Abstract
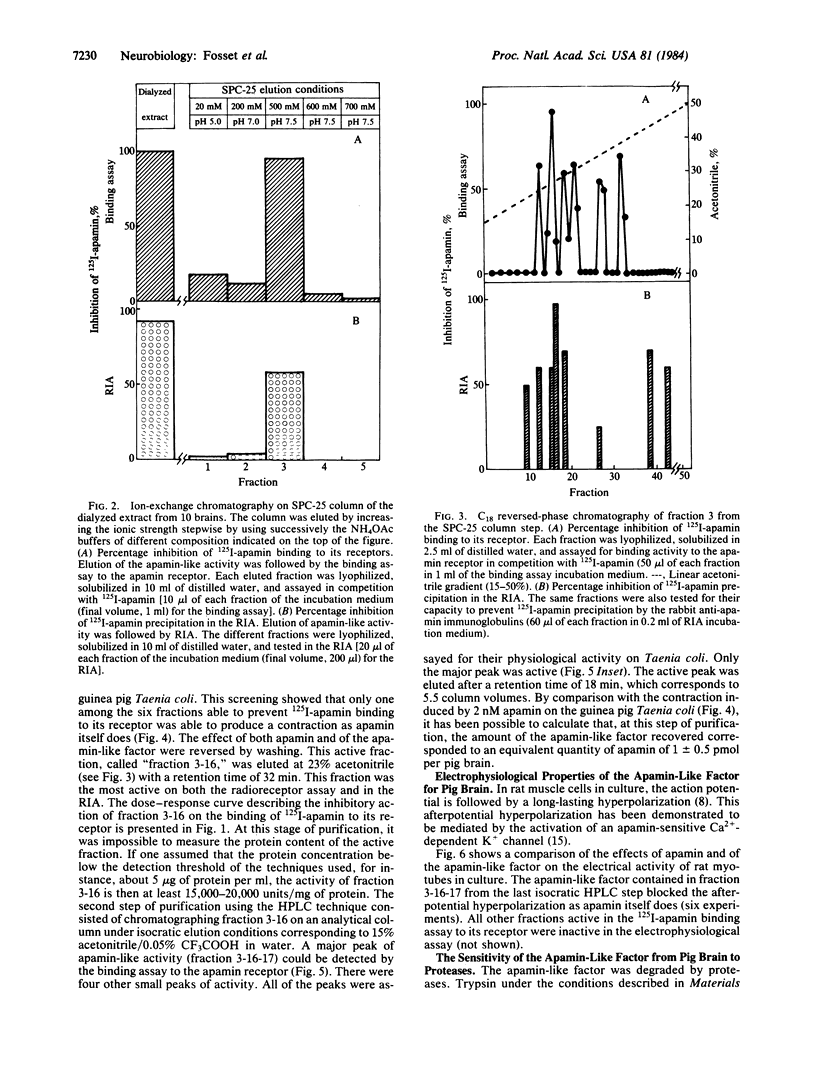
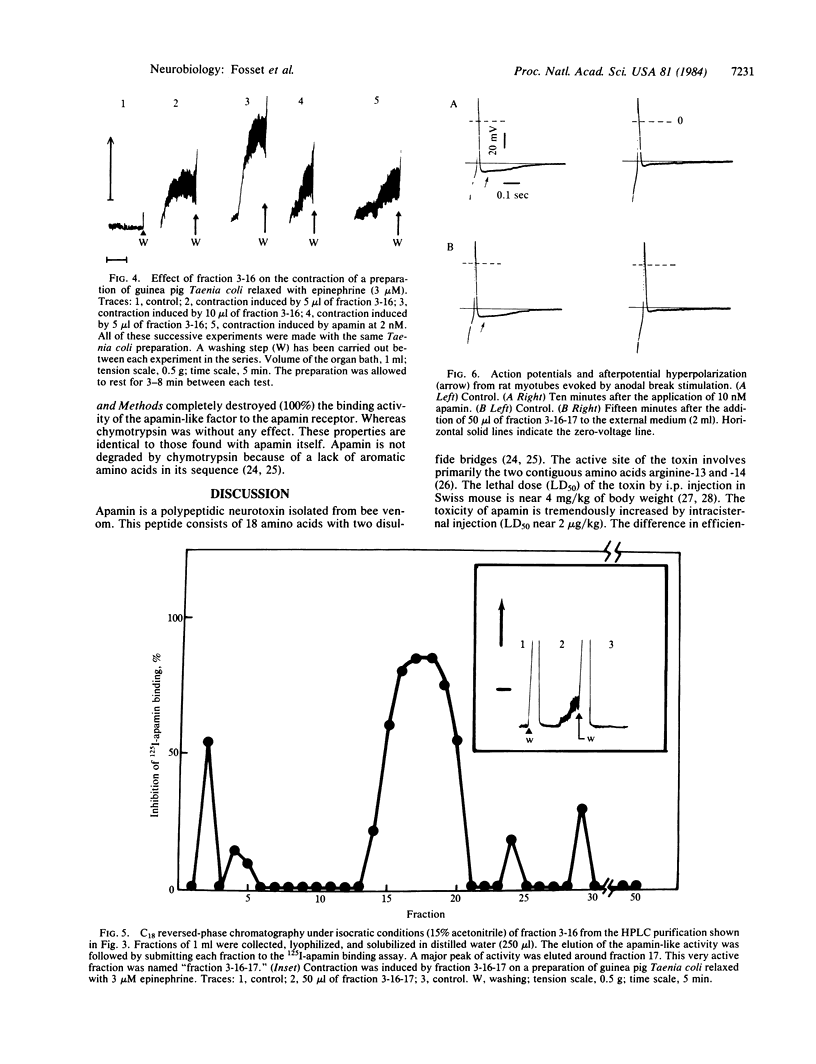
An apamin-like factor has been isolated from pig brain after extraction of the tissue and purification on sulfopropyl-Sephadex C-25 and on reversed-phase high pressure liquid chromatography. The apamin-like factor has the following properties: (i) it prevents 125I-labeled apamin binding to its specific receptor site present on rat brain synaptosomes, (ii) it is active in the radioimmunoassay for apamin (i.e., it prevents 125I-labeled apamin precipitation by anti-apamin antibodies), (iii) it induces contraction of guinea pig intestinal smooth muscle previously relaxed with epinephrine, and (iv) it blocks Ca2+-dependent K+ channels responsible for the long-lasting afterpotential hyperpolarization following the action potential in rat skeletal muscle cells in culture. All these properties are those of apamin itself. The apamin-like factor is a peptide that, like apamin, is destroyed by trypsin and unaffected by chymotrypsin. These results suggest the presence in mammalian brain of a potent Ca2+-dependent K+-channel modulator.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks B. E., Brown C., Burgess G. M., Burnstock G., Claret M., Cocks T. M., Jenkinson D. H. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):415–417. doi: 10.1038/282415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F., Dribin L. B. Calcium-dependent slow potassium conductance in rat skeletal myotubes. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. Modulation by calcium of the potassium permeability of dog heart sarcolemmal vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5763–5767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S., Haylett D. G., Strong P. N. High affinity binding of [125I]monoiodoapamin to isolated guinea-pig hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 21;152(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80393-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Fischer K. Apamin, a centrally acting neurotoxic peptide: binding and actions. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1979;3:387–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Fischer K. Bee venom neurotoxin (apamin): iodine labeling and characterization of binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar;94(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Neurotoxicity of apamin and MCD peptide upon central application. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;300(2):189–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00505050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haux P., Sawerthal H., Habermann E. Sequenzanalyse des Bienengift-Neurotoxins (Apamin) aus seinen tryptischen und chymotryptischen Spaltstücken. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jun;348(6):737–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. D., Gundersen C. B., Jr Effects and mechanisms of polypeptide neurotoxins that act presynaptically. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:307–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Duval D., Kitabgi P., Lazdunski M., Vincent J. P. Preparation of a pure monoiodo derivative of the bee venom neurotoxin apamin and its binding properties to rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2762–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Duval D., Schmid H., Kitabgi P., Lazdunski M., Vincent J. P. Specific binding and pharmacological interactions of apamin, the neurotoxin from bee venom, with guinea pig colon. Life Sci. 1982 Aug 2;31(5):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Romey G., Duval D., Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. Apamin as a selective blocker of the calcium-dependent potassium channel in neuroblastoma cells: voltage-clamp and biochemical characterization of the toxin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1308–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Schmid H., Romey G., Duval D., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. The Ca2+-dependent slow K+ conductance in cultured rat muscle cells: characterization with apamin. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1039–1042. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. EGTA and motoneuronal after-potentials. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:199–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdunski M., Renaud J. F. The action of cardiotoxins on cardiac plasma membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:463–473. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Atwater I., Claret M., Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A. Resistance to apamin of the Ca2+-activated K+ permeability in pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas A. J., Den Hertog A., Ras R., Van den Akker J. The action of apamin on guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 17;67(2-3):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas A. J., Den Hertog A. The effect of apamin on the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;58(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Boheim G. The gating of single calcium-dependent potassium channels is described by an activation/blockade mechanism. Biophys Struct Mech. 1982;9(1):35–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00536014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium current and the activation of a slow potassium conductance in voltage-clamped mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:307–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Lazdunski M. The coexistence in rat muscle cells of two distinct classes of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with different pharmacological properties and different physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. A micro-radioimmunoassay for apamin. Toxicon. 1984;22(6):985–988. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitz H. Lethal potency in mice of toxins from scorpion, sea anemone, snake and bee venoms following intraperitoneal and intracisternal injection. Toxicon. 1984;22(2):308–311. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. Structure-function relationships and site of action of apamin, a neurotoxic polypeptide of bee venom with an action on the central nervous system. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2521–2525. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Peyer J. E., Cachelin A. B., Levitan I. B., Reuter H. Ca2+ -activated K+ conductance in internally perfused snail neurons is enhanced by protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4207–4211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


