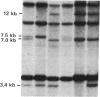
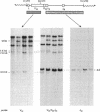
Abstract
In this study, restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) were identified with an immunoglobulin variable heavy chain region (Ig VH) probe and the inheritance of the polymorphisms was analyzed in families. Linkage within the VHII gene cluster and between the VHII and Ig CH genes was investigated by lod (logarithm of odds) score analysis. In addition, the position of the VHII genes was determined in relation to another polymorphic locus--D14S1, which is tightly linked and centromeric to the CH genes. Genetic associations between genes in the CH and VH clusters were analyzed. These RFLPs represent genetically characterized VH region polymorphisms and it is hoped that they will facilitate the study of disease correlations as well as further the understanding of the genetics of the immunoglobulin heavy chain genes in humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balazs I., Purrello M., Rubinstein P., Alhadeff B., Siniscalco M. Highly polymorphic DNA site D14S1 maps to the region of Burkitt lymphoma translocation and is closely linked to the heavy chain gamma 1 immunoglobulin locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7395–7399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Cohen J. B., Rechavi G., Zakut R., Givol D. Polymorphism of germ-line immunoglobulin VH genes correlates with allotype and idiotype markers. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Dec;11(12):1017–1020. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg B., Geckeler W. R., Weigert M. Genetics of the antibody response to dextran in mice. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Givol D. Conservation and divergence of immunoglobulin VH pseudogenes. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1795–1800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Thierfelder W., Erikson J., Nishikura K., Finan J., Lenoir G. M., Nowell P. C. Transcriptional activation of an unrearranged and untranslocated c-myc oncogene by translocation of a C lambda locus in Burkitt. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Translocation of immunoglobulin VH genes in Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5611–5615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., ar-Rushdi A., Drwinga H. L., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman M. W., Lewontin R. C., Frankin I. R., Christiansen R. B. Selection in complex genetic systems III. An effect of allele multiplicity with two loci. Genetics. 1975 Feb;79(2):333–347. doi: 10.1093/genetics/79.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Givol D., Zakut R., Effron K., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B. Diversity of germ-line immunoglobulin VH genes. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):426–430. doi: 10.1038/292426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobart M. J., Rabbitts T. H., Goodfellow P. N., Solomon E., Chambers S., Spurr N., Povey S. Immunoglobulin heavy chain genes in humans are located on chromosome. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 Oct;45(Pt 4):331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H., Crews S., Hood L. An immunoglobulin VH pseudogene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):93–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Morton C. C., Nakahara K., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes map to a region of translocations in malignant B lymphocytes. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):301–303. doi: 10.1126/science.6801764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G. Experimental approaches tohomogenous antibody populations. iIndividual antigenic specificity, cross specificity and diversity of human antibodies. Fed Proc. 1970 Jan-Feb;29(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Bech-Hansen N. T., Siminovitch L., Cox D. W. Analysis of a break in chromosome 14 mapping to the region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1997–2001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh D. Y., Bothwell A. L., White-Scharf M. E., Imanishi-Kari T., Baltimore D. Molecular basis of a mouse strain-specific anti-hapten response. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON N. E. Sequential tests for the detection of linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1955 Sep;7(3):277–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Traunecker A., Sakano H., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Exon shuffling generates an immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2138–2142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthyssens G., Rabbitts T. H. Structure and multiplicity of genes for the human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., Feder J., Cann H., van West B., Hwang J., Takahashi N., Honjo T., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Multiple DNA fragment polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin mu chain switch-like regions in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):467–471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Karjalainen K. Inherited immunoglobulin idiotypes of the mouse. Immunol Rev. 1977;34:119–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Seppälä I. J., Pelkonen J., Kaartinen M., Cazenave P. A., Gefter M. L. Crossing-over frequency in the Igh region of the mouse genome. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135C(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(84)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Tung E., Mathur S., Namboodiri K. K., Wang A. C., Fudenberg H. H., Blattner W. A., Elston R. C., Hames C. G. Linkage relationship between variable and constant region allotypic determinants of human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):406–407. doi: 10.1038/286406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak L. L., Mushinski E. B., Nisonoff A., Potter M. Evidence for the linkage of the IGC H locus to a gene controlling the idiotypic specificity of anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies in strain A mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):22–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Lieberman R. Common individual antigenic determinants in five of eight BALB-c IgA myeloma proteins that bind phosphoryl choline. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):737–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Bentley D. L., Milstein C. P. Human antibody genes: V gene variability and CH gene switching strategies. Immunol Rev. 1981;59:69–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Bienz B., Ram D., Ben-Neriah Y., Cohen J. B., Zakut R., Givol D. Organization and evolution of immunoglobulin VH gene subgroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4405–4409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Ram D., Glazer L., Zakut R., Givol D. Evolutionary aspects of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (VH) gene subgroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):855–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Gefter M. L., Brodeur P., Riblet R., Marshak-Rothstein A. The genetic basis of antibody production: the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype response of the strain A mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1023–1032. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. H., Willard H. F., Menlove L. A. Report of the Committee on Human Gene Mapping by Recombinant DNA Techniques. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):210–273. doi: 10.1159/000132011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D., Weinberg R. A. The integrated genome of murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD C. W. Allotypy in rabbit 19S protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 May 3;11:170–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Nakai S., Honjo T. Cloning of human immunoglobulin mu gene and comparison with mouse mu gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5983–5991. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Noma T., Honjo T. Rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (VH) pseudogene that deletes the second complementarity-determining region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5194–5198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Mathur S., Pandey J., Siegel F. P., Middaugh C. R., Litman G. W. Hv(1), a variable-region genetic marker of human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Science. 1978 Apr 21;200(4339):327–329. doi: 10.1126/science.416494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. V., Fudenberg H. H., Givol D. Localization of idiotypic antigenic determinants in the Fv region of murine myeloma protein MOPC-315. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1585–1587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]