilisin-like proprotein convertases. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 1;222(2):255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit A. B., Spijker S., Nagle G. T., Knock S. L., Kurosky A., Geraerts W. P. Structural characterization of a Lymnaea putative endoprotease related to human furin. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 18;343(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80600-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W. Evolution and expression of vitellogenin genes. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., Sakurai M. T., Izumi S., Tomino S. Vitellogenin gene of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: structure and sex-dependent expression. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]