Abstract
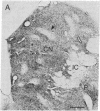
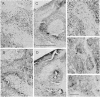
Striatal cell bodies and fibers expressing [Met]enkephalin [( Met]Enk)-like immunoreactivity were studied with two variants of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method in normal primates and cats and in cats pretreated with colchicine. Strikingly different patterns of [Met]Enk-like immunoreactivity were observed, both in fiber and cell body immunostaining, depending on the technical protocols followed; no single histochemical protocol fully revealed the compartmentalization present. In the dorsal striatum, patches of [Met]Enk-positive neuropil, known to line up with the acetylcholinesterase-poor striatal zones called striosomes, appeared in sections treated by protocols favoring fiber immunostaining. In sections stained by procedures favoring perikaryal staining, the striosomes appeared as Enk-poor patches in a field of immunoreactive cells and neuropil. When cell-body staining was enhanced by pretreatment with colchicine, cells expressing [Met]Enk-like immunoreactivity appeared both in and out of striosomes, and the striosomal neuropil appeared Enk-rich. These results suggest that there are subtypes of Enk-positive neurons in the striatum, including a "colchicine-dependent subtype" in dorsal striosomes, and suggest that the Enk-positive striatal neuropil is also made up of different components. Immunospecificity of this dorsal striosomal system was further demonstrated by the finding that neurons expressing intense immunoreactivity to substance P and to dynorphin B were largely confined to striosomes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arluison M., Conrath-Verrier M., Tauc M., Mailly P., De la Manche I. S., Cesselin F., Bourgoin S., Hamon M. Different localizations of Met-enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in rat forebrain and spinal cord using hydrogen peroxide and Triton X-100. Light microscopic study. Brain Res Bull. 1983 Nov;11(5):555–571. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(83)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronin N., Difiglia M., Graveland G. A., Schwartz W. J., Wu J. Y. Localization of immunoreactive enkephalins in GABA synthesizing neurons of the rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1984 May 23;300(2):376–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90850-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesselet M. F., Graybiel A. M. Met-enkephalin-like and dynorphin-like immunoreactivities of the basal ganglia of the cat. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFiglia M., Aronin N., Martin J. B. Light and electron microscopic localization of immunoreactive Leu-enkephalin in the monkey basal ganglia. J Neurosci. 1982 Mar;2(3):303–320. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-03-00303.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Mantyh P. W., Emson P. C., Hunt S. P. Inverse relationship between neurotensin receptors and neurotensin-like immunoreactivity in cat striatum. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):543–546. doi: 10.1038/307543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr, Yoneoka E. S., Elde R. P. An immunohistochemical study of enkephalins and other neuropeptides in the striatum of the cat with evidence that the opiate peptides are arranged to form mosaic patterns in register with the striosomal compartments visible by acetylcholinesterase staining. Neuroscience. 1981;6(3):377–397. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Mosaic distribution of opiate receptors, parafascicular projections and acetylcholinesterase in rat striatum. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):415–418. doi: 10.1038/291415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss J. Z., Mezey E., Skirboll L. Corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus become vasopressin positive after adrenalectomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1854–1858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Childers S., Snyder S. H. Met- and Leu-enkephalin immunoreactivity in separate neurones. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):407–410. doi: 10.1038/282407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Sumal K. K., Beckley S. C., Miller R. J., Reis D. J. Immunocytochemical localization of enkephalin in the neostriatum of rat brain: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Feb 15;189(4):721–740. doi: 10.1002/cne.901890408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchenko P. E., Swanson L. W., Vale W. W. Co-expression of corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin immunoreactivity in parvocellular neurosecretory neurons of the adrenalectomized rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1883–1887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. G., Dockray G. J. Differential distribution in rat basal ganglia of Met-enkephalin- and Met-enkephalin Arg6 Phe7-like peptides revealed by immunohistochemistry. Brain Res. 1982 May 20;240(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90657-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]