Abstract
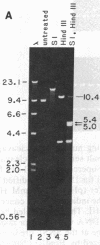
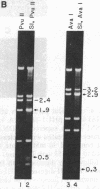
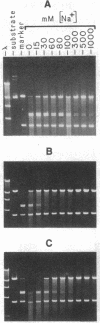
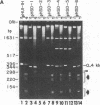
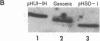
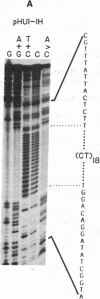
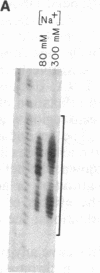
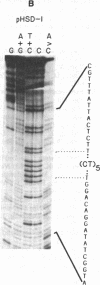
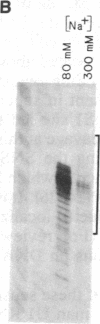
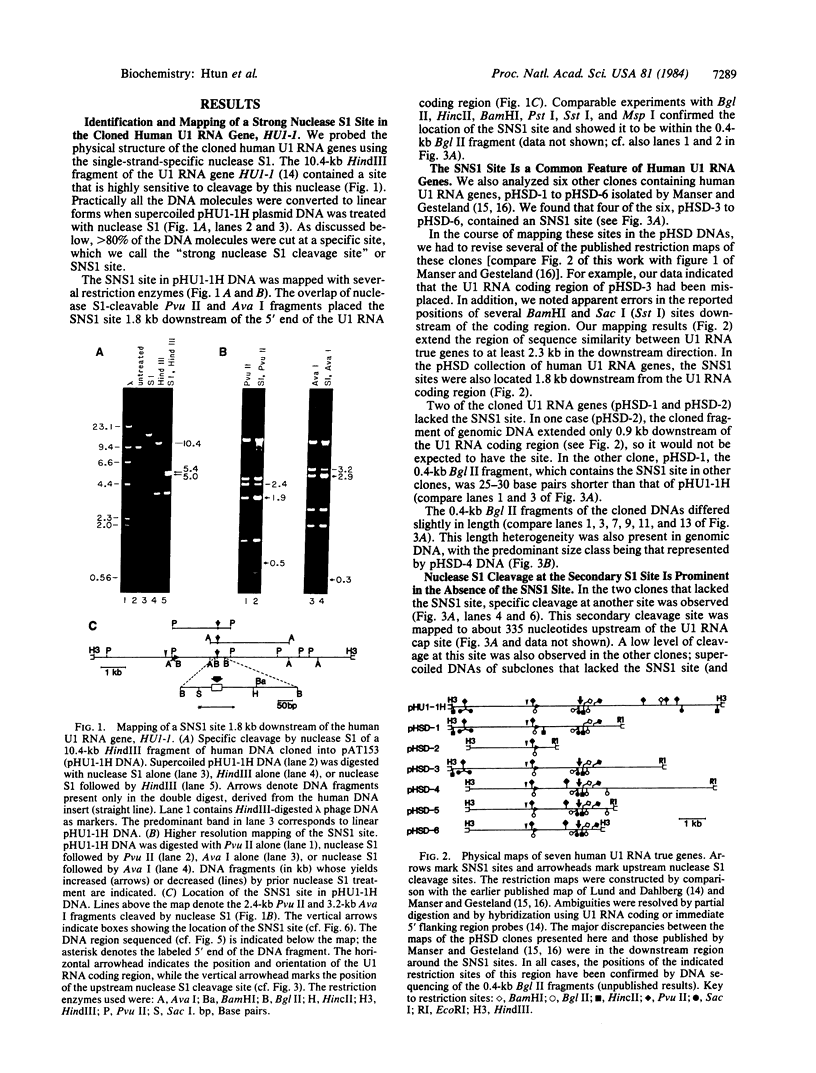
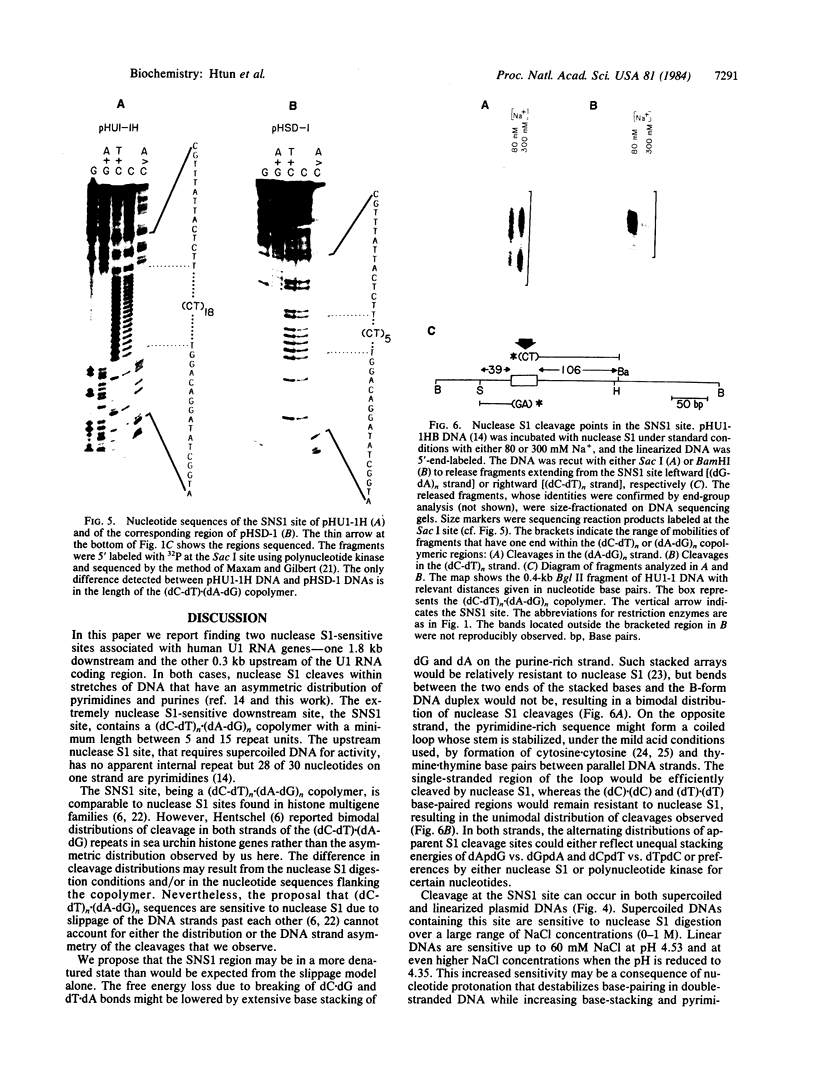
We find that the cloned DNAs of human U1 small nuclear RNA genes contain two nuclease S1-sensitive sites, one about 1.8 kilobases downstream of the U1 RNA coding region and the other around 0.3 kilobase upstream. The downstream site is unusually sensitive to the nuclease, being cleaved in both linear and negatively supercoiled DNAs. The extent of cleavage at this site is enhanced at lower pH and reduced concentrations of NaCl; the effects of salt are more apparent on linear than supercoiled DNAs. The nuclease S1 sensitivity of this downstream site is dependent on the presence of the sequence (dC-dT)n X (dA-dG)n, where n = 15-25. (One gene with n = 5 is resistant to nuclease S1 cleavage in this region.) In contrast, the nuclease S1 site upstream of the coding region is cleaved only when the DNA is supercoiled. This site also has a homopyrimidine X homopurine bias in the DNA strands, but the sequence is less regular. In the course of these studies, we detected several discrepancies between our restriction maps of some U1 RNA genes and those published by others. Our maps demonstrate that all seven cloned human U1 RNA genes are very similar in sequence for as much as 2.3 kilobases downstream of the U1 RNA coding region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland R. A., Cooke H. J., Roy K. L., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Isolation and characterization of three cloned fragments of human DNA coding for tRNAs and small nuclear RNA U1. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dybvig K., Clark C. D., Aliperti G., Schlesinger M. J. A chicken repetitive DNA sequence that is highly sensitive to single-strand specific endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8495–8508. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Gargiulo G., Rena-Descalzi L., Worcel A. Escherichia coli single-strand binding protein stabilizes specific denatured sites in superhelical DNA. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):770–774. doi: 10.1038/303770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Schamböck A., Van Den Berg J., Weissmann C. Specific excision of the inserted DNA segment from hybrid plasmids constructed by the poly(dA). poly (dT) method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 13;454(3):587–591. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Primary sequence of the 5' flanking regions of the Drosophila heat shock genes in chromosome subdivision 67B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1627–1642. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Morgan A. R. Unique structures formed by pyrimidine-purine DNAs which may be four-stranded. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1637–1641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Johnson D. A., Morgan A. R. Complexes formed by (pyrimidine)n . (purine)n DNAs on lowering the pH are three-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3073–3091. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. True genes for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Copy number, polymorphism, and methylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):2013–2021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Characterization of small nuclear RNA U1 gene candidates and pseudogenes from the human genome. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):117–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manser T., Gesteland R. F. Human U1 loci: genes for human U1 RNA have dramatically similar genomic environments. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Evans B. A., Cox D. R., Shine J., Richards R. I. Structure of mouse kallikrein gene family suggests a role in specific processing of biologically active peptides. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):300–307. doi: 10.1038/303300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E., Lund E. Transcription of a gene for human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. E., Gilliam A. C., Shen A., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Unusual sequences in the murine immunoglobulin mu-delta heavy-chain region. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):483–487. doi: 10.1038/306483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya T., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S. Mammalian tRNA genes: nucleotide sequence of rat genes for tRNAAsp, tRNAGly and tRNAGlu. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2239–2250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K. Superhelicity induces hypersensitivity of a human polypyrimidine . polypurine DNA sequence in the human alpha 2-alpha 1 globin intergenic region to S1 nuclease digestion--high resolution mapping of the clustered cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7899–7910. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):312–316. doi: 10.1038/299312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and properties of S1 nuclease from Aspergillus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):248–255. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Denison R. A. Either gene amplification or gene conversion may maintain the homogeneity of the multigene family encoding human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1141–1149. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Blakesley R. W., Hardies S. C., Horn G. T., Larson J. E., Selsing E., Burd J. F., Chan H. W., Dodgson J. B., Jensen K. F. The role of DNA structure in genetic regulation. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1977;4(3):305–340. doi: 10.3109/10409237709102561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Sundaralingam M. X-ray-structure of a cytidylyl-3',5'-adenosine-proflavine complex: a self-paired parallel-chain double helical dimer with an intercalated acridine dye. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1852–1856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Wurst R., Vournakis J., Rich A. Conformational changes of yeast tRNAPhe and E. coli tRNA2Glu as indicated by different nuclease digestion patterns. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9608–9616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B. The three-dimensional structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:395–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]