Abstract
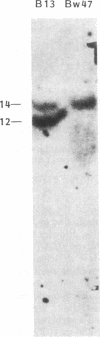
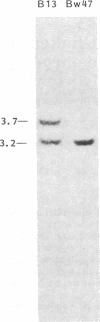
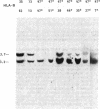
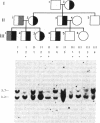
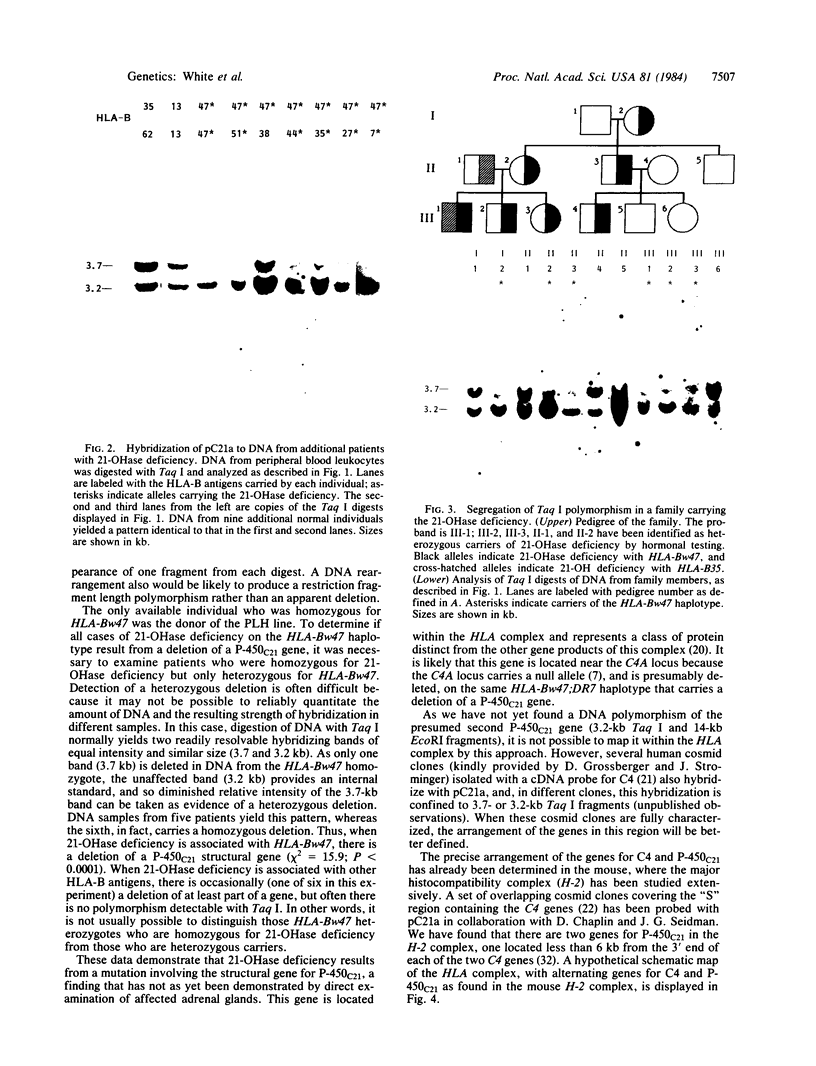
We have determined the molecular genetic basis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase (21-OHase) deficiency. This common disorder of cortisol biosynthesis is HLA-linked. The haplotype HLA-(A3);Bw47;DR7 is strongly associated with 21-OHase deficiency and always carries a null allele at the locus encoding the C4A (Rodgers) form of the fourth component (C4) of complement. It seemed likely that this haplotype carries a deletion encompassing the genes encoding both C4A and 21-OHase. We hypothesized that the HLA-linked defect involved a structural gene for the adrenal microsomal cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Using a plasmid with a 520-base-pair bovine adrenal cDNA insert encoding the middle third of the cytochrome P-450 polypeptide, we compared hybridization patterns in DNA from normal and 21-OHase-deficient individuals. Normal human DNA yielded two fragments that hybridized with the probe after digestion with either restriction endonuclease EcoRI [12- and 14-kilobase (kb) fragments] or Taq I (3.7 and 3.2 kb). One of these bands (the first mentioned in each digest) was absent in DNA from a cell line derived from a patient homozygous for HLA-Bw47. DNA from six unrelated patients homozygous for 21-OHase deficiency who were heterozygous for HLA-Bw47 yielded diminished relative intensity of the 3.7-kb Taq I band in five patients, consistent with a heterozygous deletion, and complete disappearance of the 3.7-kb band in one. This deletion segregated with HLA-Bw47 in a large pedigree carrying 21-OHase deficiency and HLA-Bw47. Thus, 21-OHase deficiency sometimes results from the deletion of a specific cytochrome P-450 gene and sometimes, presumably, from smaller mutations. This gene is probably located very near the C4A gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieter H. H., Muller-Eberhard U., Johnson E. F. Identification of rabbit microsomal cytochrome P-450 isozyme, form 1, as a hepatic progesterone 21-hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91465-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Oberfield S. E., Smithwick E. M., Lee T. D., Levine L. S. Close genetic linkage between HLA and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein M., Shaefer J. M. Inborn errors of steroid biosynthesis. Physiol Rev. 1979 Apr;59(2):353–406. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Juretic A., Baxevanis C. N., Nagy Z. A. The traditional and a new version of the mouse H-2 complex. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):455–460. doi: 10.1038/291455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami S., Ochi H., Kobayashi Y., Takemori S. Studies on the steroid hydroxylation system in adrenal cortex microsomes. Purification and characterization of cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid C-21 hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3386–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnle U., Chow D., Rapaport R., Pang S., Levine L. S., New M. I. The 21-hydroxylase activity in the glomerulosa and fasciculata of the adrenal cortex in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Mar;52(3):534–544. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-3-534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen F., Pang S., New M., Pollack M., Oberfield S., Dupont B., Chow D., Schneider B., Levine L. Studies of the C-21 and C-19 steroids and HLA genotyping in siblings and parents of patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Mar;50(3):572–577. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry R., Goguen J., Carpenter C. B., Strom T. B., Garovoy M. R. Improved B cell typing for HLA-DR using nylon wool column enriched B lymphocyte preparations. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Oct;14(4):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Dupont B., Pollack M. S., Levine L. S., New M. I. Complement C4 allotypes in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: further evidence for different allelic variants at the 21-hydroxylase locus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):312–322. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Levine L. S., O'Neill G. J., Pang S., Lorenzen F., Kohn B., Rondanini G. F., Chiumello G., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA linkage and B14, DR1, BfS haplotype association with the genes for late onset and cryptic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;33(4):540–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Maurer D., Levine L. S., New M. I., Pang S., Duchon M., Owens R. P., Merkatz I. R., Nitowsky B. M., Sachs G. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency) by HLA typing. Lancet. 1979 May 26;1(8126):1107–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91789-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Hood L. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex in mouse and man. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):727–733. doi: 10.1126/science.6356354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Old J. M. Antenatal diagnosis of the haemoglobin disorders by analysis of foetal DNA. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):151–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a bovine adrenal cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1986–1990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Colten H. R. Use of a cDNA clone for the fourth component of human complement (C4) for analysis of a genetic deficiency of C4 in guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5387–5391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkel C. A., Simpson E. R., Milewich L., MacDonald P. C. Deoxycorticosterone biosynthesis in human kidney: potential for formation of a potent mineralocorticosteroid in its site of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7069–7073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Y., Morishima Y., Collins N. H., Alton T., Pollack M. S., Yunis E. J., Dupont B. Comparison of one-dimensional IEF patterns for serologically detectable HLA-A and B allotypes. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(3):217–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00364765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]