Abstract
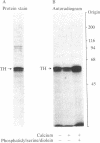
Protein kinase C, purified to homogeneity, was found to phosphorylate and activate tyrosine hydroxylase that had been partially purified from pheochromocytoma PC 12 cells. These actions of protein kinase C required the presence of calcium and phospholipid. This phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase reduced the Km for the cofactor 6-methyltetrahydropterine from 0.45 mM to 0.11 mM, increased the Ki for dopamine from 4.2 microM to 47.5 microM, and produced no change in the Km for tyrosine. Little or no change in apparent Vmax was observed. These kinetic changes are similar to those seen upon activation of tyrosine hydroxylase by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Two-dimensional phosphopeptide maps of tyrosine hydroxylase were identical whether the phosphorylation was catalyzed by protein kinase C or by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Both protein kinases phosphorylated serine residues. The results suggest that protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylate the same site(s) on tyrosine hydroxylase and activate tyrosine hydroxylase by the same mechanism.
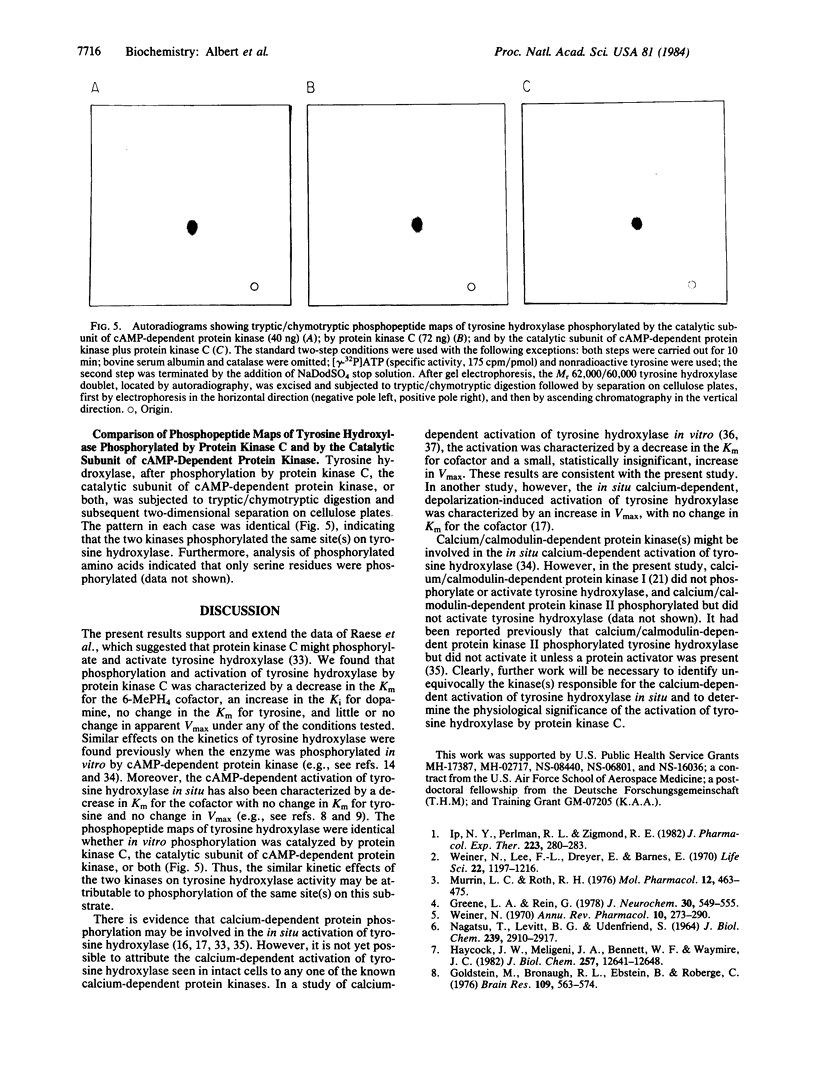
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames M. M., Lerner P., Lovenberg W. Tyrosine hydroxylase. Activation by protein phosphorylation and end product inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H., Wilson F. D., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Intracellular injection of t he catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase simulates facilitation of transmitter release underlying behavioral sensitization in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7492–7496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Settipani L., Perlman R. L. The role of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in the regulation of tyrosine 3-monooxygenase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;15(2):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Raese J. D., Lazar M. A., Barchas J. D. Tyrosine hydroxylase: studies on the phosphorylation of a purified preparation of the brain enzyme by the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):647–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Mestikawy S., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Tyrosine hydroxylase activation in depolarized dopaminergic terminals--involvement of Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):830–832. doi: 10.1038/302830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M., Bronaugh R. L., Ebstein B., Roberge C. Stimulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity by cyclic AMP in synaptosomes and in soluble striatal enzyme preparations. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 18;109(3):563–574. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Rein G. Short-term regulation of catecholamine biosynthesis in a nerve growth factor responsive clonal line of rat pheochromocytoma cells. J Neurochem. 1978 Mar;30(3):549–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Bennett W. F., George R. J., Waymire J. C. Multiple site phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase. Differential regulation in situ by a 8-bromo-cAMP and acetylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13699–13703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Meligeni J. A., Bennett W. F., Waymire J. C. Phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine hydroxylase mediate the acetylcholine-induced increase in catecholamine biosynthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12641–12648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeno T., Dickens G., Lloyd T., Guroff G. The receptor-mediated activation of tyrosine hydroxylation in the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. J Neurochem. 1981 May;36(5):1632–1640. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Perlman R. L., Zigmond R. E. Both nicotinic and muscarinic agonists acutely increase tyrosine 3-monooxygenase activity in the superior cervical ganglion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):280–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa Y., Takai Y., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Phosphorylation of calf thymus H1 histone by calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):180–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey K. A., Kondo H., Shenkman L., Goldstein M. Purification and characterization of tyrosine hydroxylase from a clonal pheochromocytoma cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson J. M., Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Possibility of shape conformers of the protein inhibitor of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):4835–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meligeni J. A., Haycock J. W., Bennett W. F., Waymire J. C. Phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine hydroxylase mediate the cAMP-induced increase in catecholamine biosynthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12632–12640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenroth V. H., 3rd, Hegstrand L. R., Roth R. H., Greengard P. Evidence for involvement of protein kinase in the activation by adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate of brain tyrosine 3-monooxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1946–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrin L. C., Roth R. H. Dopaminergic neurons: effects of electrical stimulation on dopamine biosynthesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 May;12(3):463–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. A RAPID AND SIMPLE RADIOASSAY FOR TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE ACTIVITY. Anal Biochem. 1964 Sep;9:122–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raese J. D., Edelman A. M., Makk G., Bruckwick E. A., Lovenberg W., Barchas J. D. Brain striatal tyrosine hydroxylase: activation of the enzyme by cyclic AMP-independent phosphorylation. Commun Psychopharmacol. 1979;3(5):295–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Allhiser C. L., Roskoski R., Jr Tyrosine hydroxylase activation and inactivation by protein phosphorylation conditions. J Neurochem. 1981 Jan;36(1):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb02382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Roskoski R., Jr Tyrosine hydroxylase inactivation following cAMP-dependent phosphorylation activation. J Neurochem. 1983 Jun;40(6):1692–1700. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliet P. R., Langan T. A., Weiner N. Tyrosine hydroxylase: a substrate of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):92–96. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S., Chute R. N. Pheochromocytoma. Cancer. 1972 Feb;29(2):327–331. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197202)29:2<327::aid-cncr2820290210>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner N., Lee F. L., Dreyer E., Barnes E. The activation of tyrosine hydroxylase in noradrenergic neurons during acute nerve stimulation. Life Sci. 1978 Apr 3;22(13-15):1197–1215. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner N. Regulation of norepinephrine biosynthesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:273–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi T., Fujisawa H. Tyrosine 3-monoxygenase is phosphorylated by Ca2+-, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, followed by activation by activator protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):807–813. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]