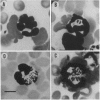
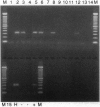
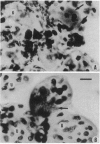
Abstract
A human-derived strain of the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis, a recently described emerging rickettsial disease, has been established by serial blood passage in mouse hosts. Larval deer ticks acquired infection by feeding upon such mice and efficiently transmitted the ehrlichiae after molting to nymphs, thereby demonstrating vector competence. The agent was detected by demonstrating Feulgen-positive inclusions in the salivary glands of the experimentally infected ticks and from field-derived adult deer ticks. White-footed mice from a field site infected laboratory-reared ticks with the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis, suggesting that these rodents serve as reservoirs for ehrlichiae as well as for Lyme disease spirochetes and the piroplasm that causes human babesiosis. About 10% of host-seeking deer ticks were infected with ehrlichiae, and of these, 20% also contained spirochetes. Cotransmission of diverse pathogens by the aggressively human-biting deer tick may have a unique impact on public health in certain endemic sites.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken J. S., Krueth J., Wilson-Nordskog C., Tilden R. L., Asanovich K., Dumler J. S. Clinical and laboratory characteristics of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. JAMA. 1996 Jan 17;275(3):199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. M., Dumler J. S., Bakken J. S., Walker D. H. Identification of a granulocytotropic Ehrlichia species as the etiologic agent of human disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Mar;32(3):589–595. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.3.589-595.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Anderson B. E., Fishbein D. B., Sanchez J. L., Goldsmith C. S., Wilson K. H., Duntley C. W. Isolation and characterization of an Ehrlichia sp. from a patient diagnosed with human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2741–2745. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2741-2745.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. E., Stallknecht D. E., Howerth E. W., Warner C., Biggie K., Davidson W. R., Lockhart J. M., Nettles V. F., Olson J. G., Childs J. E. Susceptibility of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) to infection with Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Nov;32(11):2725–2728. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.11.2725-2728.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGGIE A. The effect of thick-borne fever on the resistance of lambs to staphylococci. J Comp Pathol. 1956 Jul;66(3):278–285. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(56)80029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein D. B., Dawson J. E., Robinson L. E. Human ehrlichiosis in the United States, 1985 to 1990. Ann Intern Med. 1994 May 1;120(9):736–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-120-9-199405010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribble D. H. Equine ehrlichiosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):462–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krampitz H. E., Bäumler W. Vorkommen, Saisondynamik und Wirtskreis von Babesia microti (França, 1912) in einheimischen Nagetieren. Z Parasitenkd. 1978 Dec 21;58(1):15–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00930788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda K., Markowitz N., Hawley R. C., Ristic M., Cox D., McDade J. E. Human infection with Ehrlichia canis, a leukocytic rickettsia. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 2;316(14):853–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704023161406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall W. F., 3rd, Telford S. R., 3rd, Rys P. N., Rutledge B. J., Mathiesen D., Malawista S. E., Spielman A., Persing D. H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Peromyscus leucopus. J Infect Dis. 1994 Oct;170(4):1027–1032. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.4.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. H., Jr, Owsley M. R., Hutcheson H. J., James A. M., Chen C., Irby W. S., Dotson E. M., McLain D. K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE W. H. A quantitative analysis of the factors involved in the variations in virulence of Rickettsiae. Science. 1953 Jul 10;118(3054):49–52. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3054.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi P., Kolbert C. P., Mitchell P. D., Reed K. D., Jr, Dumler J. S., Bakken J. S., Telford S. R., 3rd, Persing D. H. Ixodes dammini as a potential vector of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. J Infect Dis. 1995 Oct;172(4):1007–1012. doi: 10.1093/infdis/172.4.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Telford S. R., 3rd, Rys P. N., Dodge D. E., White T. J., Malawista S. E., Spielman A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Ixodes dammini ticks. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1420–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2402635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Karakashian S. J., Lewengrub S., Rudzinska M. A., Spielmank A. Development of Babesia microti sporozoites in adult Ixodes dammini. Int J Parasitol. 1986 Aug;16(4):381–385. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(86)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Mather T. N., Donahue J. G., Levine J., Campbell J. D., Karakashian S. J., Spielman A. Comparative prevalence of Babesia microti and Borrelia burgdorferi in four populations of Ixodes dammini in eastern Massachusetts. Acta Trop. 1986 Sep;43(3):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Spielman A. Babesia microti: infectivity of parasites from ticks for hamsters and white-footed mice. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Apr;53(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollark R. J., Komaroff A. L., Telford S. R., 3rd, Gleit, Fagioli L., Brunet L. R., Spielman A. Borrelia burgdorferi infection is rarely found in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;20(2):467–468. doi: 10.1093/clinids/20.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. M., Caporale D. A., Telford S. R., 3rd, Kocher T. D., Hartl D. L., Spielman A. Distribution of the Ixodes ricinus-like ticks of eastern North America. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6284–6288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrimenti R. J. Erythema chronicum migrans. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Jul;102(1):104–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A., Levine J. F., Wilson M. L. Vectorial capacity of North American Ixodes ticks. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):507–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease: a growing threat to urban populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2378–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steketee R. W., Eckman M. R., Burgess E. C., Kuritsky J. N., Dickerson J., Schell W. L., Godsey M. S., Jr, Davis J. P. Babesiosis in Wisconsin. A new focus of disease transmission. JAMA. 1985 May 10;253(18):2675–2678. doi: 10.1001/jama.253.18.2675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford S. R., 3rd, Lepore T. J., Snow P., Warner C. K., Dawson J. E. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in Massachusetts. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Aug 15;123(4):277–279. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-123-4-199508150-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford S. R., 3rd, Mather T. N., Moore S. I., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Incompetence of deer as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jul;39(1):105–109. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford S. R., 3rd, Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Babesia microti. J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):223–227. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Western K. A., Benson G. D., Gleason N. N., Healy G. R., Schultz M. G. Babesiosis in a Massachusetts resident. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 15;283(16):854–856. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010152831607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]