Abstract
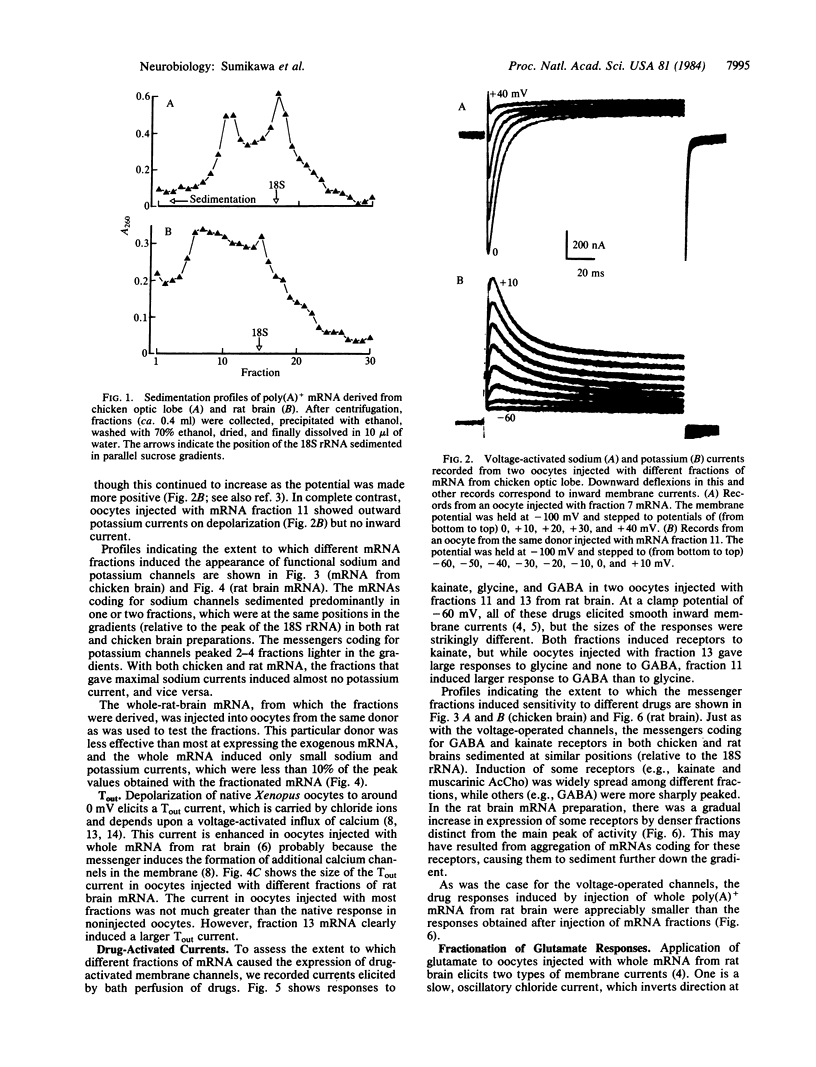
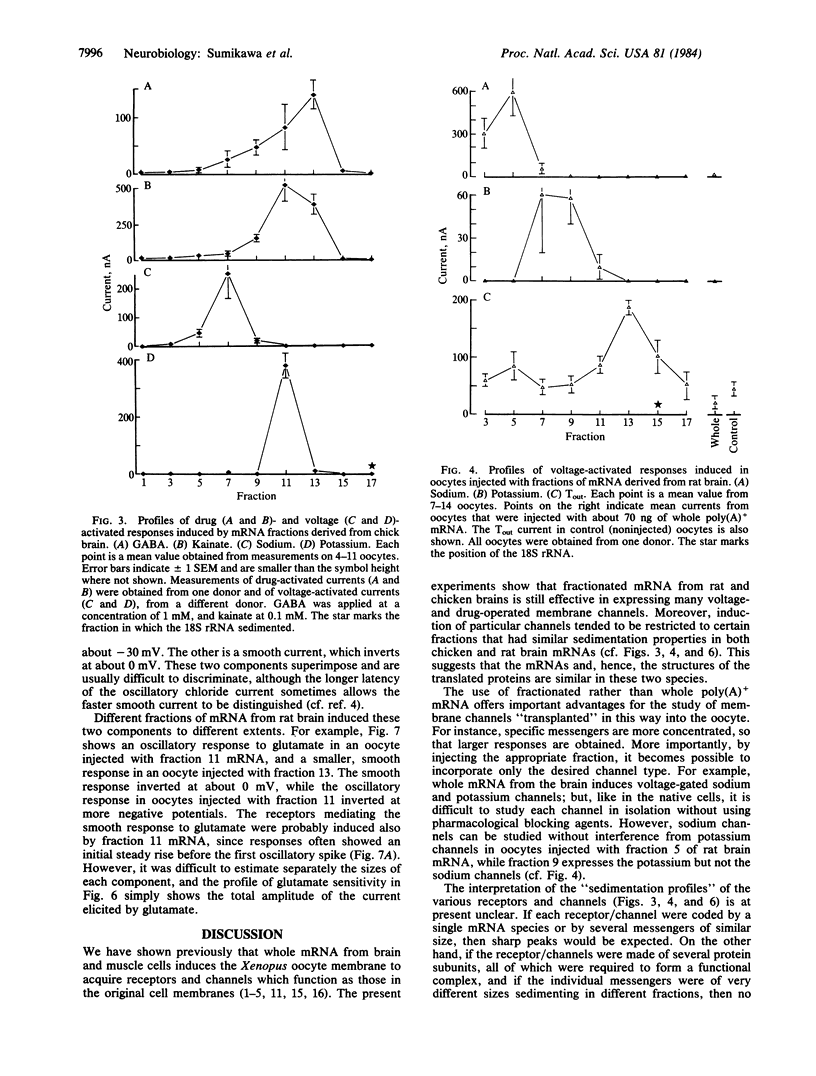
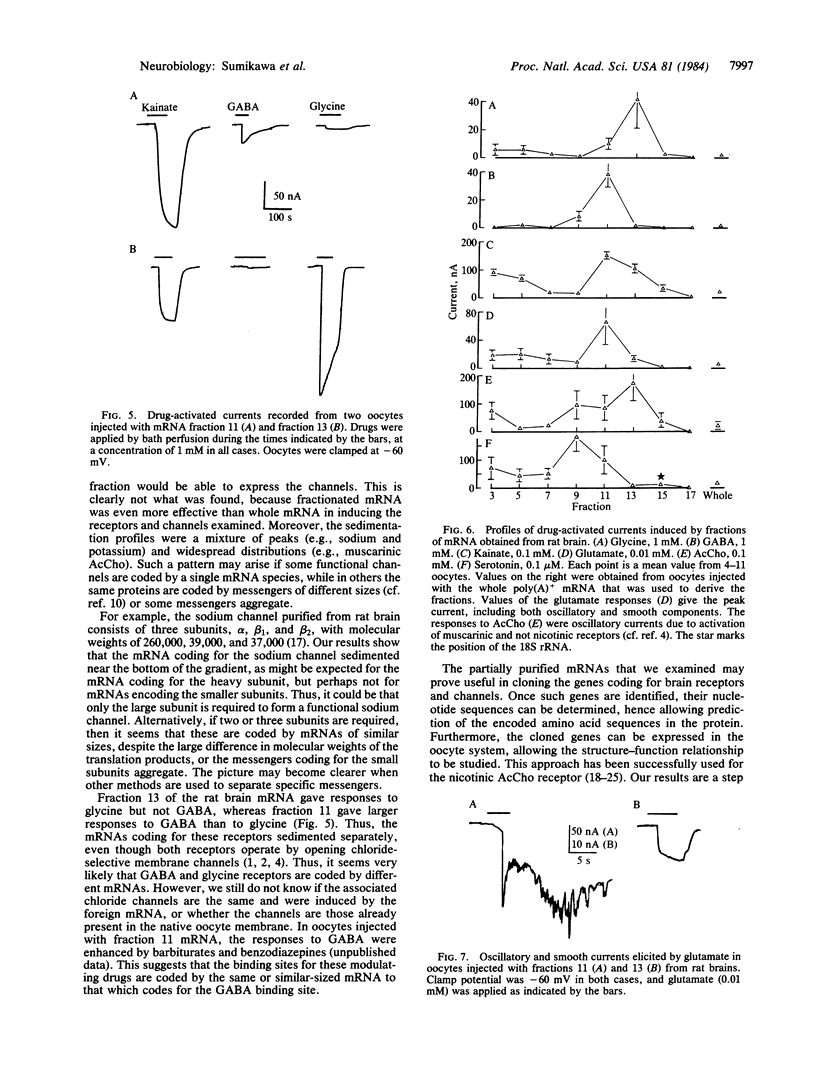
Poly(A)+ mRNAs extracted from embryonic chicken brain and from adult rat brain were fractionated on sucrose density gradients. The fractions were subsequently injected into Xenopus oocytes where the mRNA was translated. The products were processed and incorporated into the oocyte membrane where they formed functional neurotransmitter receptors and voltage-operated channels. Different mRNA fractions induced the incorporation of different transmitter receptors and voltage-operated channels into the oocyte membrane. These experiments provide a useful step towards the understanding of the structure and function of neurotransmitter receptors and channels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barish M. E. A transient calcium-dependent chloride current in the immature Xenopus oocyte. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:309–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Miledi R., Sumikawa K. Translation of exogenous messenger RNA coding for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors produces functional receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 May 22;215(1199):241–246. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Giraudat J., Bentaboulet M., Changeux J. P. Complete mRNA coding sequence of the acetylcholine binding alpha-subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor: a model for the transmembrane organization of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen C. B., Miledi R., Parker I. Glutamate and kainate receptors induced by rat brain messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Apr 24;221(1223):127–143. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen C. B., Miledi R., Parker I. Messenger RNA from human brain induces drug- and voltage-operated channels in Xenopus oocytes. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):421–424. doi: 10.1038/308421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen C. B., Miledi R., Parker I. Properties of human brain glycine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Apr 24;221(1223):235–244. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen C. B., Miledi R., Parker I. Serotonin receptors induced by exogenous messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Aug 22;219(1214):103–109. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen C. B., Miledi R., Parker I. Voltage-operated channels induced by foreign messenger RNA in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Nov 22;220(1218):131–140. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Cholinergic and catecholaminergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:143–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Sumikawa K. Properties of acetylcholine receptors translated by cat muscle mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1307–1312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Sumikawa K. Recording of single gamma-aminobutyrate- and acetylcholine-activated receptor channels translated by exogenous mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 22;218(1213):481–484. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Sumikawa K. Synthesis of chick brain GABA receptors by frog oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 22;216(1205):509–515. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Kurosaki T., Tobimatsu T., Morimoto Y., Noda M., Yamamoto T., Terao M., Lindstrom J., Takahashi T., Kuno M. Expression of functional acetylcholine receptor from cloned cDNAs. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):604–608. doi: 10.1038/307604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Structural homology of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor subunits. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):528–532. doi: 10.1038/302528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Smith J. C., Bell L., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. The molecular cloning and characterisation of cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5809–5822. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Parker I., Amano T., Miledi R. Separate fractions of mRNA from Torpedo electric organ induce chloride channels and acetylcholine receptors in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2291–2294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



