Abstract
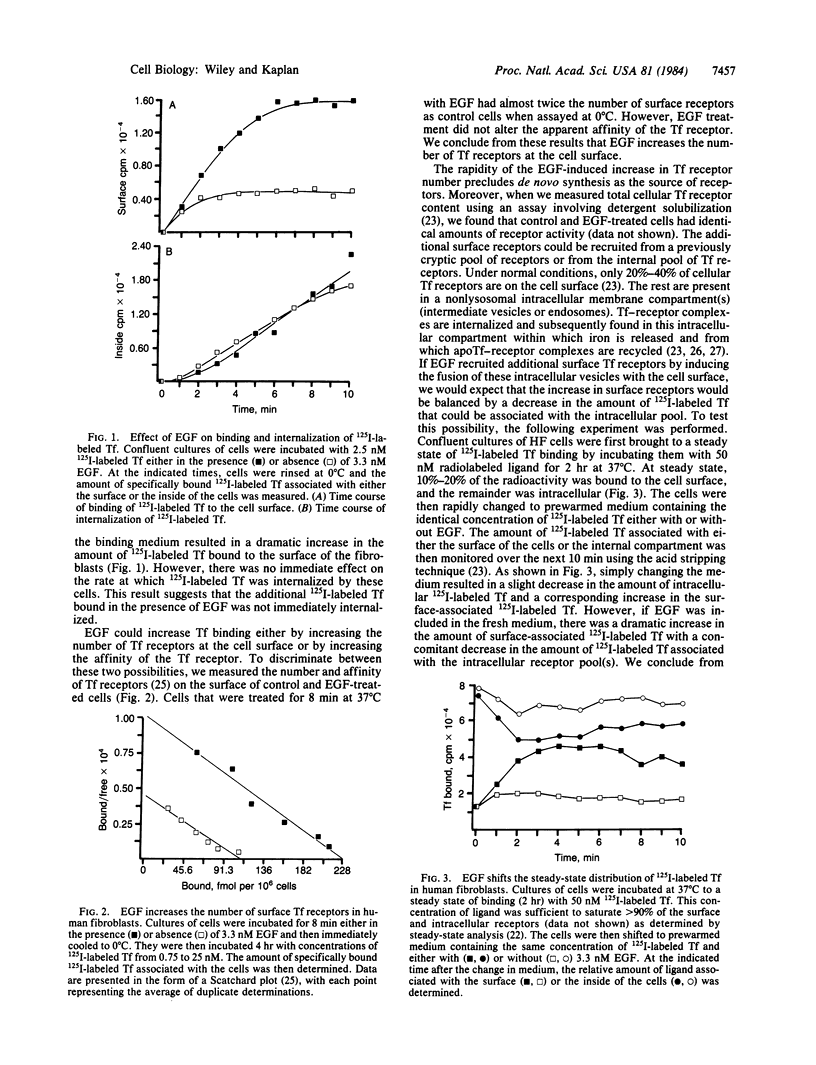
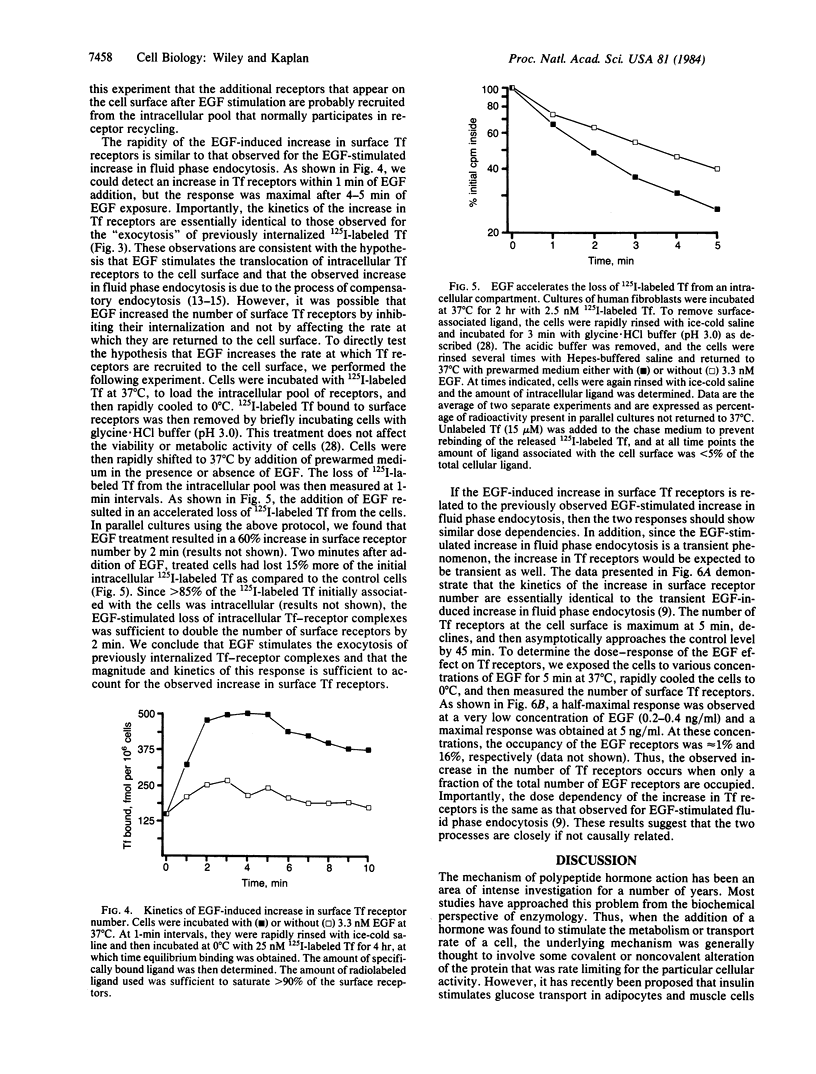
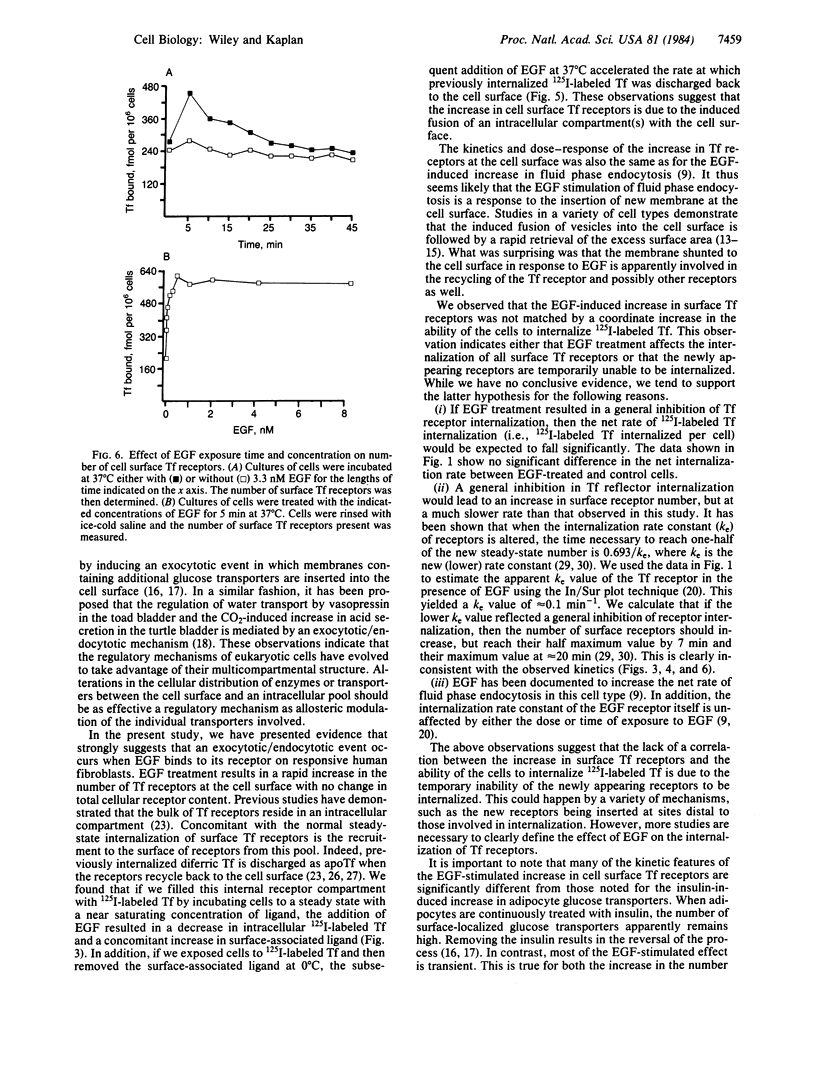
Treatment of human fibroblasts with epidermal growth factor (EGF) results in a rapid increase (less than 5 min) in the ability of the cells to bind 125I-labeled transferrin to surface receptors. Scatchard analyses of EGF-treated cells indicate that this increase was due to an increase in the number of transferrin receptors at the cell surface rather than to alterations in ligand-receptor affinity. The EGF-induced increase in transferrin receptors was transient, reaching a peak by 5 min and then declining back to near basal levels by 45 min. Increases in transferrin receptor number were observed when approximately equal to 1% of the EGF receptors were occupied and were maximal at 16% occupancy. EGF treatment accelerated the rate at which previously internalized 125I-labeled transferrin-receptor complexes were returned to the cell surface. The kinetics and magnitude of the loss of intracellular transferrin receptors was sufficient to account for the increase in surface transferrin receptors. We conclude from these studies that one of the earliest effects of EGF treatment is the induced translocation of an intracellular compartment to the cell surface. This intracellular compartment contains transferrin receptors and may be part of the pathway involved in the normal recycling of cell surface proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D., Rees A. R. Epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Feb 11;34(3):129–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02359619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aharonov A., Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Epidermal growth factor. Relationship between receptor regulation and mitogenesis in 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3970–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buys S. S., Keogh E. A., Kaplan J. Fusion of intracellular membrane pools with cell surfaces of macrophages stimulated by phorbol esters and calcium ionophores. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Human epidermal growth factor and the proliferation of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jun;88(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid induction of morphological changes in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):260–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. L., Greene L. A., Viscarello R. R., Riley W. D. Rapid, sequential changes in surface morphology of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells in response to nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):820–827. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautry-Varsat A., Ciechanover A., Lodish H. F. pH and the recycling of transferrin during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Cannon C., Al-Awqati Q. Exocytosis regulates urinary acidification in turtle bladder by rapid insertion of H+ pumps into the luminal membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Carpenter G. Production and characterization of antibody blocking epidermal growth factor:receptor interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 23;598(2):314–325. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid stimulation of pinocytosis in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):82–90. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. The origin and fate of secretory packages, especially synaptic vesicles. Neuroscience. 1977;2(3):327–355. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Blevins T. L., Ezaki O. Evidence that translocation of the glucose transport activity is the major mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10942–10947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. E., Ray F., Ward J. H., Kushner J. P., Kaplan J. Internalization and subcellular localization of transferrin and transferrin receptors in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8751–8758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd C. E., Ascoli M. On the mechanisms involved in the regulation of the cell-surface receptors for human choriogonadotropin and mouse epidermal growth factor in cultured Leydig tumor cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):521–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. D., Bergstrom-Porter B., Torres A. R., Shelton E. Regulation of surface topography of mouse peritoneal cells. Formation of microvilli and vesiculated pits on omental mesothelial cells by serum and other proteins. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):783–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur S. K., Holtzman E., Walter R. Hormone-stimulated exocytosis in the toad urinary bladder. Some possible implications for turnover of surface membranes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):211–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Yarden Y., de Laat S. W., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces electrically silent Na+ influx in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8502–8506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Villereal M. L. Efflux of 45Ca2+ from human fibroblasts in response to serum or growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Oct;117(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P., Glaser L., Schlesinger P., Cassel D. Activation of Na+/H+ exchange by epidermal growth factor elevates intracellular pH in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12644–12653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P., Glaser L., Schlesinger P., Cassel D. Epidermal growth factor stimulates amiloride-sensitive 22Na+ uptake in A431 cells. Evidence for Na+/H+ exchange. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4883–4889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P., Reuss L., Glaser L. Serum and epidermal growth factor transiently depolarize quiescent BSC-1 epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7783–7787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Enhancement of calcium uptake and phosphatidylinositol turnover by epidermal growth factor in A-431 cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6280–6286. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacher S., Holtzman E., Hood D. C. Synaptic activity of frog retinal photoreceptors. A peroxidase uptake study. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jul;70(1):178–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segaloff D. L., Ascoli M. Removal of the surface-bound human choriogonadotropin results in the cessation of hormonal responses in cultured Leydig tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11420–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villereal M. L. Sodium fluxes in human fibroblasts: effect of serum, Ca+2, and amiloride. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Jun;107(3):359–369. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041070307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. H., Kushner J. P., Kaplan J. Regulation of HeLa cell transferrin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10317–10323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. A steady state model for analyzing the cellular binding, internalization and degradation of polypeptide ligands. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. Epidermal growth factor stimulates fluid phase endocytosis in human fibroblasts through a signal generated at the cell surface. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(4):383–394. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. The endocytotic rate constant. A cellular parameter for quantitating receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4222–4229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


